Note:
Before starting configuration, a new module instance must be created.Click here for more information about creating Module instances.
Module Configuration
To access the Historian module configuration, navigate within the WebUI module to Config → Modules → [Historian instance name].
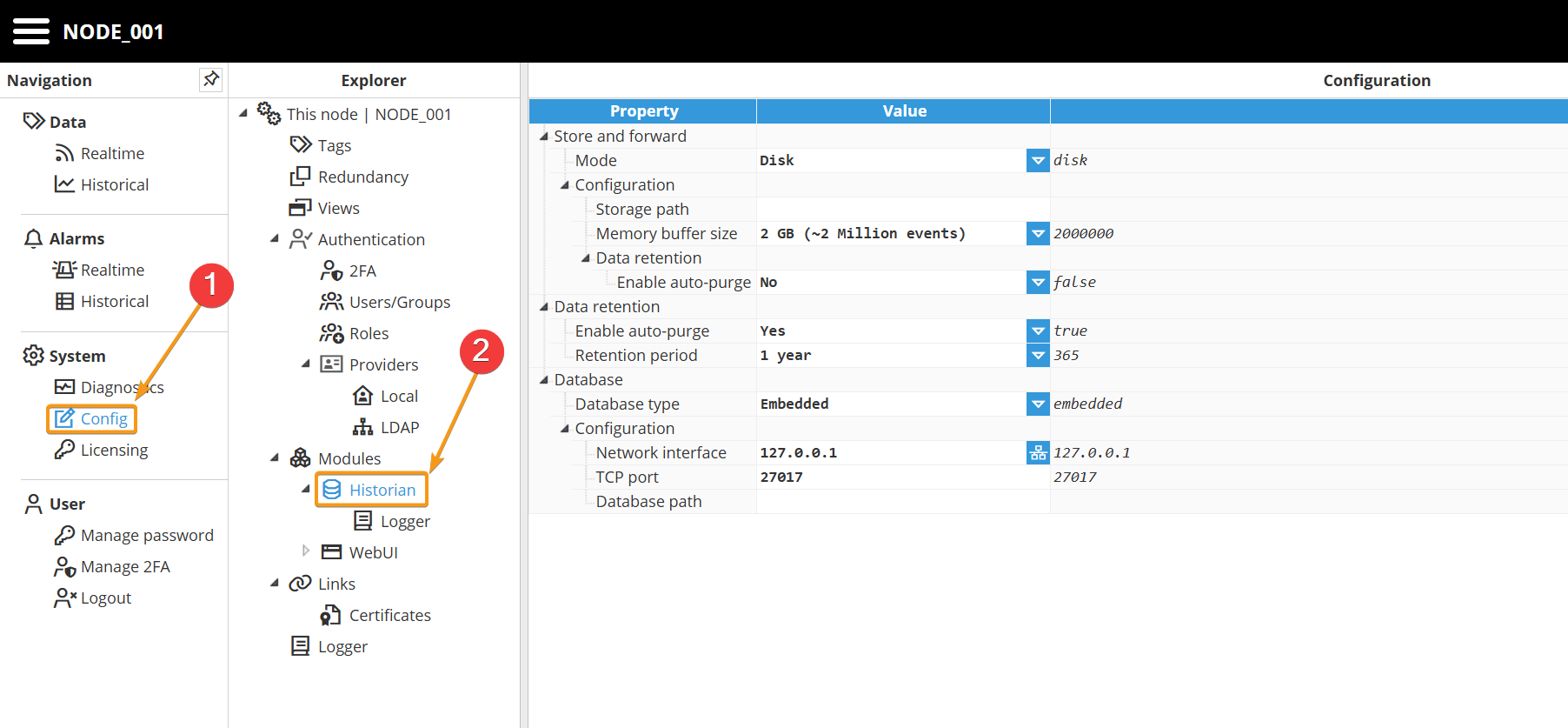
Store and Forward
The Historian module in N3uron v1.22 introduces a new built-in Store and Forward (S&F) mechanism for historical data, designed to ensure maximum data durability in scenarios such as network interruptions, database outages, or during database maintenance operations.
The Store and Forward has two operational modes, Memory and Disk.
Memory
In this mode, Store and Forward (S&F) data is stored exclusively in memory, with no persistence to disk. A configurable buffer size is provided to prevent out-of-memory conditions. When the buffer limit is reached, the oldest events are discarded to make room for new events.
This mode does not provide data persistence and is therefore not recommended for production environments; use only in development or testing environments.
Configurable settings for Memory mode:
Setting | Description |
Memory events limit | Specifies the maximum number of events that can be kept in memory to prevent out-of-memory conditions. Once this limit is reached, the oldest events are discarded. |
Disk
In this mode, Store and Forward (S&F) data is initially stored in a memory buffer and is automatically persisted to disk to prevent data loss in the event of power failures or unexpected system shutdowns.
Disk mode guarantees data durability and ensures delivery to the database once the connection is restored. This is the recommended mode for production environments.
The configurable settings for Disk mode are as follows:
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Storage path | Path to the directory where the Store and Forward (S&F) data will be persisted. If left empty (default), a folder named sf is created inside the module data directory. |
Memory buffer size | Specifies the maximum amount of memory that the buffer is allowed to use in order to prevent out-of-memory conditions. When this limit is reached, buffered events are flushed to disk and are never discarded. The buffer size should be configured based on the available system RAM |
Data retention
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Enable auto-purge | Enables automatic purging of Store and Forward data that is older than the configured maximum retention period. Use this setting to prevent disk space exhaustion. |
Retention period (hours) | Specifies the number of hours that Store and Forward data is retained on disk. Data older than the configured retention period is automatically deleted. Ensure sufficient disk space is available to store all Store and Forward data for the duration of this period. As a guideline, 1 million events require approximately 1 GB of disk space. |
Data Retention
Configure the desired retention period for historical data. Once this period expires, the data is automatically removed from the database to free storage resources and reduce costs.
Configurable settings for Data Retention:
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Enable auto-purge | Enables automatic purging of historical data that is older than the configured maximum retention period. |
Retention period | Specifies the number of days that data is retained in the historian database. Data older than the configured retention period is automatically deleted. |
Database
Embedded
To use the EmbeddedDB make sure to have the following hardware requirements:
x64: The CPU must support AVX instructions.
ARM64: The CPU must use the ARMv8.2-A microarchitecture or later.
The EmbeddedDB is included out-of-the-box in all N3uron installations (x64 and ARM64) and ready to be used in the Historian module for local historization.

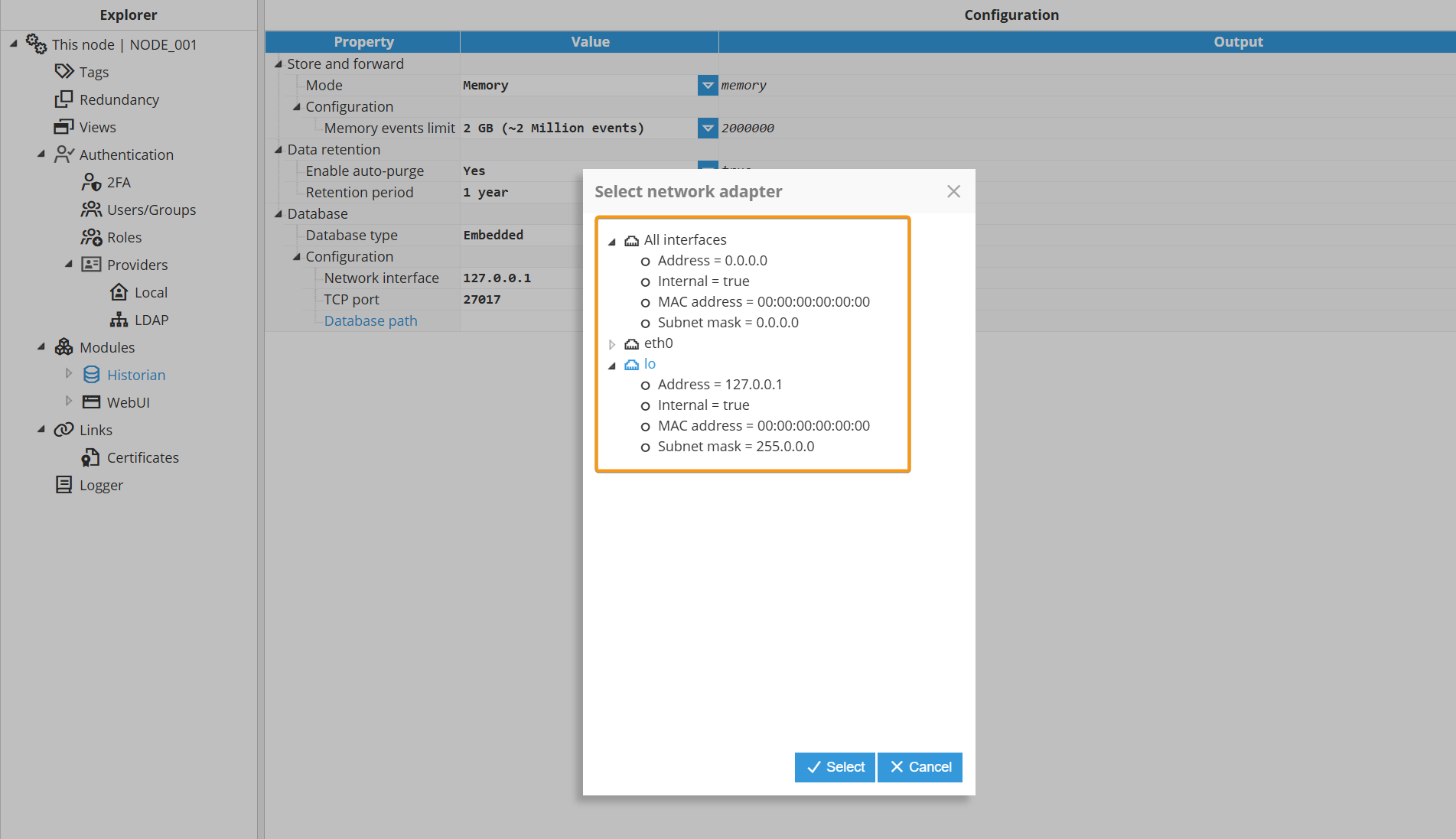
Configuration
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Network interface | Specifies a comma-separated list of network interfaces through which the embedded database accepts incoming connections. Examples:
You may also specify one or more individual IP addresses for fine-grained access control (for example, Note: The database always listens on |
TCP port | Specifies the TCP port used to connect to the embedded database. The default value is 27017, Valid range: 1 to 65,535 |
Database path | Specifies the directory where the embedded database files are stored. You can provide either an absolute or a relative path.
|
Use the Network Interface selector to customize the Network interface setting. Otherwise, leave the default configuration unchanged.

MongoDB
In this mode, the N3uron Historian uses MongoDB as the storage backend for historical data.
You must have a MongoDB database available. N3uron currently supports MongoDB versions 3.6 through 8.2. We recommend using the latest MongoDB release that is under active support and receives security patches. Refer to the official documentation to install MongoDB.
The MongoDB Historian supports the following deployment options:
Standalone: Single MongoDB instance. It can be installed on the same machine as N3uron, but a separate host is recommended.
Replica Set: High-availability, fault-tolerant MongoDB replica set for redundant deployments.
MongoDB Atlas Cluster: A fully managed, high-availability, fault-tolerant replica set deployment hosted on MongoDB Atlas.
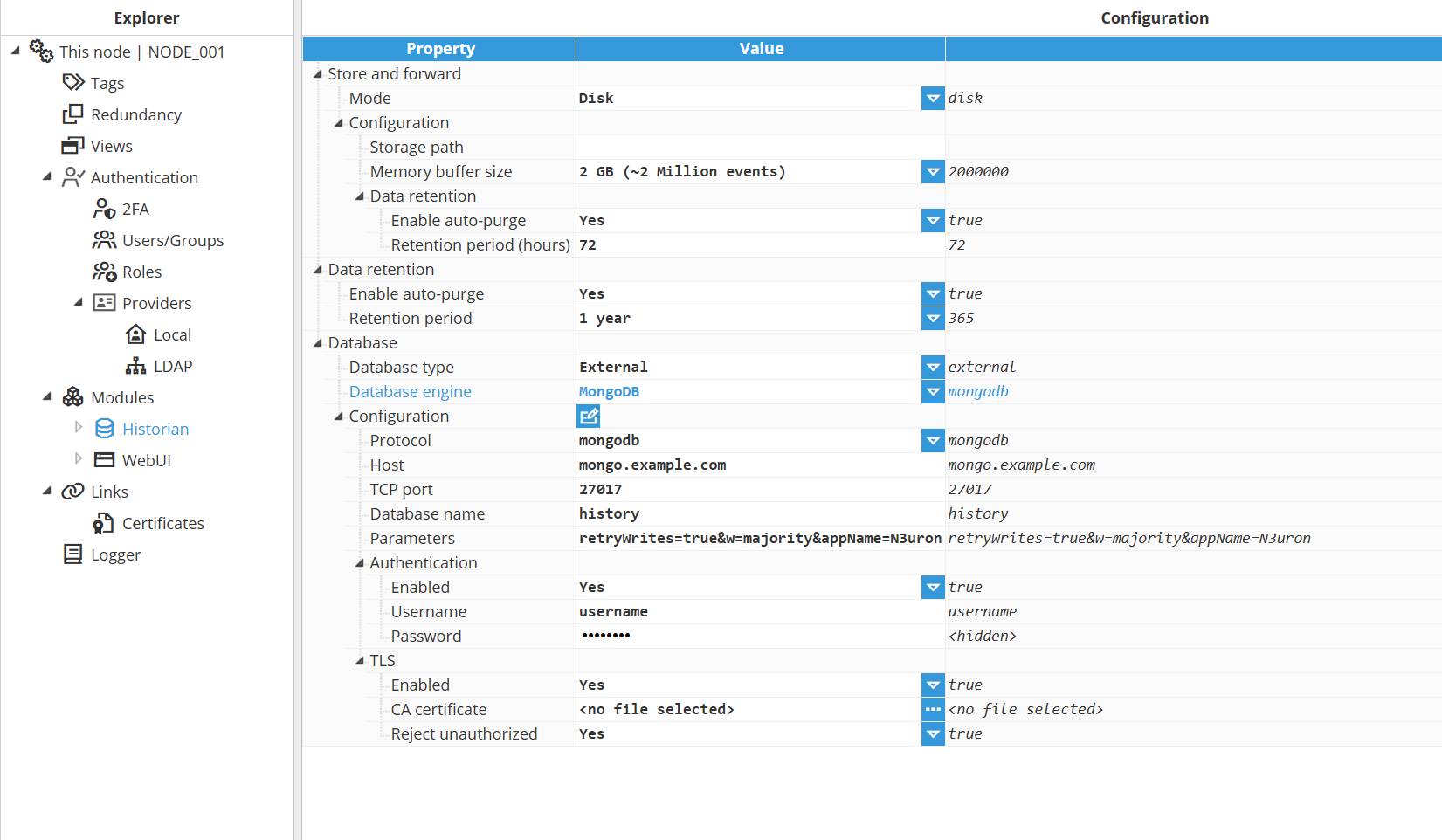
Configuration
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Protocol | Specifies the connection string format used to connect to the MongoDB server.
For additional details, refer to the MongoDB documentation on connection string formats. |
Host | Hostname or IP address of the MongoDB server or cluster. |
TCP port | Specifies the TCP port used to connect to the MongoDB server. Default port: Valid range: |
Database name | Name of the database where the data is stored. N3uron creates the database automatically if it does not already exist. If authentication is enabled, the provided credentials are validated against this database. Ensure that the user has the appropriate read and write permissions on the specified database. |
Parameters | Provide additional parameters in query string format to customize your connection. Use standard TimescaleDB URI options, such as:
|
Authentication
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Enabled | Enables or disables authentication when connecting to the MongoDB server. |
Username | Username used to authenticate with the database. |
Password | Password used to authenticate with the database. |
TLS
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Enabled | Enables or disables the use of Transport Layer Security (TLS) to encrypt communications with the database. |
CA certificate | The Certificate Authority (CA) certificate used to validate the certificate presented by MongoDB when establishing a TLS connection. If left empty, N3uron uses the operating system’s certificate store for validation. |
Reject unauthorized | Enforces certificate validation and rejects the connection if the TLS certificate presented by the database is not trusted. Disable this option only for staging or testing environments. |
TimescaleDB
Note
TimescaleDB support was introduced in N3uron v1.22
In this mode, the Historian module uses a PostgreSQL instance with TimescaleDB to store historical data.
You must have TimescaleDB installed. Refer to the official TimescaleDB documentation for installation and operational guidance
The TimescaleDB Historian supports the following database deployments:
Self-hosted TimescaleDB: A self-managed PostgreSQL instance with the TimescaleDB extension installed.
Tiger Data Cloud: A fully managed TimescaleDB service provided by TigerData.
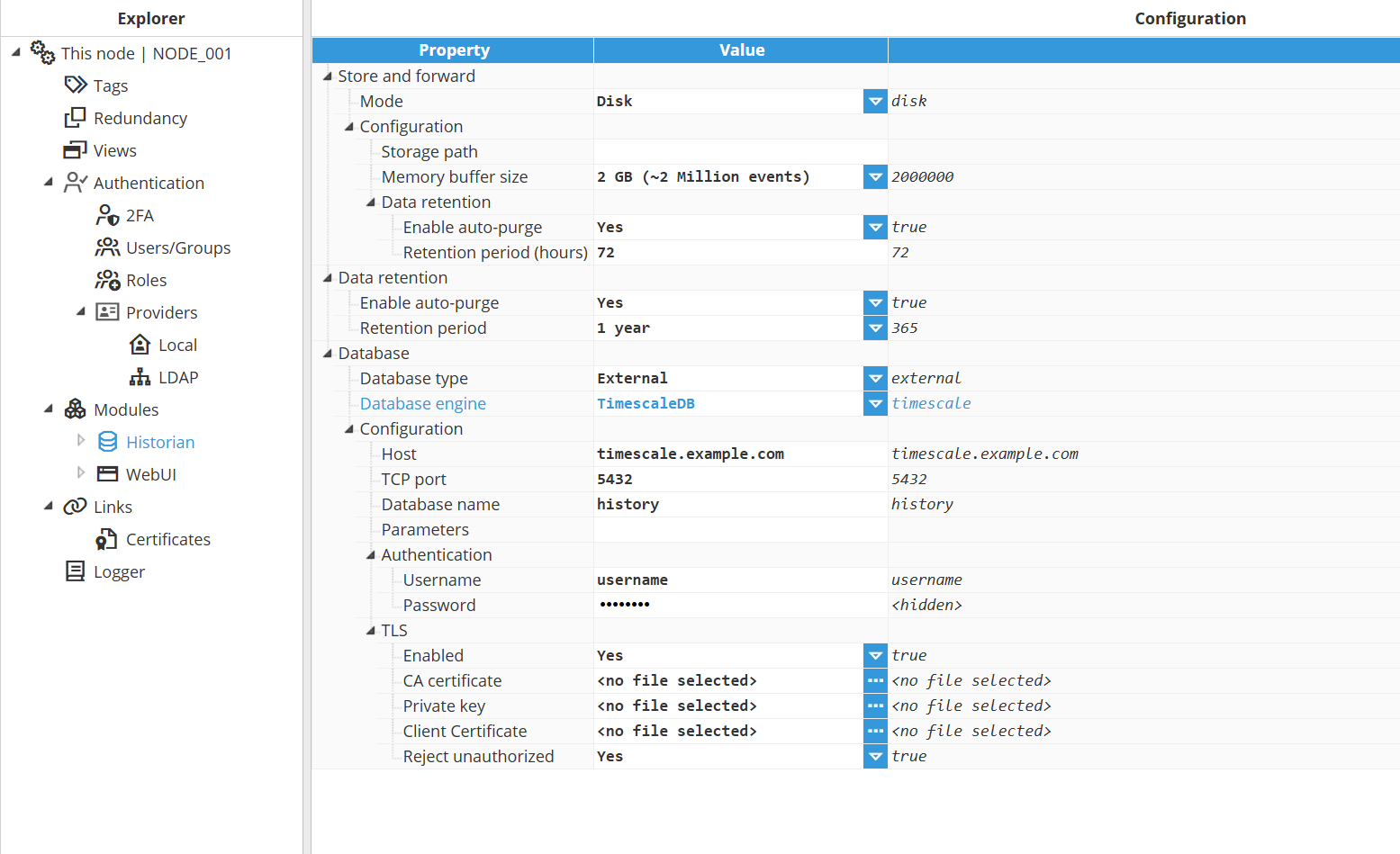
Configuration
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Protocol | Specifies the connection string format used to connect to the TimescaleDB server. For additional details, refer to the TimescaleDB documentation on connection string formats. |
Host | Hostname or IP address of the TimescaleDB server. |
TCP port | Specifies the TCP port used to connect to the TimescaleDB instance. Default port: Valid range: |
Database name | Name of the database inside TimescaleDB where the data is stored. Ensure that the user has the appropriate read and write permissions on the specified database. |
Parameters | Provide additional parameters in query string format to customize your connection. Use standard PostgreSQL options, such as:
|
Authentication
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Enabled | Enables or disables authentication when connecting to the TimescaleDB server. |
Username | Username used to authenticate with the database. |
Password | Password used to authenticate with the database. |
TLS
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Enabled | Enables or disables the use of Transport Layer Security (TLS) to encrypt communications with the database. |
CA certificate | The Certificate Authority (CA) certificate used to validate the certificate presented by MongoDB when establishing a TLS connection. If left empty, N3uron uses the operating system’s certificate store for validation. |
Private key | Optional private key used for client authentication when TLS is enabled. Provide the PEM-encoded private key that corresponds to the client certificate. This is required when the server enforces mutual TLS (mTLS) authentication. |
Client certificate | Optional client certificate used for authentication when TLS is enabled. Provide the PEM-encoded certificate that identifies the client to the server. This parameter is required when the server enforces mutual TLS (mTLS) authentication. |
Reject unauthorized | Enforces certificate validation and rejects the connection if the TLS certificate presented by the database is not trusted. Disable this option only for staging or testing environments. |
Tag Configuration
After configuring the Historian module, users can define the historization settings for individual tags. The following screenshot illustrates the available options in the Tag→History configuration section.
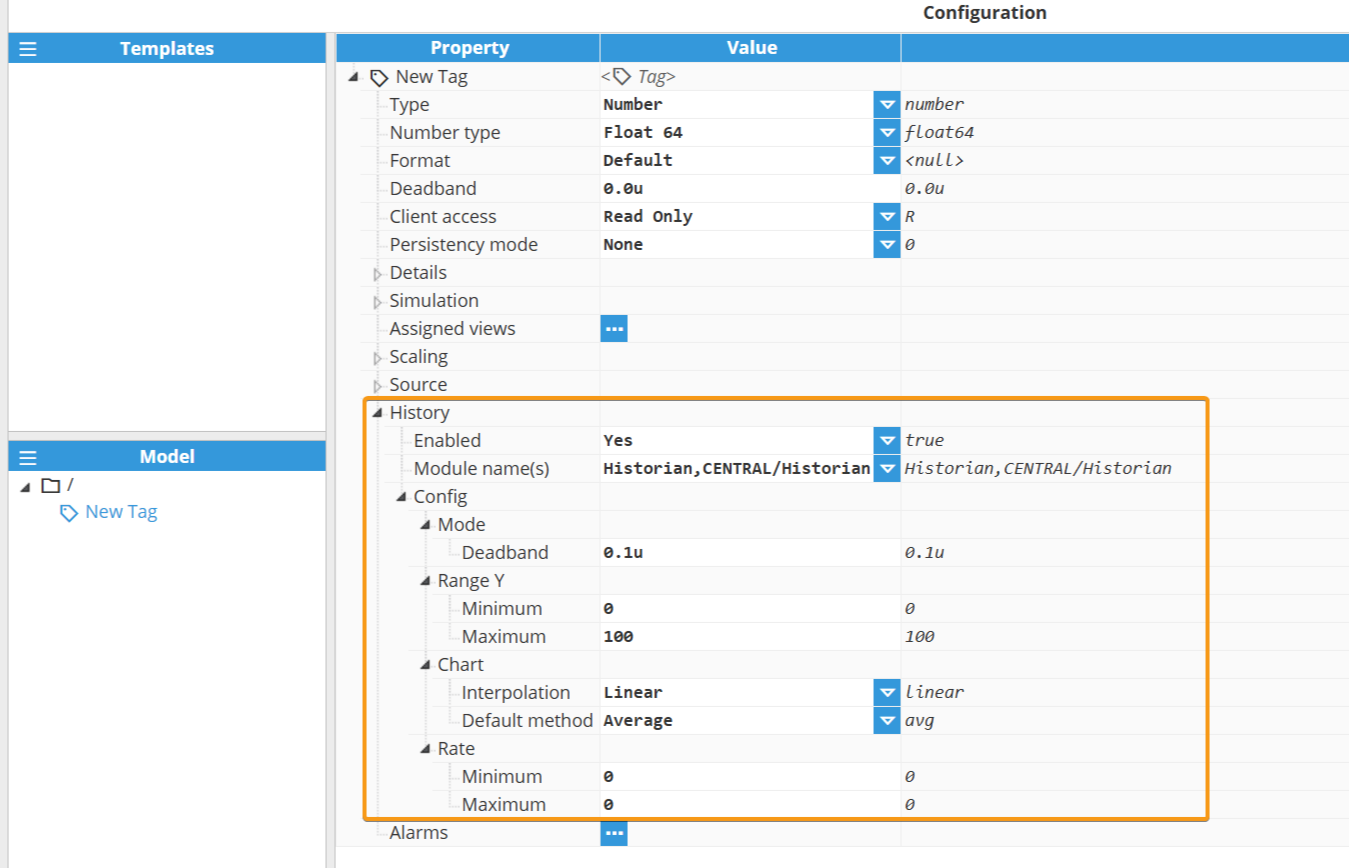
History
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Enabled | Enables or disables historization for the tag. |
Module name(s) | Specifies the name or names of the modules that will historize the tag. Multiple modules can be defined using a comma-separated list.
|
Mode
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Deadband | Specifies the deadband used to determine whether an event should be historized. Both absolute and percentage-based deadbands are supported. Examples:
|
Range Y
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Minimum | Default Y-axis minimum value, in Engineering units. |
Maximum | Default Y-axis Maximum value, in Engineering units. |
Chart
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Interpolation | Specifies the default representation of historical values.
|
Default aggregation method | Specifies the default aggregation method used to retrieve historical values.
|
Rate
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Minimum | Specifies the minimum historization rate, expressed in milliseconds. It defines the shortest allowed time interval between storing two consecutive change events. Events stored as a result of reaching the Maximum rate setting are not considered when calculating this minimum interval. Example: |
Maximum | Specifies the maximum historization rate, expressed in milliseconds. This interval defines the longest time allowed between storing records when no new events occur. If the time difference between two consecutive values exceeds this interval, virtual values are generated on the fly for each historical request to fill the gap. Example: |
Data retrieval
Historian stores events (changes in value, quality, or timestamp). Data can be retrieved from the storage in different modes:
Raw: Data retrieved contains all values for all events stored in the database.
Aggregated: Data is consolidated into aggregation periods. The following aggregation methods are available:
Average: Returns the weighted time average during the aggregation period.
Minimum: Returns the minimum value in the aggregation period.
Maximum: Returns the maximum value in the aggregation period.
First: Returns the first value in the aggregation period.
Last: Returns the last value in the aggregation period.
Delta: Returns the difference between the first and last sample during the aggregation period.
Standard deviation: Returns the Standard deviation during the aggregation period.
Note:
Delta and Standard deviation aggregates are available from N3uron version 1.21.10.
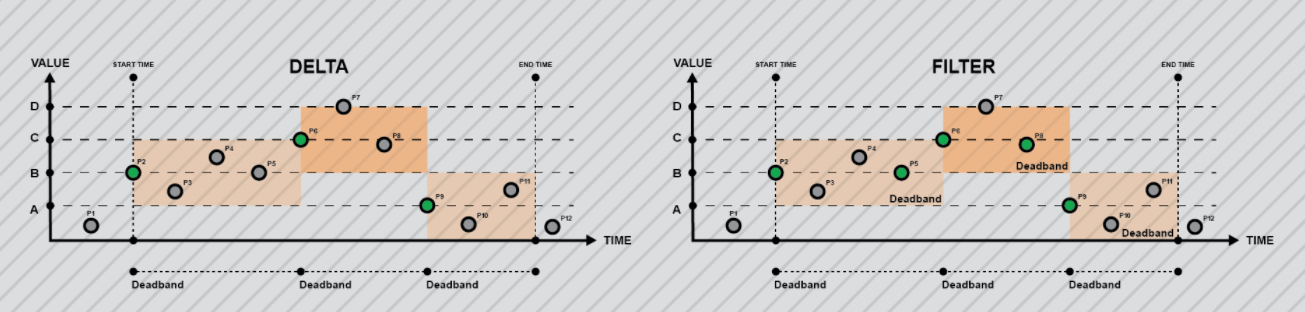
Delta: The data retrieved contains all the values of all events displaying incremental changes compared to any previous event that is larger than the configured deadband. It only contains the second event (the one taking place after the first event that surpassed the deadband).
Filter: Data retrieved contains all the values for all events displaying changes compared to any previous event that is larger than the configured deadband. In this case it contains both events, the one before the change that surpassed the deadband and the one after the change.