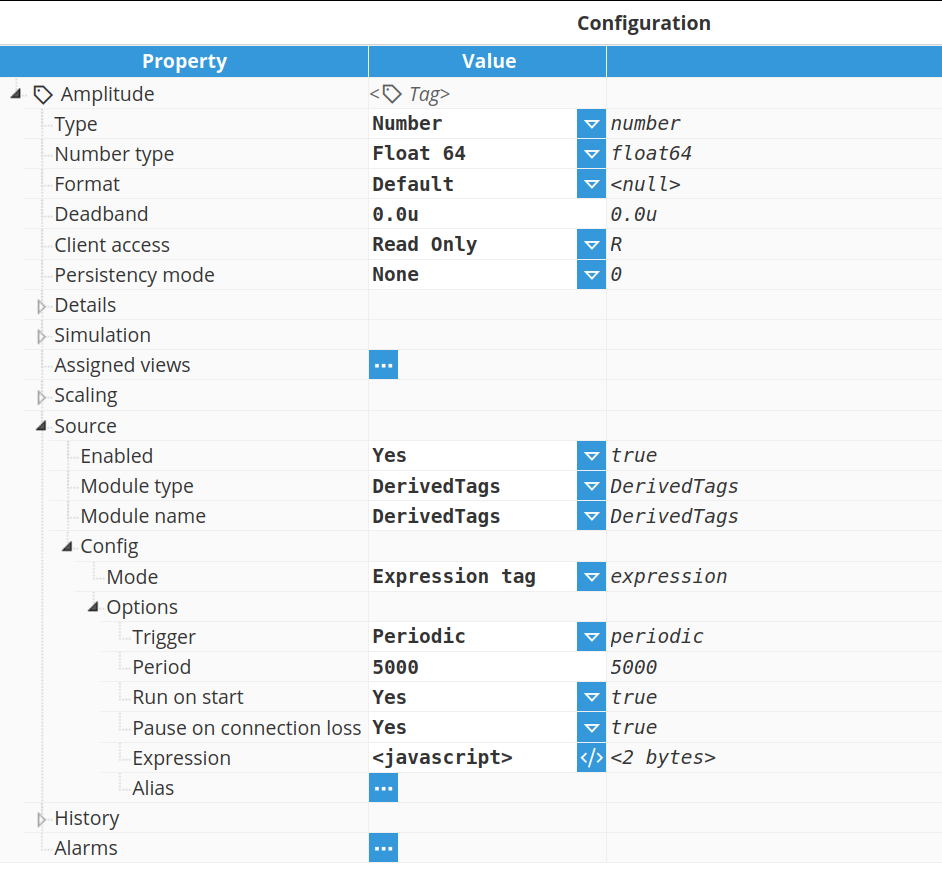
To configure a tag as a Derived Tag, you must set the source to DerivedTags. First, create the tag and enable the source. Then, select the module type and choose the module instance as the source, as illustrated in the screenshot below:
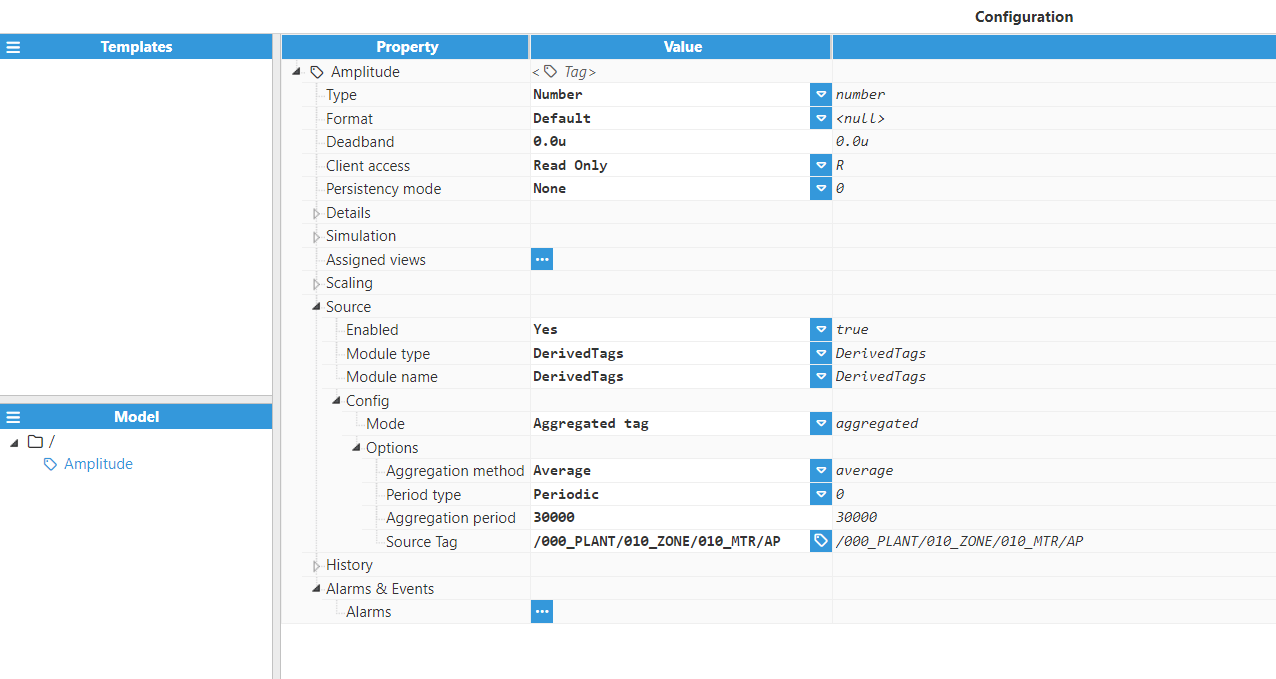
After setting the source to DerivedTags, the following options will appear:
Mode:
Mode | Description |
Aggregated Tag | Used to generate aggregated values based on the values of another tag acting as a data source. |
Expression Tag | |
Alias Tag | Used to change the name or tagpath of the input tag without coding. |
Redundant Tag | Used to create tags with several inputs acting as redundant sources. |
Node Tag | Used to read information about the node, including diagnostics, links, and modules. |
Options: This section contains options for the currently selected DerivedTag mode.
Aggregated Tags
Aggregated Tags are used to generate aggregated values based on the values of another tag acting as a data source. The following screenshot displays the available options for an Aggregated Tag:
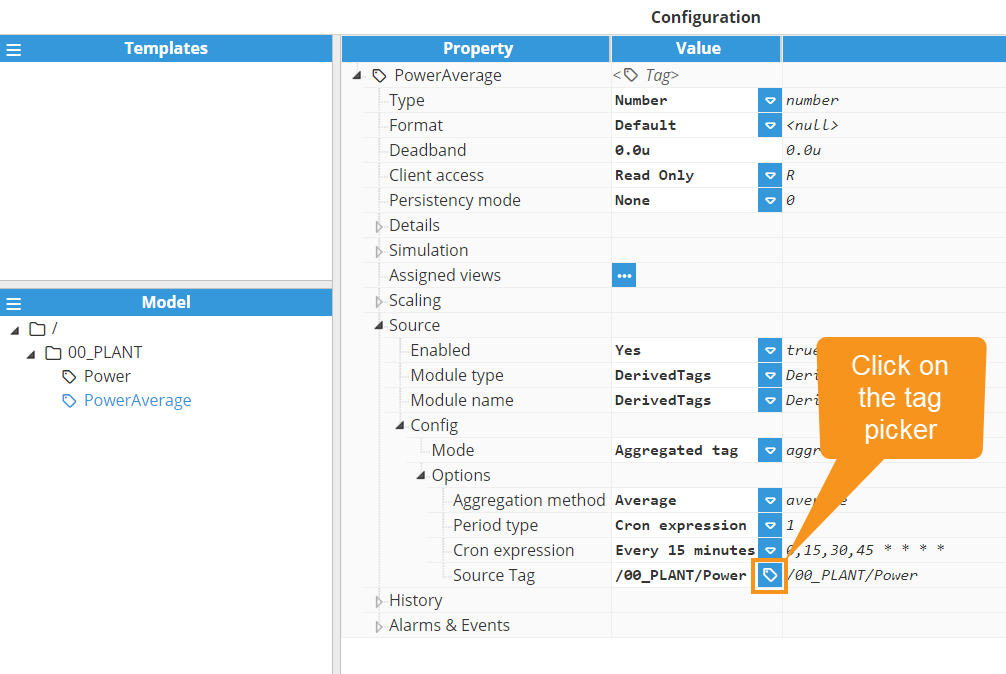
Aggregation method: Selects which aggregation to use in order to calculate the value for this tag. The valid values are:
Average: Returns the calculated time-weighted average of all good quality values received during the specified period. Periods with bad quality data are excluded from the calculation. If no good quality values are present throughout the entire period, the result will be a bad quality data point.
Minimum: Returns the lowest good quality value received during the period. If no good quality values exist during the entire period, a bad quality data point is returned.
Maximum: Returns the highest good quality value received during the period. If no good quality values exist during the entire period, a bad quality data point is returned.
First: Returns the value and its quality at the end of the aggregation period. The timestamp also reflects the end of the period.
Last: Returns the value and its quality at the end of the aggregation period. The timestamp also reflects the end of the period.
Count: Returns the total number of tag values received during the period.
Good: Returns the percentage of time the value maintained good quality throughout the period. (1.0 = good quality entire time, 0.0 = bad quality entire time).
Delta: Returns the difference between the values at the end and beginning of the period, but only if both have good quality. A bad quality data point is returned if either value has bad quality.
Standard Deviation: Returns the time-weighted standard deviation of all good quality values received during the period. Periods with bad-quality data are excluded from the calculation. A bad-quality data point is returned if no good-quality values exist during the entire period.
Custom: Allows you to define a script to calculate the aggregation in a way that best suits your needs.
Note:
Custom aggregation only supports the use of the return statement to provide output. The $.output object is not available in this context.
The timestamps returned by the aggregation methods correspond to the end of the chosen aggregation period.
Period type:
Periodic: The tag executes periodically in fixed intervals.
Cron expression: The tag executes according to a Cron expression.
Note:
For more information on Cron expressions, readers can explore them further at Crontab Guru.
Note:
Cron expressions are evaluated according to the System Timezone.
Aggregation period: Specifies the aggregation period. The minimum value is 10,000ms.
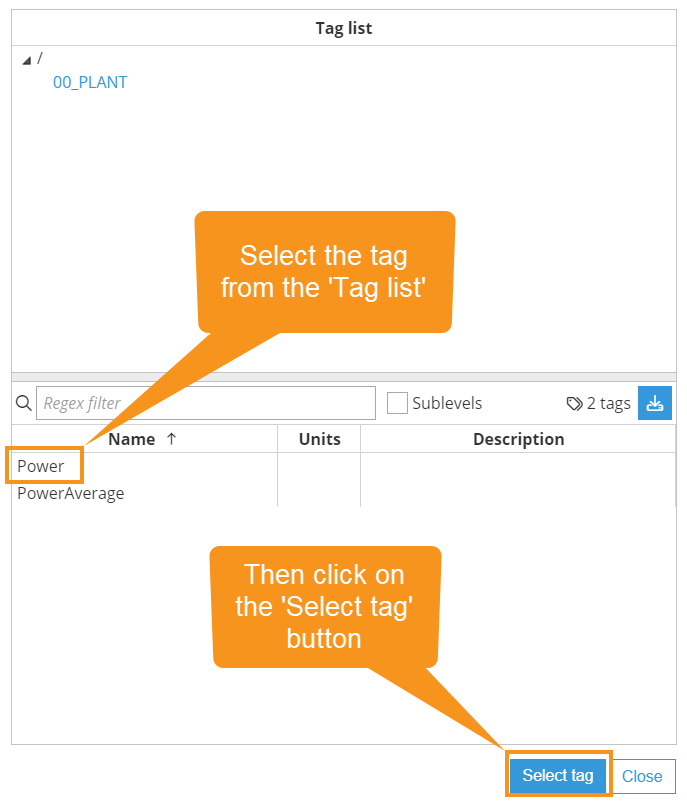
Source Tag: Specifies the tag used as the source for the aggregation. This can be a local tag or a tag from a remote node. It's possible to browse and discover the source tag by clicking on the button to the right.
Expression Tags
Expression Tags are used to generate a value based on a JavaScript expression. This can either be standalone or can involve a different source tag whose values are available in this expression. After setting the Type to Expression Tag, the following options will be shown:
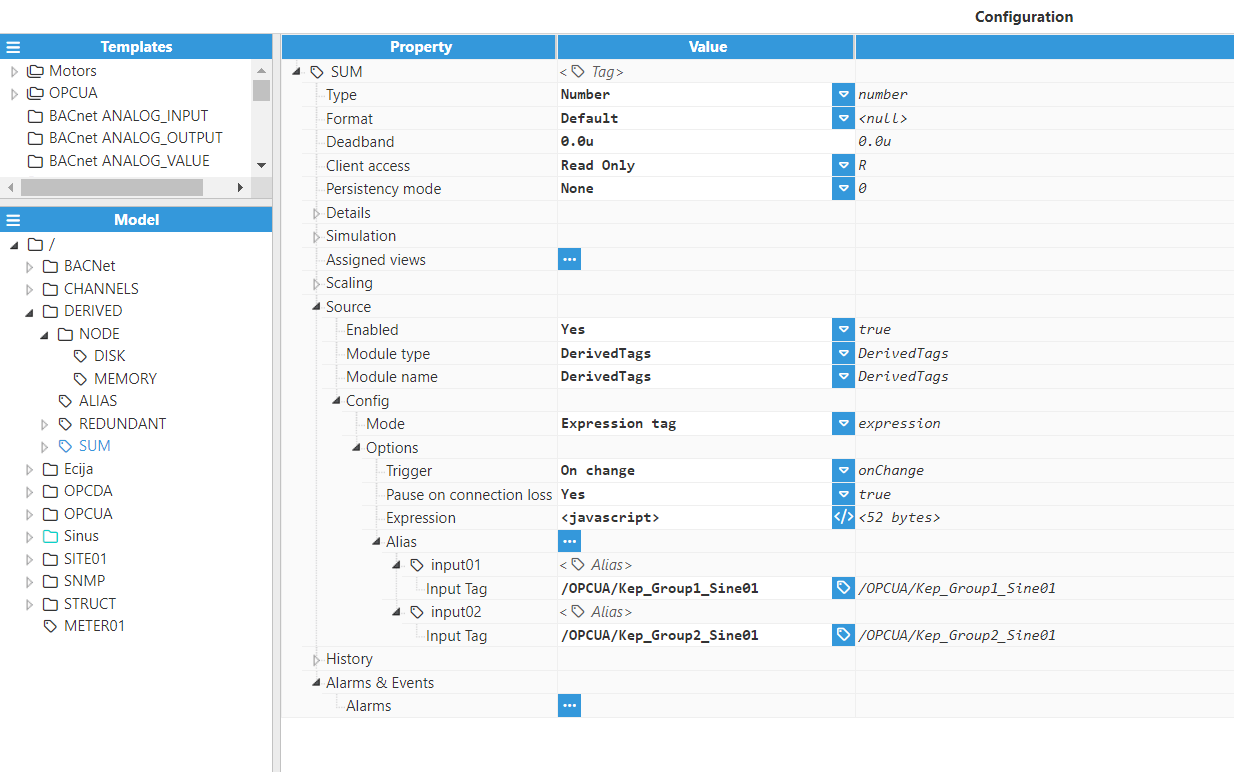
Trigger: Specifies the type of execution trigger. The available options are:
On change: The Expression Tag will execute every time one of the inputs changes.
Periodic: The Expression Tag will execute after the specified period elapses.
Cron expression: The Expression Tag will execute according to a cron expression.
Period: The time period between executions, displayed in milliseconds. This only applies when the Trigger is set to “Periodic”.
Cron expression: Cron expression that determines when the script will be executed. This only applies when the Trigger is set to "Cron expression".
Run on start: When enabled, the expression will be evaluated once at module startup (ignoring the period), and after each subsequent period thereafter.
Pause on connection loss: Enables or disables tag execution to be paused while the link for any remote input tag is down and the tag is of uncertain quality. This setting only applies if there are remote tags involved in the expression. A remote tag is a tag received from another node through a N3uron link.
Expression: Specifies the expression that will be executed whenever the Expression Tag triggers to obtain the value, quality, and timestamp of the derived tag. By clicking on this icon, a text box pop-up will appear, allowing for expressions that span multiple lines. See more information in Expressions.
Alias: This is used to define aliases for other tags within the model so that they can be referenced in the expression for this tag.
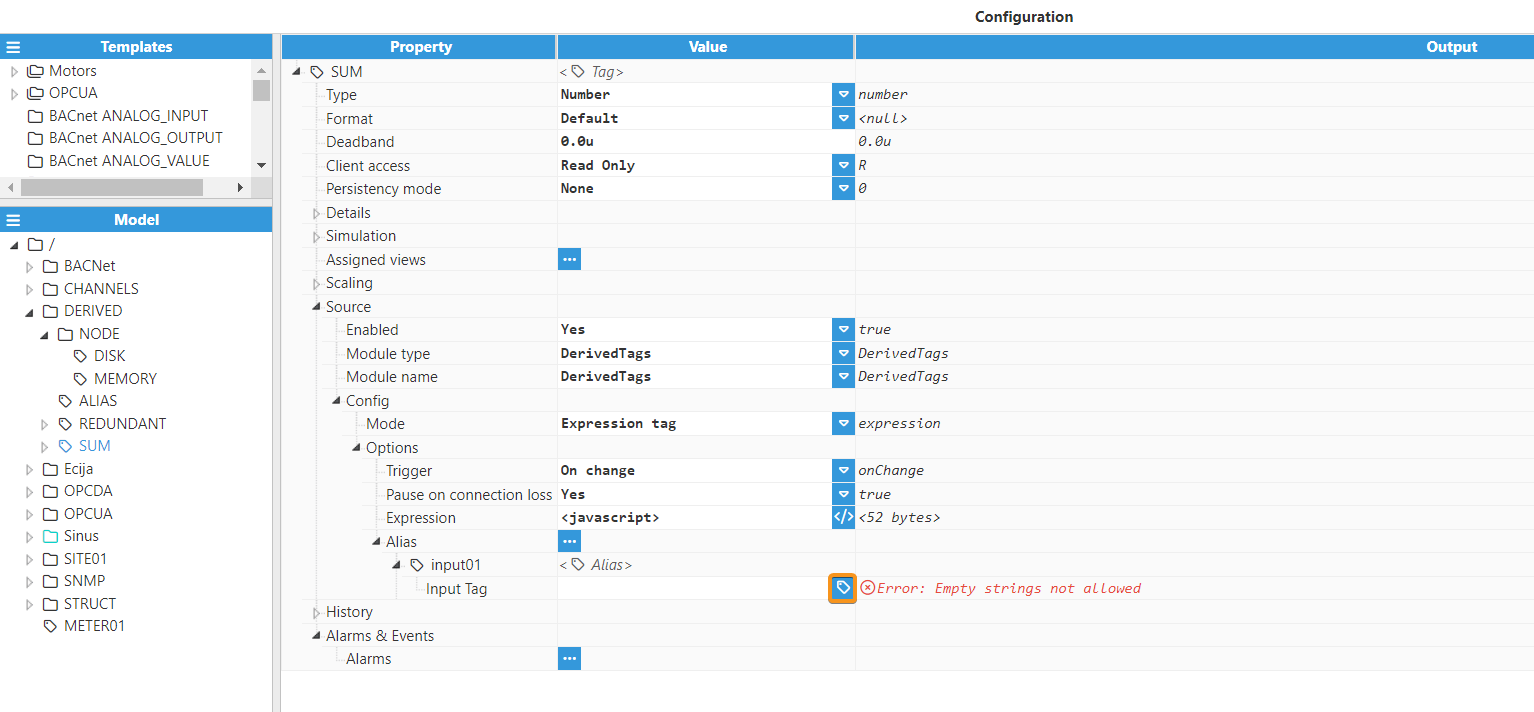
Input tag: Specifies the tag associated with the corresponding alias. It can point to any local or remote tag. If this tag is not present on startup, the subscription to the source tag fails, and the expression cannot be executed. This tag path can either be absolute (beginning with /) or relative to the current group (optionally beginning with ./). The tag path can be left blank, in which case this alias will be ignored (and as such, it will not exist in $.input).
Note:
Each alias must be unique. If two aliases point to the same tag, a warning is logged and the expression is not executed.
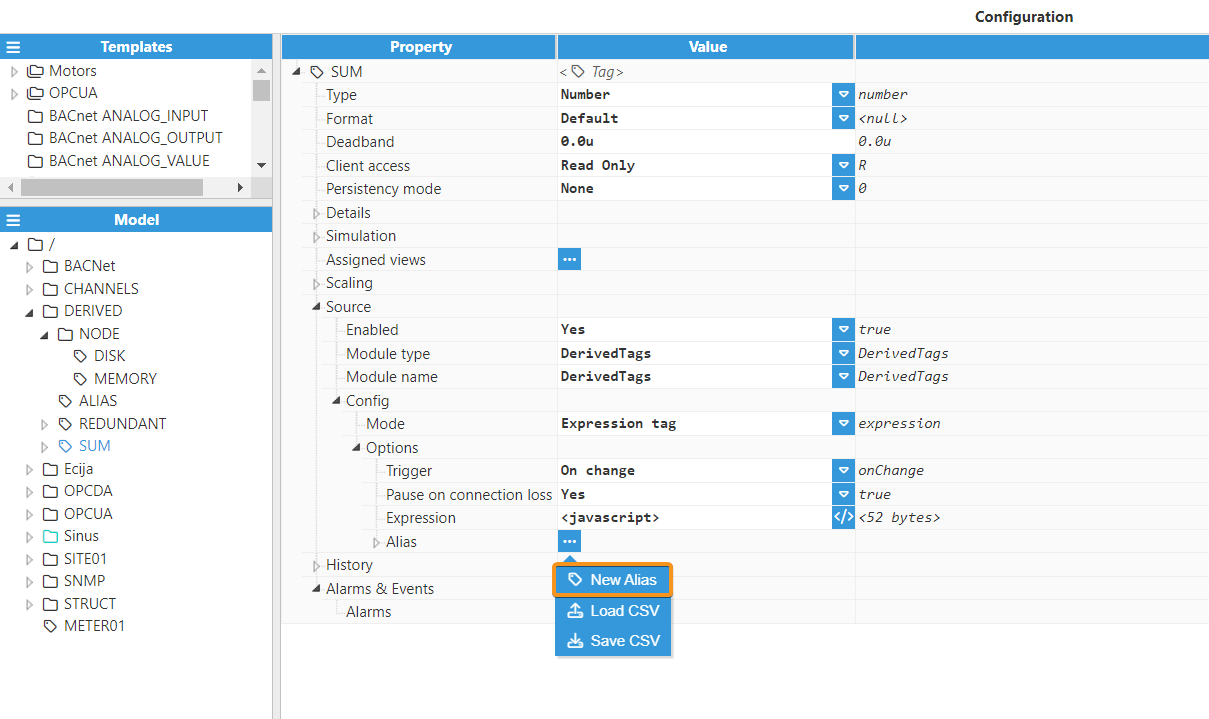
Note:
Users are free to add any number of aliases, but it’s important to be careful and ensure that only those with associated tags are used in the expression, as shown in the example below.
//$.output=$.input.alias1.value+$.input.alias2.value+$.input.alias3.value+$.input.alias4.value // Initialize the output to 0 $.output = 0; // Define an array of aliases const aliases = ['alias1', 'alias2', 'alias3', 'alias4']; // Use a for loop to iterate through the aliases for (let i = 0; i < aliases.length; i++) { const alias = aliases[i]; // Check if the alias exists in $.input if ($.input[alias]) { // If the alias exists, add its value to the output $.output += $.input[alias].value; } else { // If the alias is missing, you can handle it here, e.g., set a default value $.output += 0; // Set to 0 for missing aliases, or handle the error as needed } } // $.output now contains the sum of values of existing aliases
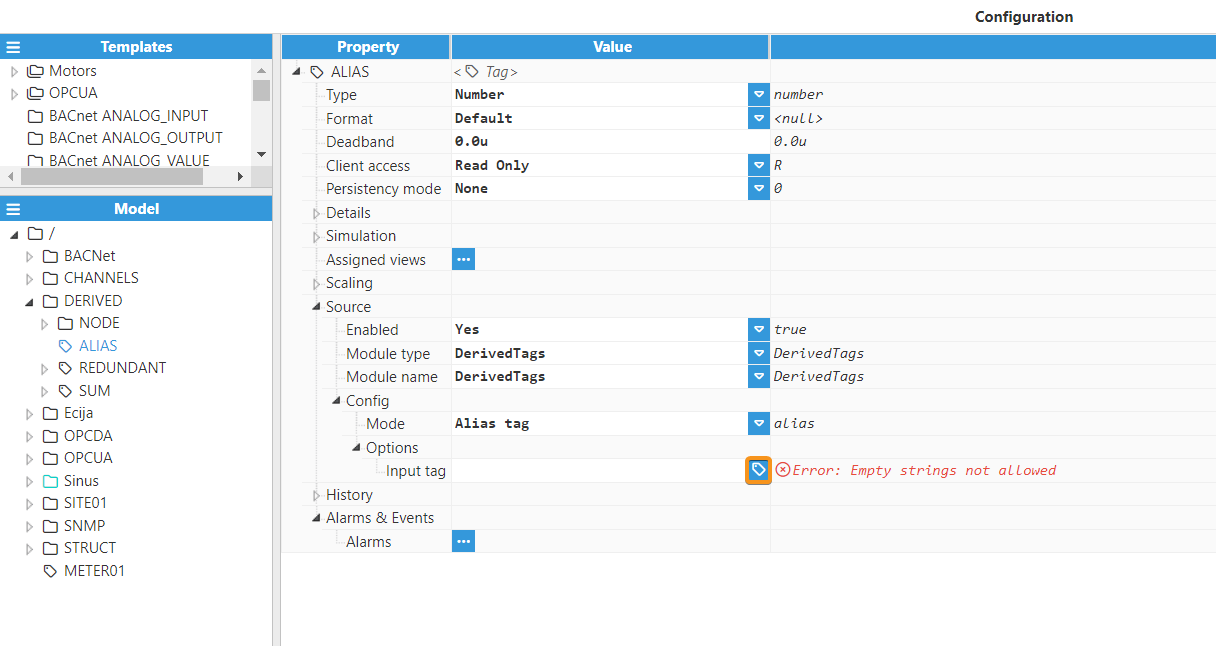
Alias Tags
An Alias Tag is a copy of its input tag. That is, its value, timestamp, and quality will be a replica of those in the original tag. After setting the Type to Alias Tag, the following options will be shown:
.png)
Input Tag: Selects the input tag that will be copied to this tag. This tag must be present in the tag model. Otherwise, a configuration error will be raised during runtime. It's possible to browse and discover the tag by clicking on the button to the right.
.png)
Redundant Tags
Note:
Read/Write permissions can be granted to the Redundant Tag, allowing any values written to it to be mirrored in the input tags.
Redundant Tags are used to create tags with several inputs acting as redundant sources. The value, quality, and timestamp of the output tag correspond to the input tag with the highest quality. After setting the Type to Redundant Tag, the following options will be shown:
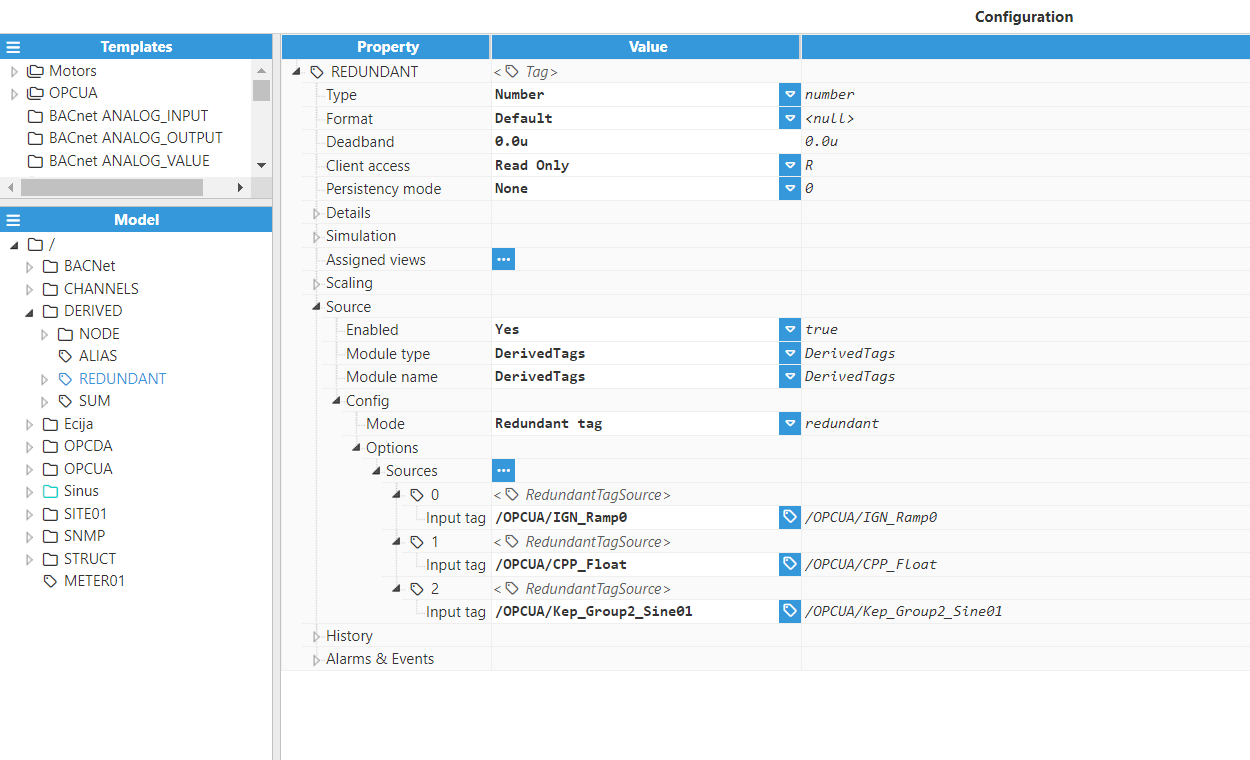
Sources:
Input tag: Selects the input tag that will be copied to this tag. This tag must be present in the tag model. Otherwise, a configuration error will be raised during runtime. It's possible to browse and discover the tag by clicking on the button to the right.
Node tags
Note:
Starting from N3uron version 1.22.0, new Node Tags variables are available.
See the tables below for details.
Node Tags are used to retrieve information about the node, including diagnostics, performance, links, and module status. After setting the Type to Node Tag, the following options will be shown:
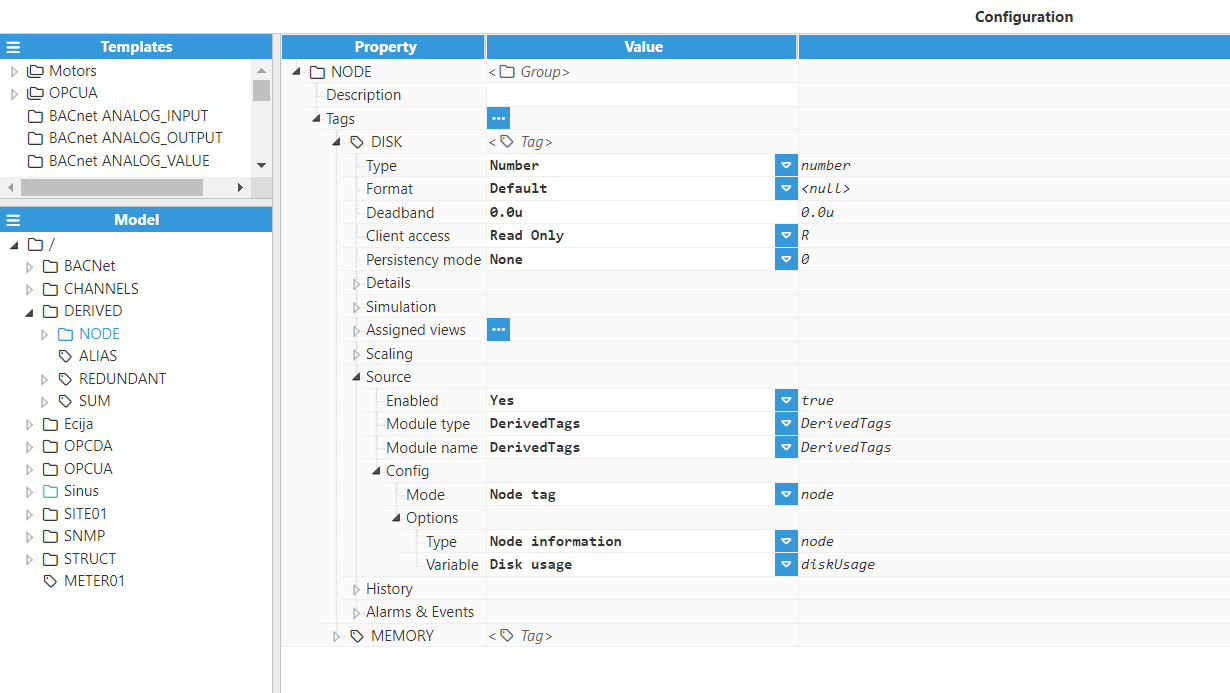
Node information variables
Name | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
Bootstrap build time | The timestamp corresponding to the Bootstrap build time. | string/number |
Bootstrap CPU usage (%) | Shows the current CPU utilization of the Bootstrap process as a percentage. | string/number |
Bootstrap memory usage (GB) | Shows the current memory (RAM) usage of the Bootstrap process, measured in gigabytes (GB). | string/number |
Bootstrap PID | Process identifier (PID) used by the operating system for the Bootstrap process. | string/number |
Bootstrap start time | The timestamp corresponding to when the Bootstrap process started. | string/number |
Bootstrap uptime (ms) | Displays the time the Bootstrap process has been operational, in milliseconds (ms). | string/number |
Bootstrap version | Displays the current version of the Bootstrap. | string |
Bootstrap virtual memory usage (GB) | Shows the current virtual memory usage of the Bootstrap process, measured in gigabytes (GB). | string/number |
Node build time | The timestamp corresponding to the node build time. | string/number |
Node error count | Displays the total number of errors registered by the node. | string/number |
Node installation disk available (GB) | Shows the available disk space (GB) on the disk/partition where the node is installed. | string/number |
Node installation disk total (GB) | Shows the total disk space (GB) on the disk/partition where the node is installed. | string/number |
Node installation disk usage (GB) | Shows the used disk space (GB) on the disk/partition where the node is installed. | string/number |
Node local tag count | Displays the total number of local tags for the node. | string/number |
Node name | Name of the node. | string |
Node remote tag count | Displays the total number of remote tags for the node. | string/number |
Node total tag count | Displays the total number of tags for the node, whether local or remote. | string/number |
Node version | Displays the current version of the node executable. | string |
OS distribution ID | Displays the operating system distribution identifier. | string |
OS kernel version | Displays the operating system kernel version. | string |
OS long version | Displays the operating system long version string. | string |
OS name | Displays the operating system name. | string |
OS version | Displays the operating system version. | string |
System boot time | The timestamp indicating when the host system started. | string/number |
System CPU0 frequency (MHz) | Displays the frequency of CPU0, measured in megahertz (MHz). | string/number |
System CPU0 model | Displays the model of CPU0. | string |
System CPU0 vendor ID | Displays the vendor identifier for CPU0. | string |
System disk available (GB) | Shows the available disk space for the host system disk, measured in gigabytes (GB). | string/number |
System disk file system | Displays the file system type used by the system disk (e.g., ntfs, ext4, xfs). | string |
System disk kind | Displays the disk kind (e.g., HDD, SSD, NVMe, virtual). | string |
System disk mount point | Displays the mount point path for the system disk (e.g., /, /mnt/data). | string |
System disk name | Displays the system disk device name (e.g., sda1, nvme0n1p1). | string |
System disk read-only | Indicates whether the system disk is mounted as read-only. | string/boolean/number |
System disk removable | Indicates whether the system disk is removable. | string/boolean/number |
System disk total (GB) | Shows the total disk space for the host system disk, measured in gigabytes (GB). | string/number |
System disk usage (GB) | Shows the used disk space for the host system disk, measured in gigabytes (GB). | string/number |
System global CPU idle (%) | Shows the overall percentage of time the CPU is idle across all CPUs/cores. | string/number |
System global CPU usage (%) | Shows the overall CPU utilization as a percentage across all CPUs/cores. | string/number |
System hostname | Displays the host name of the system. | string |
System logical core count | Displays the number of logical CPU cores (including hyperthreading, if available). | string/number |
System physical core count | Displays the number of physical CPU cores. | string/number |
System RAM available (GB) | Shows the current available memory (RAM), measured in gigabytes (GB). | string/number |
System RAM total (GB) | Shows the total memory (RAM), measured in gigabytes (GB). | string/number |
System RAM usage (GB) | Shows the current memory (RAM) usage, measured in gigabytes (GB). | string/number |
System specific CPU frequency (MHz) | Displays the frequency of a specific CPU/core, measured in megahertz (MHz). | string/number |
System specific CPU idle (%) | Shows the percentage of time a specific CPU/core is idle. | string number |
System specific CPU model | Displays the model information for a specific CPU/core. | string |
System specific CPU usage (%) | Shows the CPU utilization for a specific CPU/core as a percentage. | string/number |
System specific CPU vendor ID | Displays the vendor identifier for a specific CPU/core. | string |
System swap free (GB) | Shows the current free swap space, measured in gigabytes (GB). | string/number |
System swap total (GB) | Shows the total swap space, measured in gigabytes (GB). | string/number |
System swap usage (GB) | Shows the current swap usage, measured in gigabytes (GB). | string/number |
System time | Displays the host time in UTC. | string/number |
System uptime (ms) | Displays the time the host has been operational, in milliseconds (ms). | string/number |
Link information variables
Name | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
Endpoint | Host or IP address of the remote node. | string |
Local - Allow alarm ACK | Indicates whether the remote node is permitted to acknowledge the alarms of the local node. | string/boolean/number |
Local - Include alarms | Indicates if the alarms are part of the published content in the local node. | string/boolean/number |
Local - S&F enabled | Indicates whether the storage of events when the remote node goes offline is enabled or not. | string/boolean/number |
Local - S&F paused | Indicates whether the storage of events is currently active or paused in the local node. | string/boolean/number |
Local - Subscription | This field shows the remote tag groups this node is subscribed to. | string |
Local - Tag count | The total amount of tags published from the local node through the link. | string/number |
Local - View name | Shows the name of the View if the local node is not publishing the Full Model. | string |
Local - View RW | Indicates whether the View or the Full Model is published in Read-only mode or Read/Write mode in the local node. | string/boolean/number |
Name | The name of the link. | string |
Online | Indicates whether the link is online or not. | string/boolean/number |
Remote - Allow alarm ACK | Indicates whether the local node is permitted to acknowledge the alarms of the remote node. | string/boolean/number |
Remote - Include alarms | Indicates if the alarms are part of the published content in the remote node. | string/boolean/number |
Remote - S&F enabled | Indicates whether the remote node will store events whenever the connection goes offline or not. | string/boolean/number |
Remote - S&F paused | Indicates whether the storage of events is currently active or paused in the remote node. | string/boolean/number |
Remote - Subscription | This field shows the local tag groups the remote node is subscribed to. | string |
Remote - Tag count | The total amount of tags published from the remote node through the link. | string/number |
Remote - View name | Shows the name of the View if the remote node is not publishing the Full Model. | string |
Remote - View RW | Indicates whether the View or the Full Model is published in Read-only mode or Read/Write mode in the remote node. | string/boolean/number |
Type | The type of connection, inbound or outbound. | string |
Module information variables
Name | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
API connection | Indicates whether the module’s API is connected or not. | string/boolean/number |
Build time | The timestamp corresponding to the module build time. | string/number |
CPU (%) | Shows the current CPU utilization of the module process as a percentage. | string/number |
License | Displays whether the license state is in 'Production' or 'Demo' mode. | string |
Memory (GB) | Shows the current memory (RAM) usage of the module process, measured in gigabytes (GB). | string/number |
Name | The name of the module instance. | string |
PID | Process identifier used by the operating system. | string/number |
Running | Indicates whether the module is running or not. | string/boolean/number |
Runtime (ms) | Displays the time the module process has been operational, in milliseconds (ms). | string/number |
Start date | The timestamp corresponding to the module start. | string |
Stop date | The timestamp corresponding to the module stop. | string |
Type | The type of instance, e.g. ModbusClient, DerivedTags, etc. | string |
Version | Displays the module’s version. | string |
Virtual memory (GB) | Shows the current virtual memory usage of the module process, measured in gigabytes (GB). | string/number |
Note:
In N3uron version 1.22.0, the Module Information variable called Auto-restart has been deprecated. Use the Running variable to check the module’s current status instead.
Expressions
When using Expressions, JavaScript code can be created to perform calculations, custom logic, and even advanced data analysis. The result of the expression can be the value, quality, timestamp and initial (indicate when the event is received in response to a new subscription) of the destination tag, expressed as an object with value, quality, ts, and initial properties and assigned to $.output.
Quality and timestamp properties are optional. If quality is omitted, then 192 - Good Quality is automatically assigned and if ts is omitted, then the current timestamp is assigned.
To use other tags as inputs in the expression, an alias per input tag must be created, pointing to its tag path. These input tags are then referred to using their alias instead of the tag path. The properties of the aliases are accessed using value, quality, ts, and initial. For example, accessing the value, quality, and timestamps of a tag withthe alias "tag1" is done in the following way: tag1.value, tag1.quality, tag1.ts and tag1.initial. More information about tag aliases and their properties can be found in Alias.
Expressions also have access to the global variables defined in the module configuration (see more information in Global Variables). A global variable can be accessed directly by using its name (for example, if there is a global variable called counter, it can be incremented by simply using counter++).
Expressions have access to the following Node.js libraries: os, process, Moment.js, and sprintf. These libraries can be accessed by using process, os, moment, or sprintf, in lowercase. For instance, obtaining the RAM memory can be done using: $.output = os.totalmem()/1024/1024;
Nevertheless, the $ object provides access to the following properties:
$.input
This object contains the values of all the input tag aliases defined for this tag. Each input contains the value, quality, ts and initial. For example, for a tag with alias name tag1: $.input.tag1.value provides the value, $.input.tag1.quality provides the quality, $.input.tag1.ts provides the timestamp in UNIX Epoch with milliseconds format and $input.tag1.initial (boolean) indicates whether the value is an event value or comes as a result of the tag being subscribed to other tags.
$.output
This object is used to set the value returned by the expression. It can support a plain value (string, Boolean, or number) that is assigned directly to the value of the derived tag, or an object with value, quality, ts (timestamp displayed in UNIX Epoch with milliseconds), and initial. Quality, timestamp and initial properties are optional. If quality is omitted, then 192 - Good Quality is automatically assigned and if ts is omitted, then the current timestamp is assigned.
Example: $.output = 23.5; assigns this value to the derived tag with good quality and the current timestamp. $.output = {value:23.5, quality:192, ts:1531410114945, initial:True}; assigns the value, quality, timestamp and initial provided.
$.logger
Allows for user-defined messages to be sent to the log file. It allows for messages to be organized in the following log levels: $.logger.error, $.logger.warn, $.logger.info, $.logger.debug, and $.logger.trace. It takes two arguments; a format string using % as a placeholder and a set of arguments that replace the placeholders.
For example, $.logger.trace("Value of tag1 is: %.2f", $.input.tag1.value) logs the message Value of tag1 is: 12.34 when the log of the module is in trace level.
$.links
This object contains the status of the links for the remote tags involved in the expression. The status is a Boolean with a true value when the link is online, and false when it is offline.
For example, if $.links.link01 is `true`, then the link link01 is online.
$.currentValue
This object contains the current value, quality, and timestamp of the derived tag in an object like this: {value:23.5, quality:192, ts:1531410114945}.
For example, $.currentValue.value returns the current value, $.currentValue.quality returns the current quality, and $.currentValue.ts returns the current timestamp in UNIX Epoch format with milliseconds.
$.variables
This object contains user-defined variables. These variables are maintained between tag executions, but cannot be shared with other tags. It is only dropped when the tag configuration is modified or the module is restarted.
For example, to make a counter:
if ($.variables.counter === undefined){
$.variables.counter = 0;
}
const count = $.variables.counter++;
$.output = countbuffer
buffer is an array that stores tag events occurring during a specified aggregation period. These events are used for performing custom calculations when Custom Aggregation is selected. Examples of custom calculations include summing values, averaging values, identifying minimum and maximum values, and calculating statistical measures, all within the given period. The buffer can be accessed within Custom Aggregation JavaScript code to perform these calculations. Each tag event in the buffer contains the following properties:
value: The measurement or reading value of the tag event.
quality: The quality rating of the tag event, indicating a level of confidence in the tag value.
timestamp: The exact time when the tag event was recorded.
virtual: A boolean flag indicating whether the tag event is virtual. Virtual events did not occur within the current interval; they are pulled from the last interval or represent the last sample in the current interval.
$.browse(path, options)
The $.browse() function enables dynamic discovery of tags within the N3uron tag namespace. This function returns an array of tag path strings that match the specified path and optional filtering criteria, allowing Expression Tags to build flexible, data-driven logic based on the current tag model.
Syntax:
const items = $.browse(path, options);Parameters | Type | Require | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
path | String | Yes | Tag namespace path to browse. Examples: "/Plant01", "/BESS/Bank01", "/" (root). |
options | Object | No | Configuration object with the following properties: • recurrent (boolean): When true, browse recursively through all nested groups and tags. When false, browse only the first level. Default: false. • filter (string): Regular expression pattern provided as a string (without delimiters) to filter tag paths. The pattern is case-sensitive and matched against the full tag path. |
Returns an array of strings representing the full paths of discovered tags. Each element in the array is a complete tag path (e.g., "/BESS/Bank01/Power"). The array is empty if no tags match the criteria.
Note:
To verify what $.browse() returns in your environment, create a String Expression Tag and use:
// Browse tags under "/path/" recursively, take only the first 10 results to keep output small, and serialize them to a JSON string $.output = JSON.stringify($.browse("/path/", { recurrent: true }).slice(0, 10));
Examples:
Count matching tags (Number Expression Tag):
const items = $.browse("/BESS/", { recurrent: true, filter: "Power" });
$.output = items.length;List matching tag paths (String Expression Tag):
const items = $.browse("/BESS/", { recurrent: true, filter: "Power" });
$.output = items.join("\n");Check if tags exist (Boolean Expression Tag):
const items = $.browse("/BESS/", { recurrent: true, filter: "Current" });
$.output = items.length > 0;Match multiple patterns using regex groups:
const items = $.browse("/BESS/", { recurrent: true, filter: "Bank0(1|2)" });
$.output = items.length;Post-filter to exclude unwanted matches:
let items = $.browse("/BESS/", { recurrent: true, filter: "Power" });
items = items.filter(p => !String(p).includes("Reactive"));
$.output = items.length;Read value of first matching tag (using $.read()):
const items = $.browse("/BESS/", { recurrent: true, filter: "Current" });
if (items.length === 0) {
$.output = 0;
} else {
$.output = $.read(items[0]).value;
}Build a summary string:
const items = $.browse("/BESS/", { recurrent: true, filter: "Power" });
const first = items.slice(0, 5).join(", ");
$.output = `Matches: ${items.length}` + (items.length ? ` | First: ${first}` : "");Sum values of all matching tags (Number Expression Tag):
const items = $.browse("/BESS/", { recurrent: true, filter: "Power" });
let sum = 0;
for (const p of items) {
const r = $.read(p);
if (r && r.quality >= 192 && typeof r.value === "number") {
sum += r.value;
}
}
$.output = sum;Debug output as JSON (String Expression Tag):
const items = $.browse("/BESS/", { recurrent: true });
$.output = JSON.stringify(items.slice(0, 20));$.read(path)
The $.read() function retrieves the current value, quality, and timestamp of any tag in the N3uron tag namespace. This function is particularly useful when combined with $.browse() to dynamically read values from discovered tags or to access tags outside the Expression Tag's current location.
Syntax:
const tagData = $.read(path);Parameters | Type | Require | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
path | String | Yes | Tag path to read. Supports three path formats:
|
Returns an object containing the tag's current state with the following properties:
value: The current value of the tag (data type depends on the tag configuration).
quality: The quality of the current value.
ts: The timestamp of the current value in Unix epoch format with milliseconds.
{
value: 23.5,
quality: 192,
ts: 1735934485000
}Examples:
Read value using absolute path:
const temp = $.read("/Plant/Area1/TemperatureSensor01");
$.output = temp.value;Read value using relative path from current location:
const data = $.read("./SetPoint");
$.output = data.value;Read value using relative path from parent location:
const voltageData = $.read("../Inverter/Voltage");
$.output = voltageData.value;Validate tag quality before using the value:
const voltageData = $.read("/Inverter/Voltage");
if (voltageData.quality < 192) {
$.logger.warn("Invalid quality voltage tag value: " + voltageData.quality);
$.output = 0;
} else {
$.output = voltageData.value;
}Combine $.browse() and $.read() to dynamically read multiple tags:
const items = $.browse("/BESS/", { recurrent: true, filter: "Current" });
let total = 0;
for (const tagPath of items) {
try {
const data = $.read(tagPath);
if (data.quality >= 192) {
total += data.value;
}
} catch (error) {
$.logger.error("Error reading tag: " + tagPath + " - " + error.message);
}
}
$.output = total;Calculate the arithmetic mean of the current values of dynamically discovered tags (filtered by ‘Current’) with Good quality:
const items = $.browse("/Inverter/", { recurrent: true, filter: "Current" });
let sum = 0;
let count = 0;
for (const tagPath of items) {
const data = $.read(tagPath);
if (data.quality >= 192) {
sum += data.value;
count++;
}
}
$.output = count > 0 ? sum / count : 0;Error handling when reading dynamic tags:
try {
const currentData = $.read("/Inverter/Current");
$.output = currentData.value;
} catch (error) {
$.logger.error("Error reading current tag: " + error.message);
$.output = 0;
}Alias
Aliases are used to reference other source tags in the expression of an Expression Tag, as well as triggers for Expression Tags whose trigger is set to “On change”. A tag can have aliases that are not used in the expression. This allows for tags to trigger whenever those aliases change in order to update a value, even if they don’t depend directly on the alias.
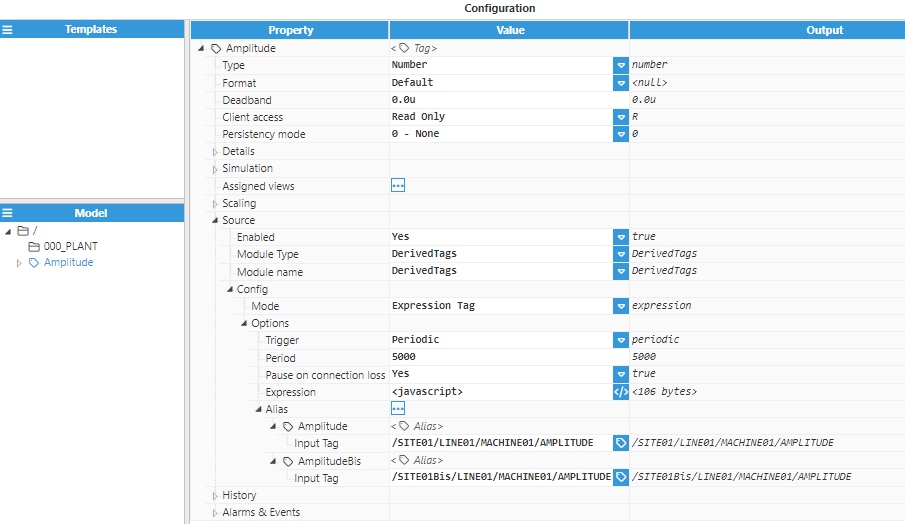
Aliases can be configured with the following options:
Input tag: Provides the tag path to the source tag linked to this alias.
The tag path cannot be used directly in the expression. Instead, the alias must be used. The value, timestamp, quality and initial of the source tag can be accessed using the following syntax (using data1 as the alias):
Value: $.input.data1.value
Timestamp: $.input.data1.ts
Quality: $.input.data1.quality
Initial: $input.data1.initial
Using Relative and Absolute Tag Paths
Tag paths that begin with /... are known as absolute paths. Absolute paths are useful when the path of the source tags might change in reference to the Derived Tag (for example, the Derived Tag can be in different nested levels, /Derived/Nested/Tag_example).
Paths that don't begin with /... are relative paths (for example, Tag1 or ./Tag2). These paths are relative to the group that contains the Derived Tag. The relative path can begin either with the name of the target tag (For example, Tag1), with a reference to the local tag group followed by the tag name (./Tag1, which has the same meaning as the previous example), or with a reference to the parent group (../Tag2). When targeting a group, multiple of these references can be used (For example, ../../Group1/Group2/Tag3 goes up two levels from the current group, then into Group1, next into Group2, and finally selects Tag3 in that group).