What is SparkPipe
SparkPipe is a cutting-edge connectivity solution designed for IIoT and DataOps that seamlessly bridges operational data at the edge with advanced data processing in the cloud. This service integrates operational data into various data-driven applications, such as stream processing, advanced analytics, machine learning, and predictive maintenance. By leveraging open protocols and standardized data models, SparkPipe ensures the efficient and effective use of data from industrial assets and systems.
SparkPipe is a cloud-native service that utilizes the MQTT Sparkplug v3 specification to securely connect to any MQTT 3.1 compatible broker, capturing all the events published by any Sparkplug-enabled edge node, and routing this data to cloud-based services and applications.
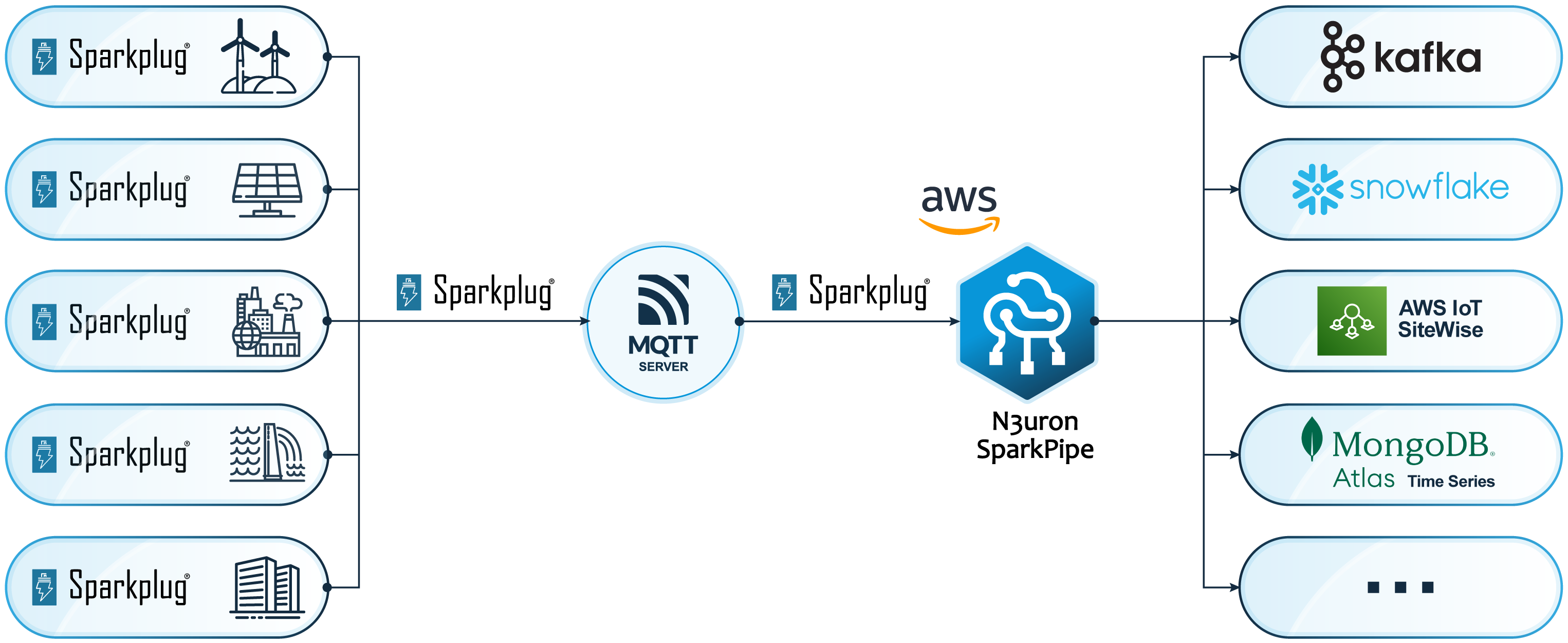
Designed to be highly reliable, secure by default, easy to configure, and simple to operate, SparkPipe is a no-code solution that integrates natively with AWS deployment systems, security features, and access mechanisms, making it accessible to a broad range of users.
SparkPipe transforms raw OT data into actionable insights, driving operational efficiency and unlocking the full potential of your Industrial IoT and DataOps initiatives.
Connectors
Apache Kafka
The Apache Kafka connector simplifies the use of Kafka for IIoT by integrating MQTT Sparkplug data into the Kafka messaging flow. It publishes all events to Kafka clusters, such as Amazon MSK or Confluent Cloud, using a JSON representation of the Sparkplug payload. It supports various authentication methods including SASL/PLAIN, SASL/SCRAM, mTLS, and AWS IAM. Additionally, it supports data compression to reduce bandwidth and disk usage, and topic partitioning to scale throughput.
MongoDB Time Series
The SparkPipe connector for MongoDB leverages the MongoDB Time Series engine to ingest every event in your Sparkplug network in a time series collection along with it’s context and metadata.
AWS IoT SiteWise
Provides a no-code integration of Sparkplug OT data with the AWS IoT SiteWise service, automatically creating Asset models and Assets to match your edge data model while continuously ingesting real-time data into the IoT SiteWise time-series engine.
Snowflake
The Snowflake connector streams Sparkplug events directly into Snowflake tables, enabling no-code, zero-ETL, and cost-effective ingestion of Sparkplug OT data into the Snowflake Data Cloud. Each event is accessible in a ready-to-use SQL table with its context and metadata for seamless analytics and integration.
Stdout
The Stdout connector is provided for testing purposes; it logs the Sparkplug metrics to the console’s standard output using an easy-to-read JSON format that represents the Sparkplug payload.