MING Stack: The Power of balena and N3uron in Industrial Data Management
Overview
In a previous post, we described how to simplify industrial data management by deploying a complete Industrial Edge node using Docker containers and our customized MING stack (MQTT, InfluxDB, N3uron and Grafana). As we explained, this architecture enables consistent, versioned, portable and scalable deployments that increase operational efficiency.
Let’s take a closer look at the components of this stack:
- MQTT: A lightweight and efficient, publish-subscribe protocol.
- InfluxDB: A time-series database optimized for storing, querying and visualizing time-stamped data.
- N3uron: A lightweight industrial platform for DataOps that runs on devices at the edge of the network.
- Grafana: A popular open-source interactive data visualization platform for visualizing and analyzing data from any source.
When it comes to scaling projects, remotely managing all connected devices can become a daunting task for an IT team. Deploying software updates and critical fixes, as well as performing scheduled maintenance across multiple Edge Nodes and vast geographical distances can be challenging. That’s where balena comes in, balena is a complete IoT fleet management platform that allows deploying, managing, and scaling fleets of IoT Linux devices.
In this article, we present a variant of the above-mentioned architecture that uses balena. Additionally, for this example, we will substitute HiveMQ for Mosquitto to make the solution even lighter.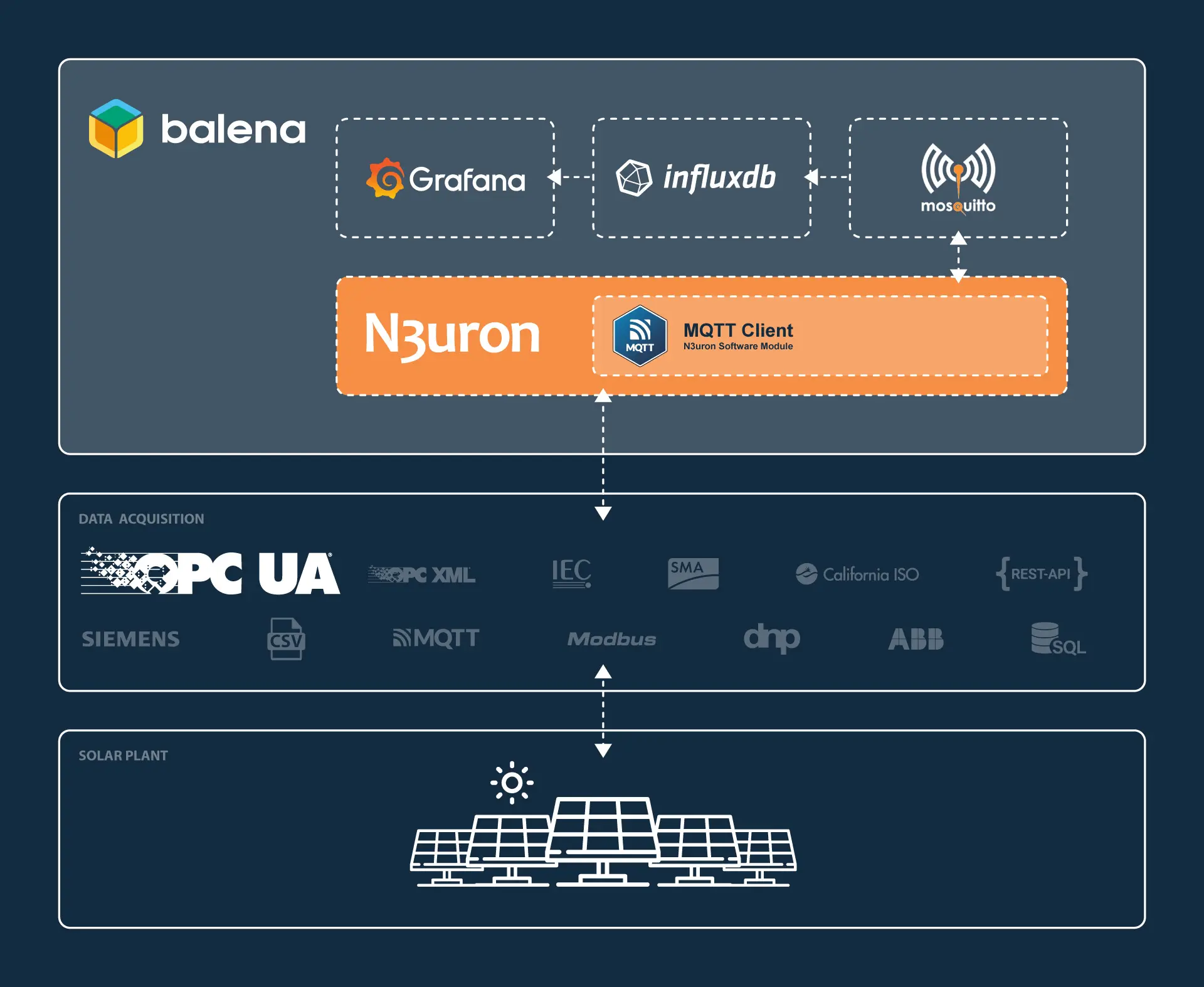
We have also drastically simplified the deployment process compared to our previous post. Now Telegraf (responsible for subscribing to the MQTT topics and inserting data into InfluxDB) and InfluxDB work out-of-the-box without any additional steps or configurations.
As you will see for yourself, the resulting solution is easier to manage, operate and scale to address organizations' data challenges than other legacy solutions on the market.
The addition of N3uron to the MING stack provides several advantages including:
- The ability to adapt and scale in complex and growing environments.
- Lightweight and powerful edge computing capabilities.
- Secure communications, modern authentication strategies, user auditing, and control over system access to safeguard data and applications.
- Built-in tools for remote control, data visualization and analysis, provided by modules such as Web Vision and Historian.
- Templates, which allow for rapid building of complex data structures and communication configurations which help drastically reduce the amount of required work for deployments.
- The licensing model is server-based and unlimited, allowing for easy deployment of unlimited web clients, tags, connections, and devices.
By leveraging the capabilities of all these technologies working together, businesses can unlock new insights and efficiencies in their operations. Some potential use cases for the MING stack include:
- Real-time monitoring and analysis of industrial equipment and processes
- Integration of industrial data with enterprise systems for business intelligence and decision-making
- Energy management and optimization for industrial facilities
- Remote monitoring and control of distributed assets
- Integration of legacy industrial systems with modern data platforms
- Quality control and assurance for manufacturing processes
- Environmental monitoring and compliance reporting
- Predictive maintenance and anomaly detection for industrial machinery
- Asset tracking and inventory management
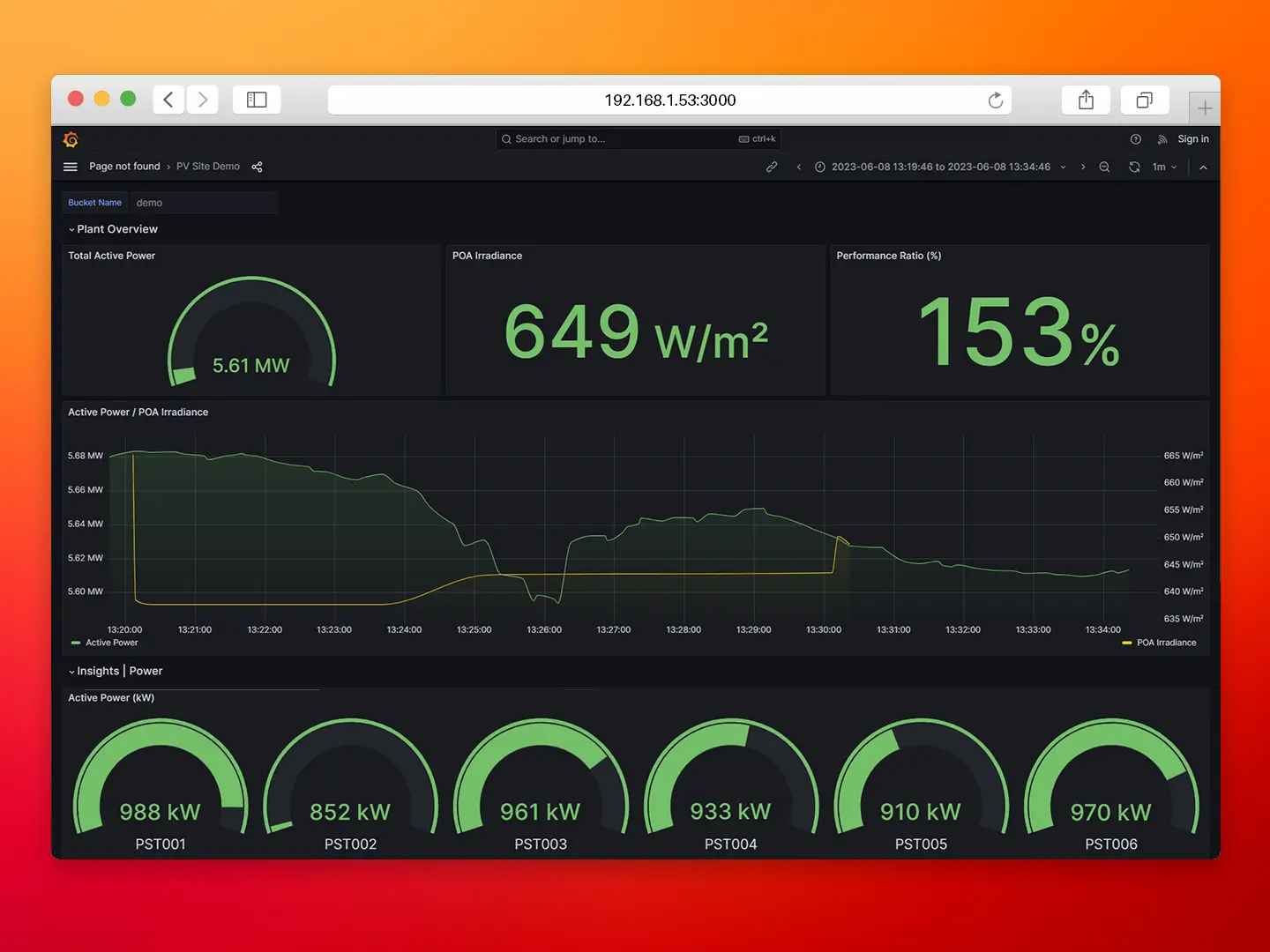
Alike in the previous post, once you have completed the configuration steps outlined in the following sections, you will have a fully functional proof of concept with real-time data streaming from a Photovoltaic Plant located in Italy. The data, received through a remote OPC UA Server, will flow seamlessly through your local N3uron instance and be displayed on your Grafana dashboard.
Deploy MING with balena
Deploy from balenaHub (Recommended)
BalenaHub is a marketplace that offers ready-to-deploy applications for small device fleets. With just a few clicks, it is possible to deploy and manage these applications centrally using balenaCloud.

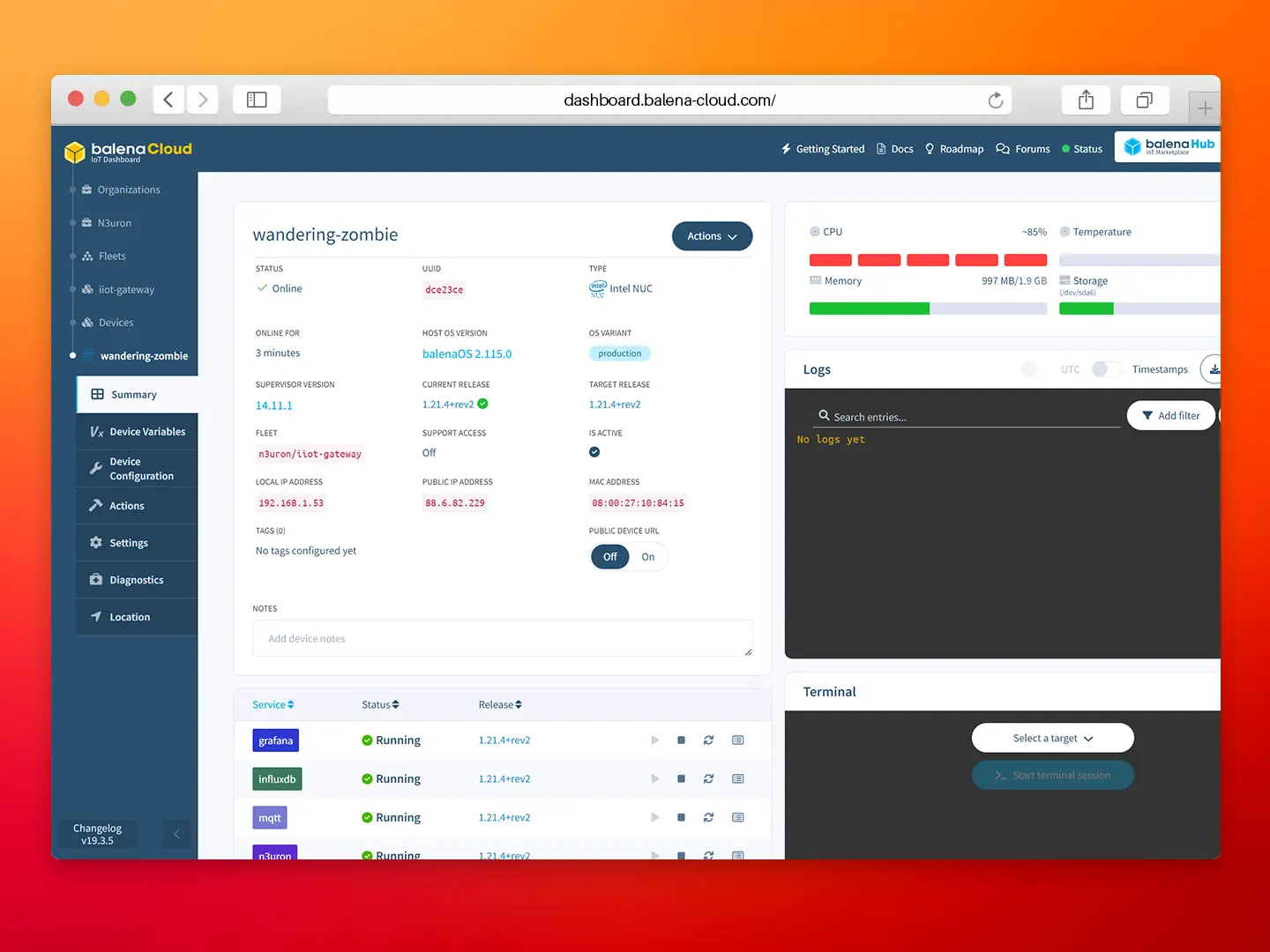
- Step 1: To deploy the N3uron application, simply visit https://hub.balena.io/apps/2047510/MING) and click on the Deploy button. You will then be prompted to log in to your balenaCloud account. Once logged in, you can choose to deploy the app to either a new or an existing fleet.
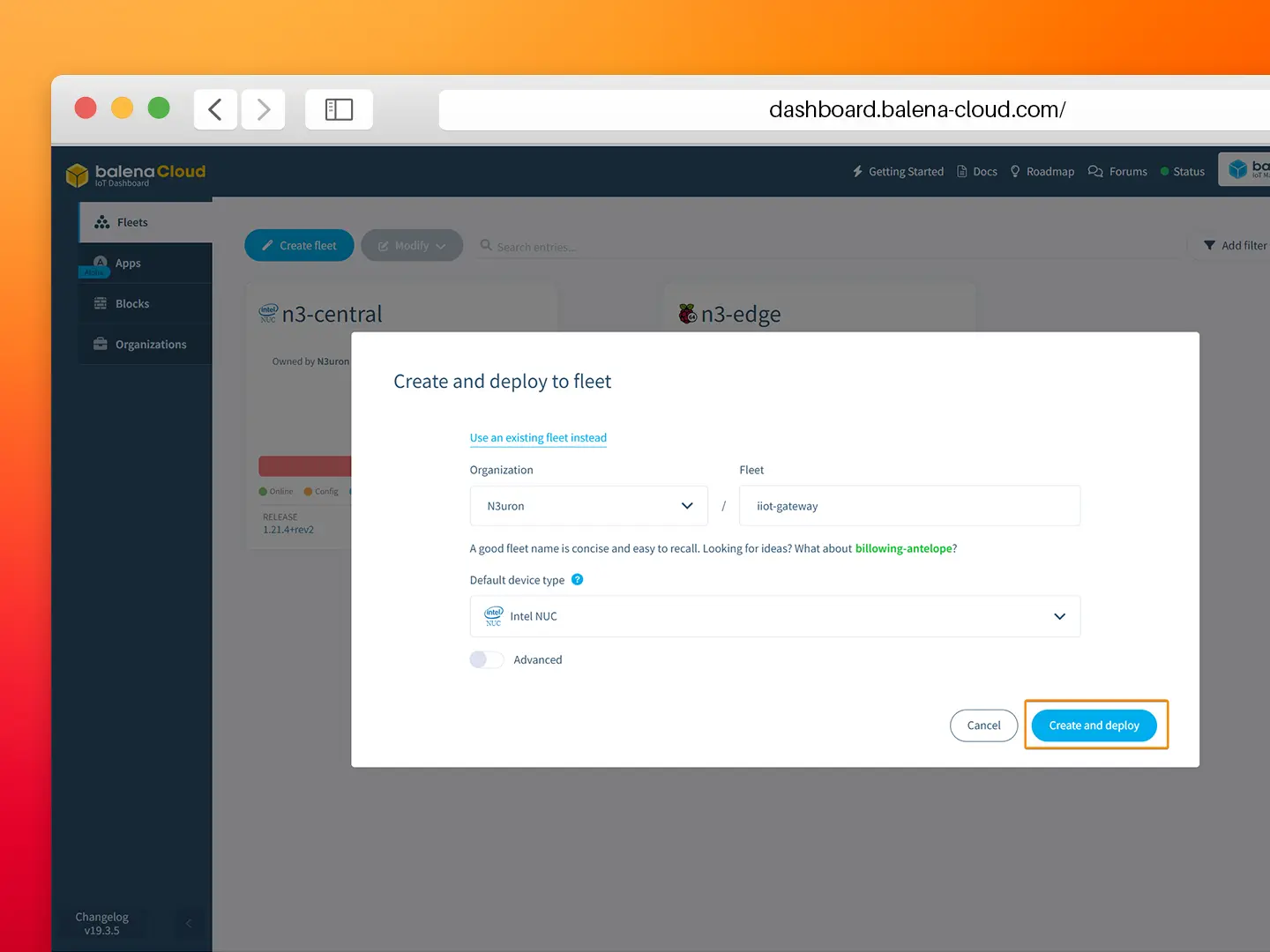
- Step 2: Click on Add device.
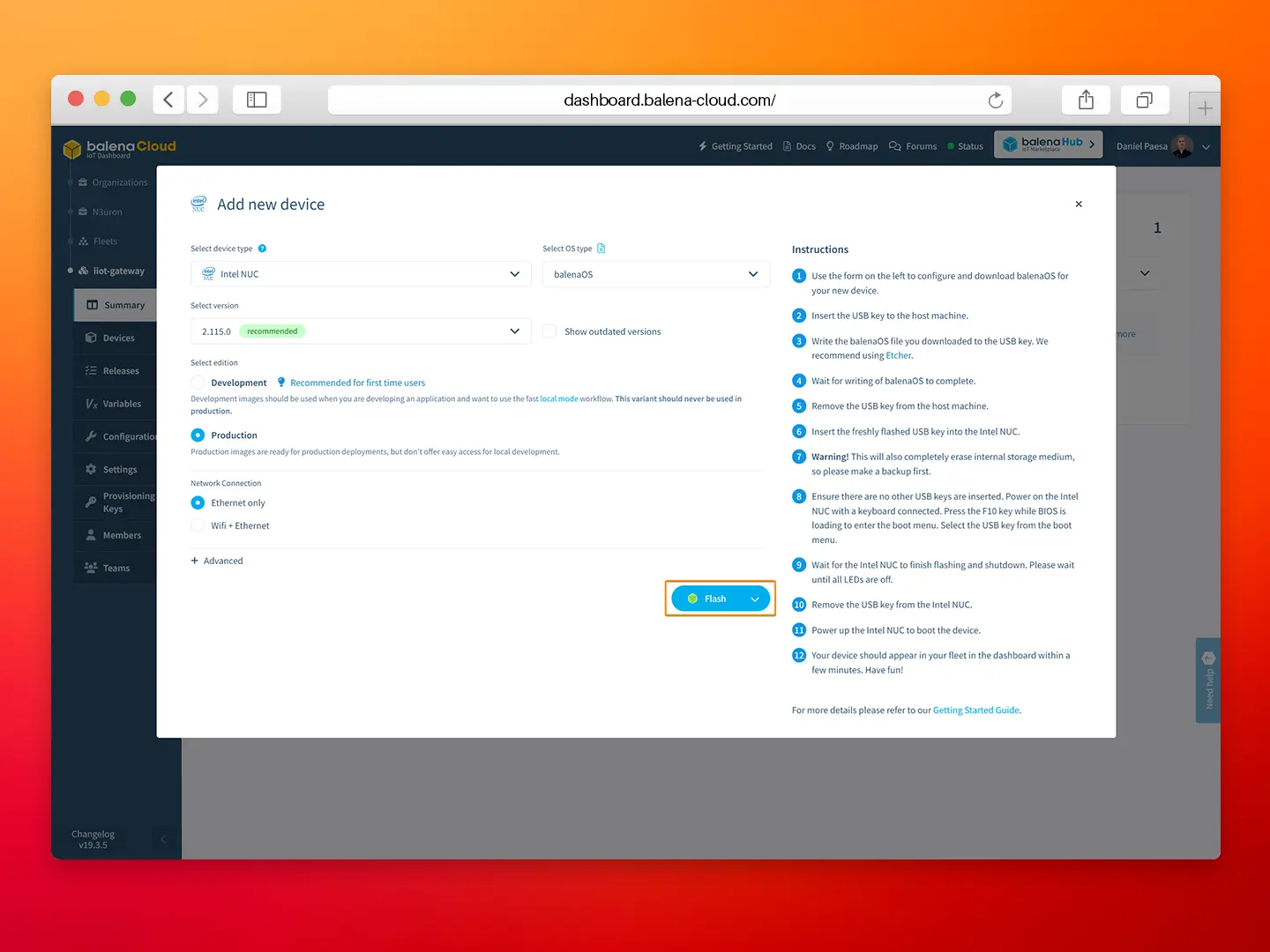
- Step 3: Configure the new device and flash it with balenaEtcher, follow the step-by-step instructions from balena.
- Step 4: After powering up the device it’ll appear on your balenaCloud dashboard. All the services are automatically downloaded and launched by balena.
Deploy from the Github repository (For advanced users)
If you are a balena CLI expert, feel free to use balena CLI. This option lets you configure in detail some aspects, like adding new services to your deploy or configure the existing but requires that you have both Git and the balena CLI installed on your system.
To do this, create an application in your balenaCloud dashboard, clone our repository, customize it to your needs and use the balena push command to deploy the stack to your fleet of devices.
git clone https://github.com/n3uron/ming-balena
cd ming-balena
balena login && balena push <fleet-name>Configure N3uron
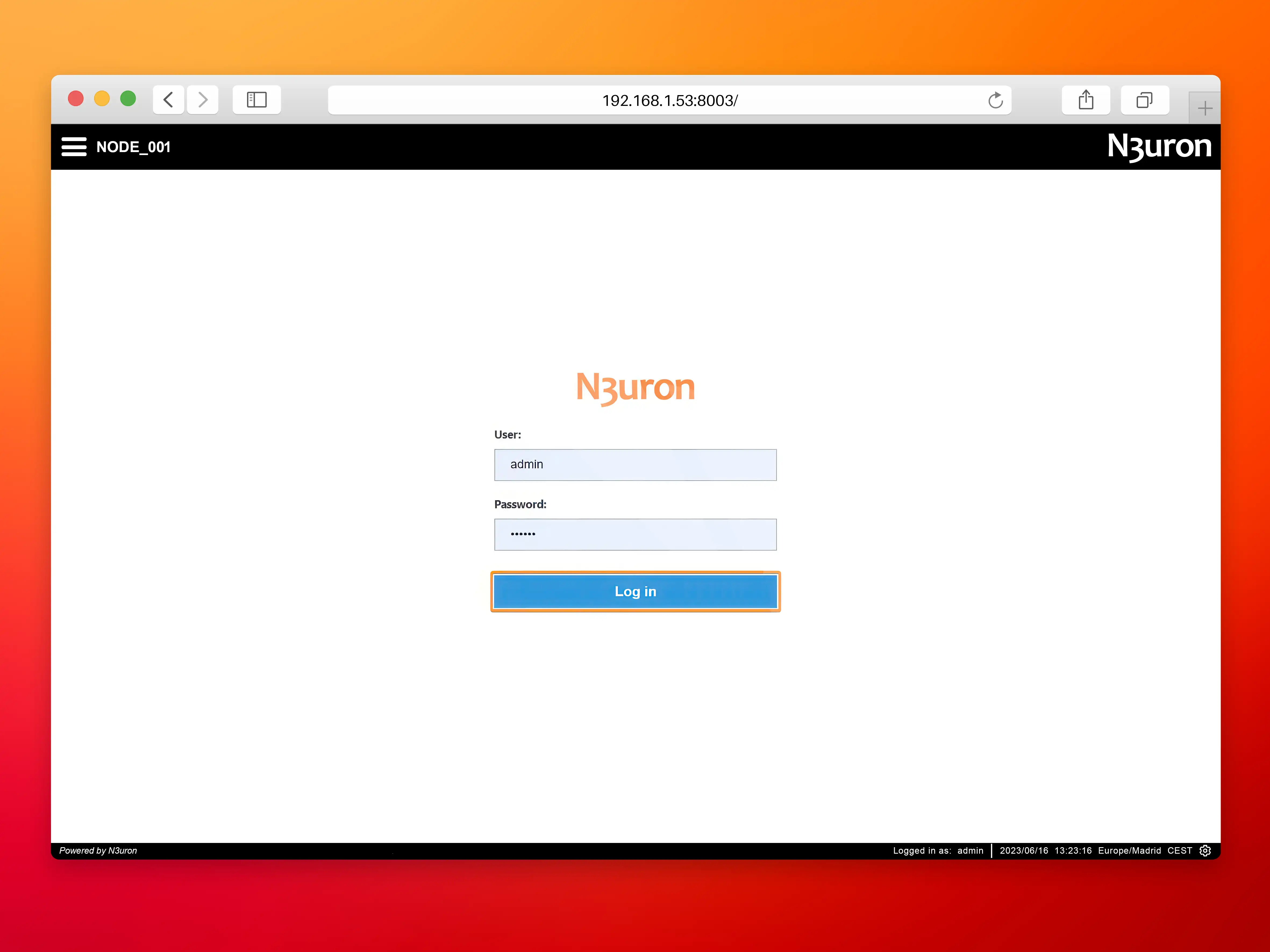
- Step 1: Open your web browser and go to http://<Local-IP>:8003 (in our case http://192.168.1.53:8003/) and login to N3uron’s WebUI.
- User: admin
- Password: n3uron
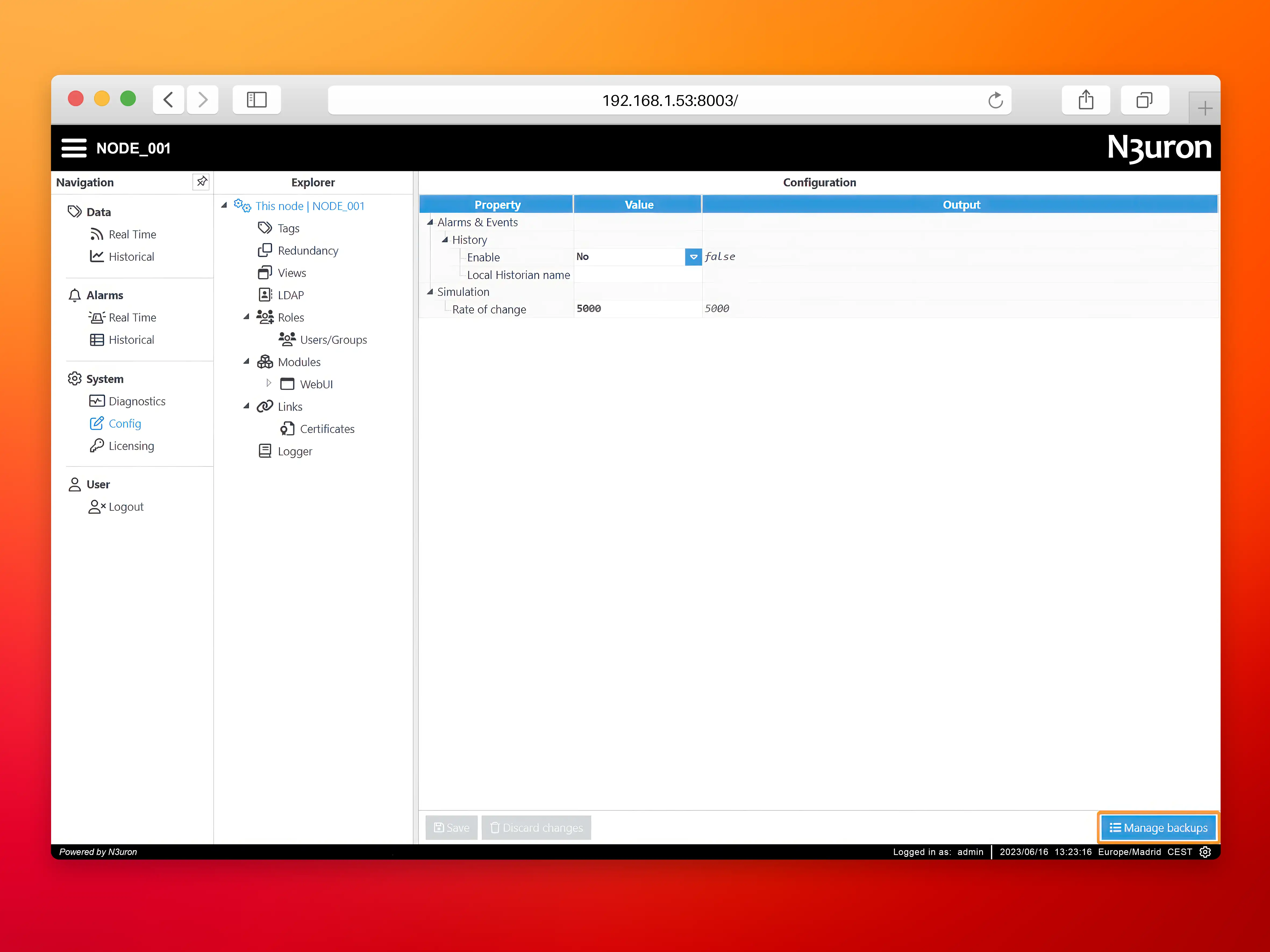
- Step 2: Navigate to the Config menu and click on Manage backups.
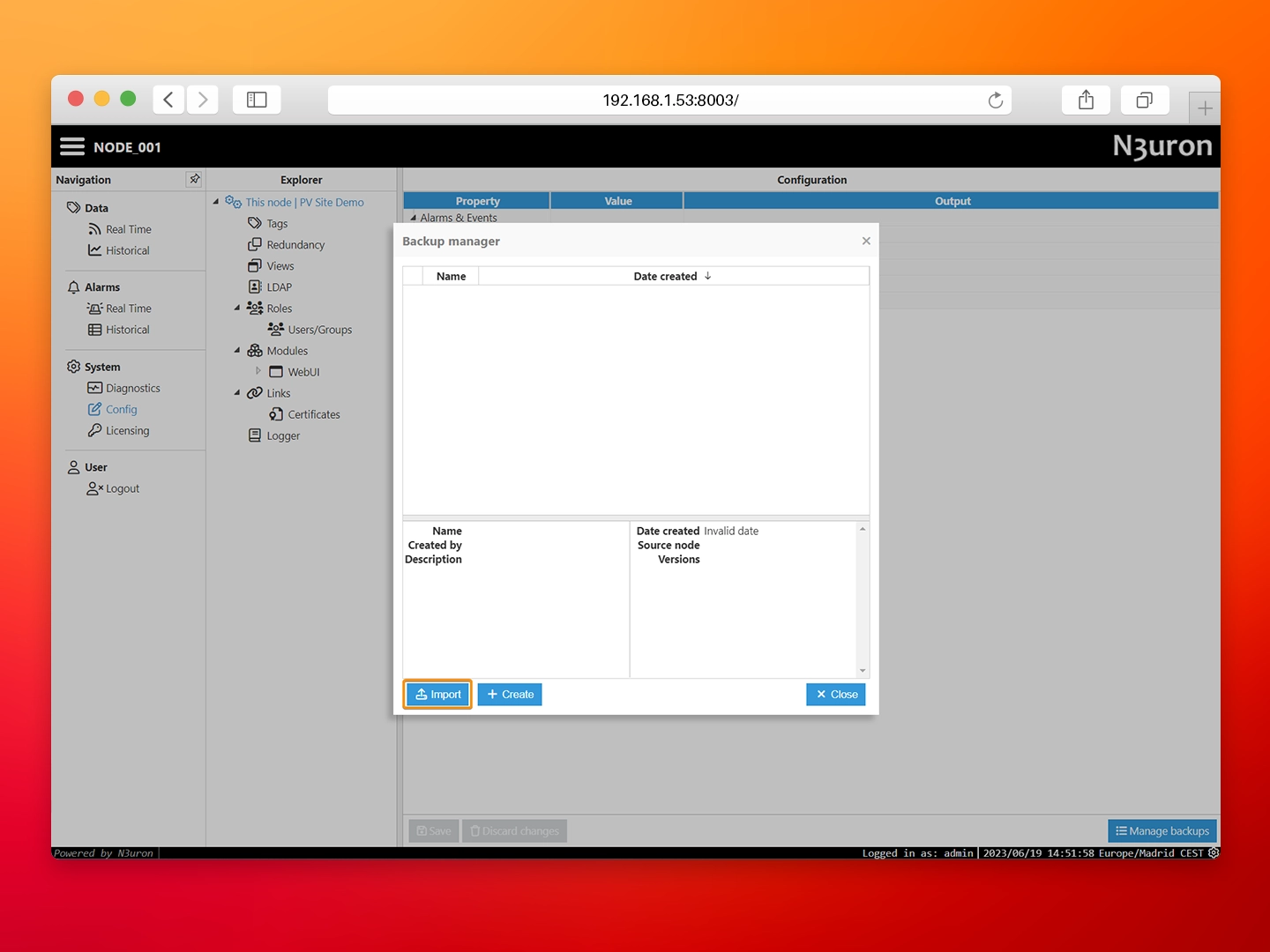
- Step 3: Download the N3uron backup file for this demo, click on Import and select the file.
- Step 4: Next, load the backup. When prompted to restart, select Close and manually restart the service from the balenaCloud dashboard.
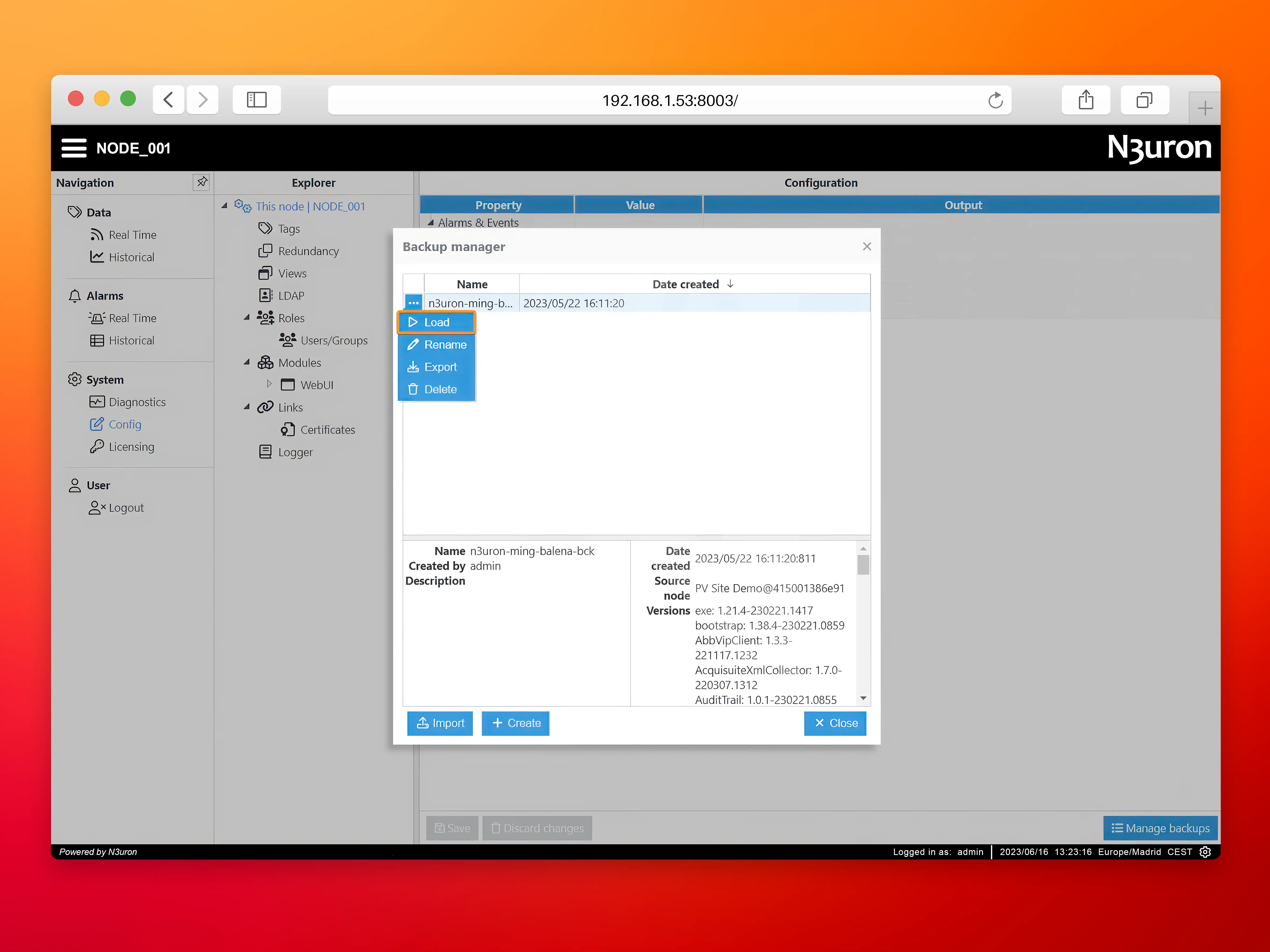
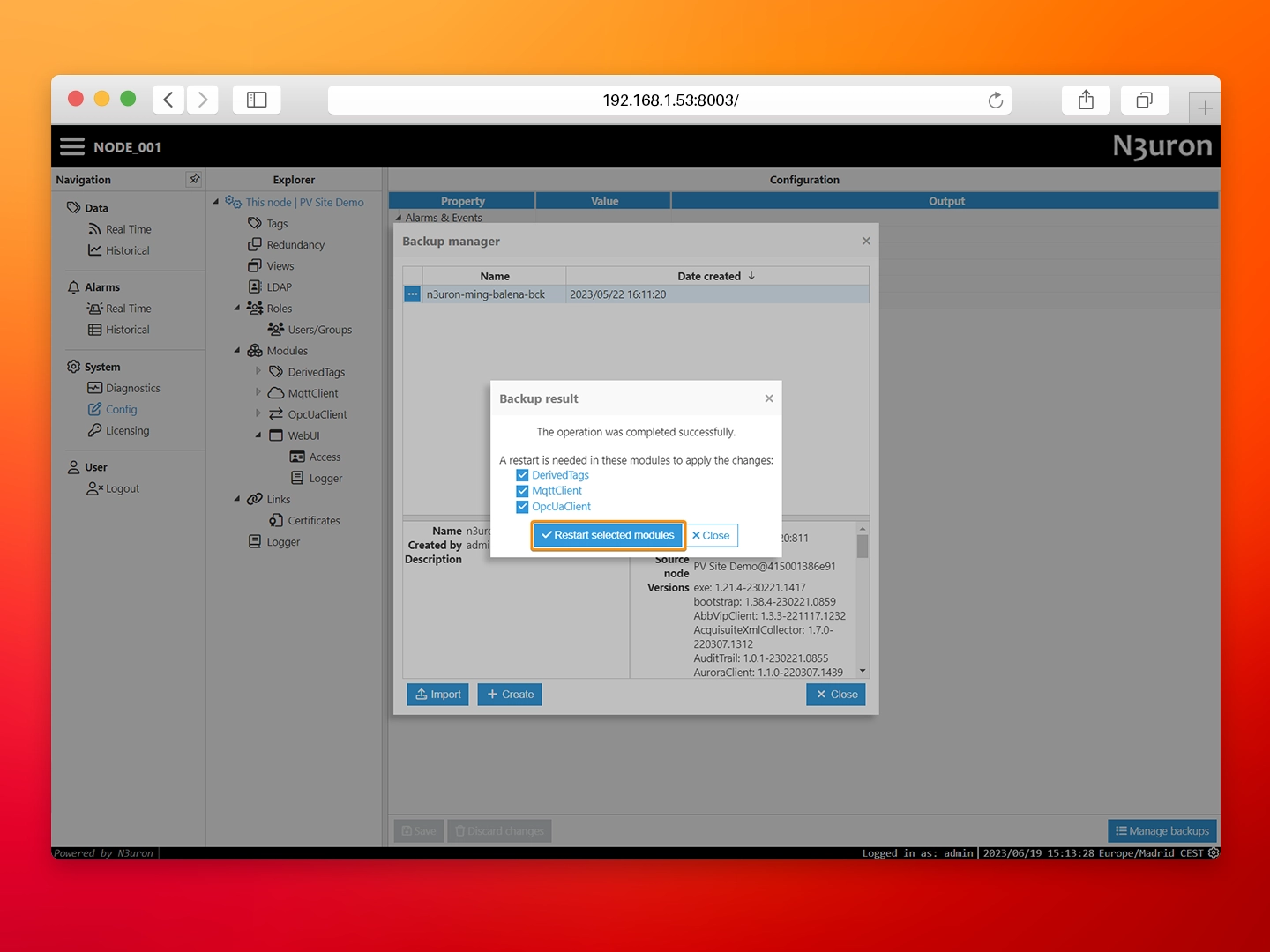
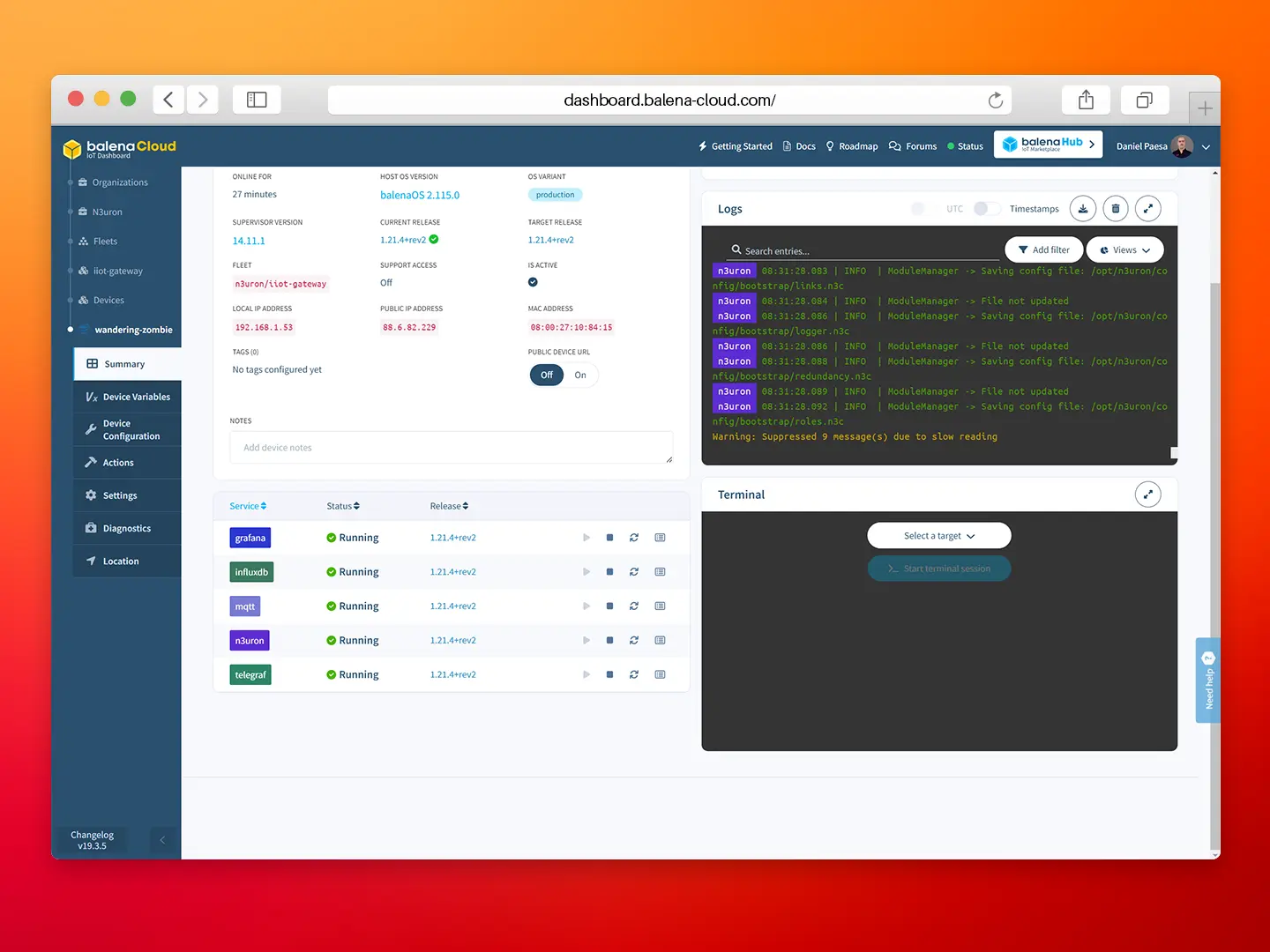
After restoring the node backup you will get a fully configured N3uron instance. Take some time to review the node and its configuration.
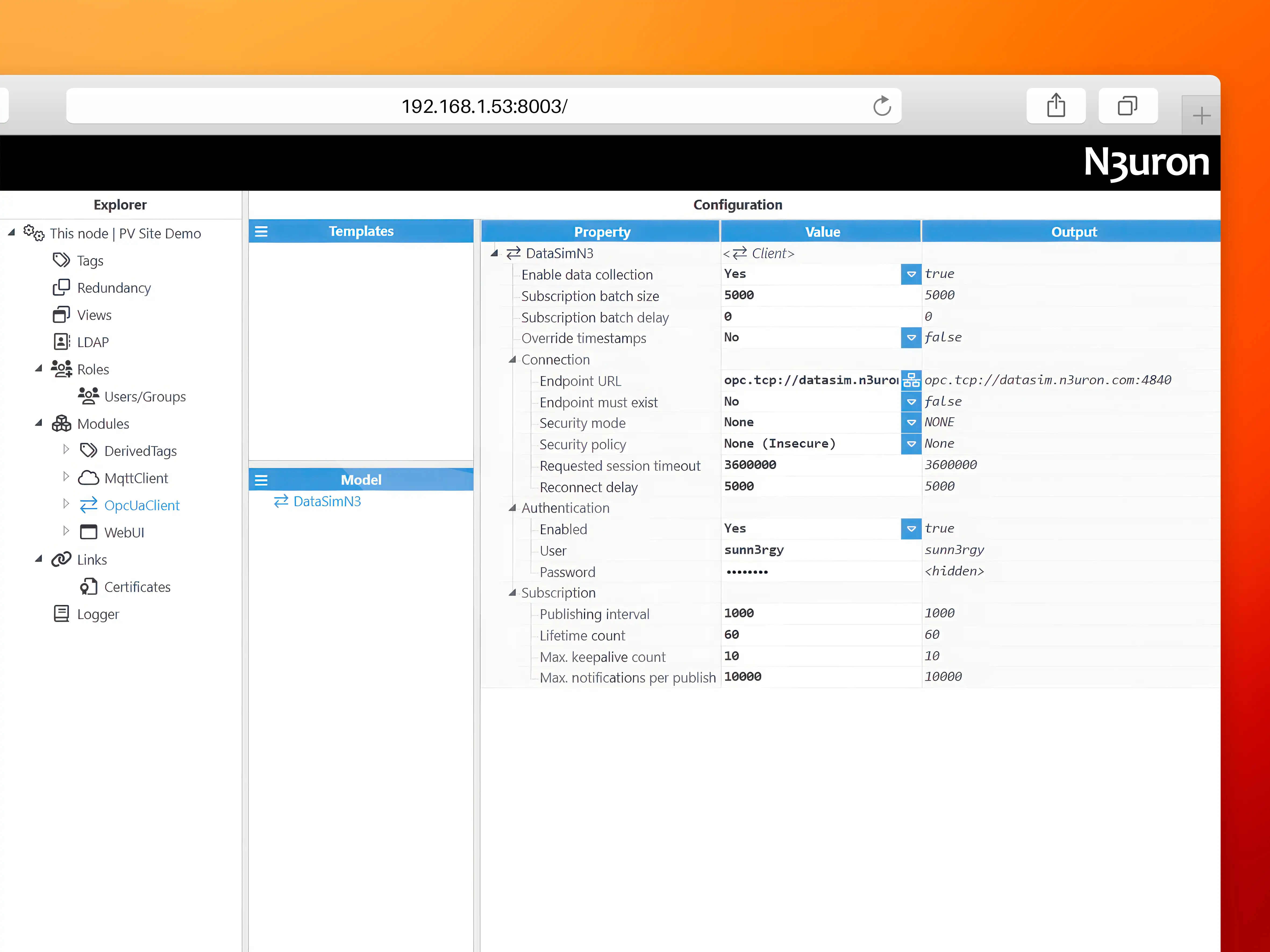
For example, you may see an OPC UA Client connected to datasim.n3uron.com:4840, which is receiving real-time data from a PV Plant located in Europe.
To visualize all the tags and their real time values, go to the Data→Real Time. In the example shown below, the Power Station 1 (PST001) is selected and the Sublevels checkbox is enabled.
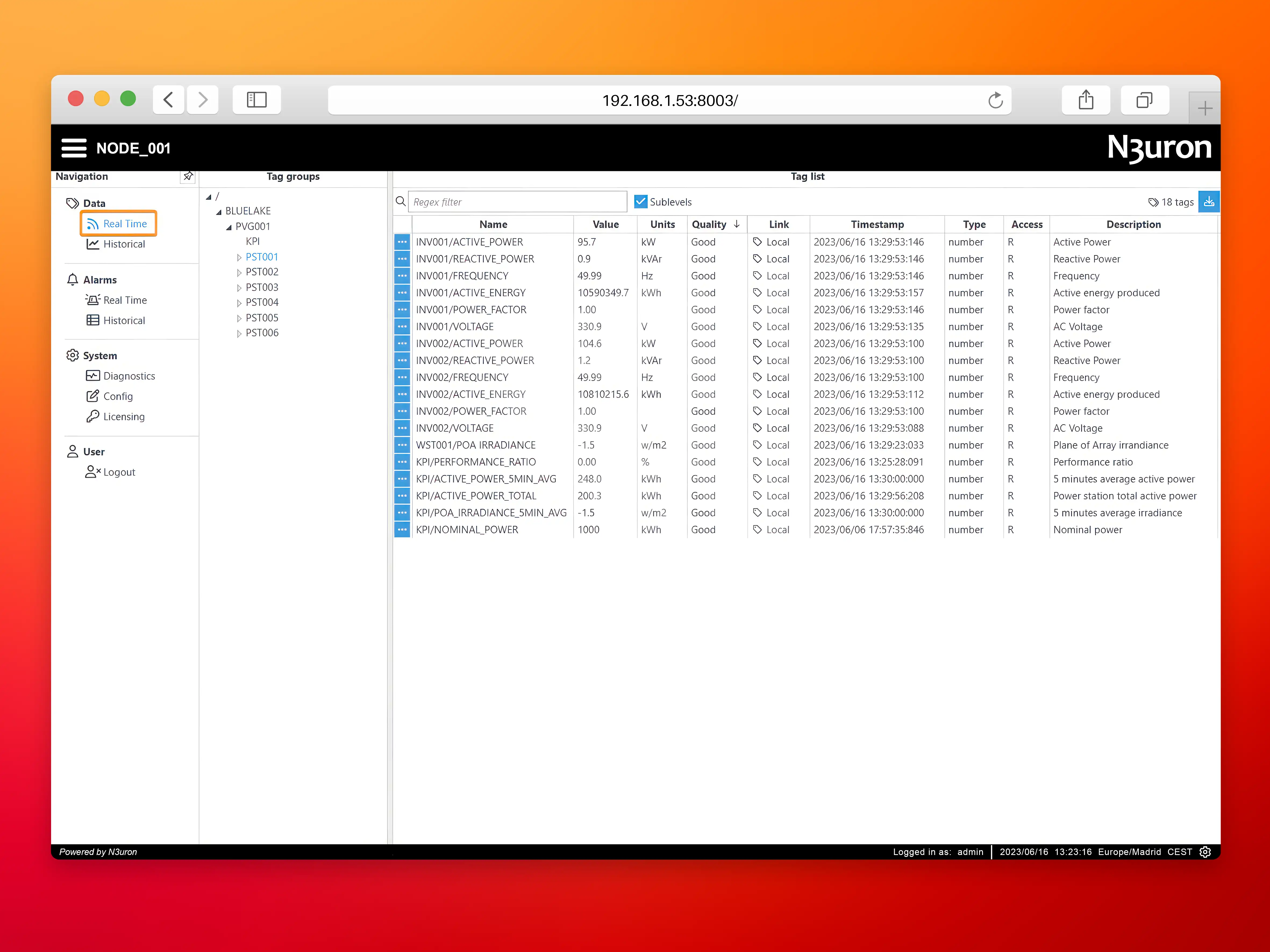
The data model used in this demo represents a Photovoltaic Plant with inverters and weather stations. By using templates you can quickly generate new instances to rapidly build complex data structures. Any changes made to a template definition will be inherited by all its instances.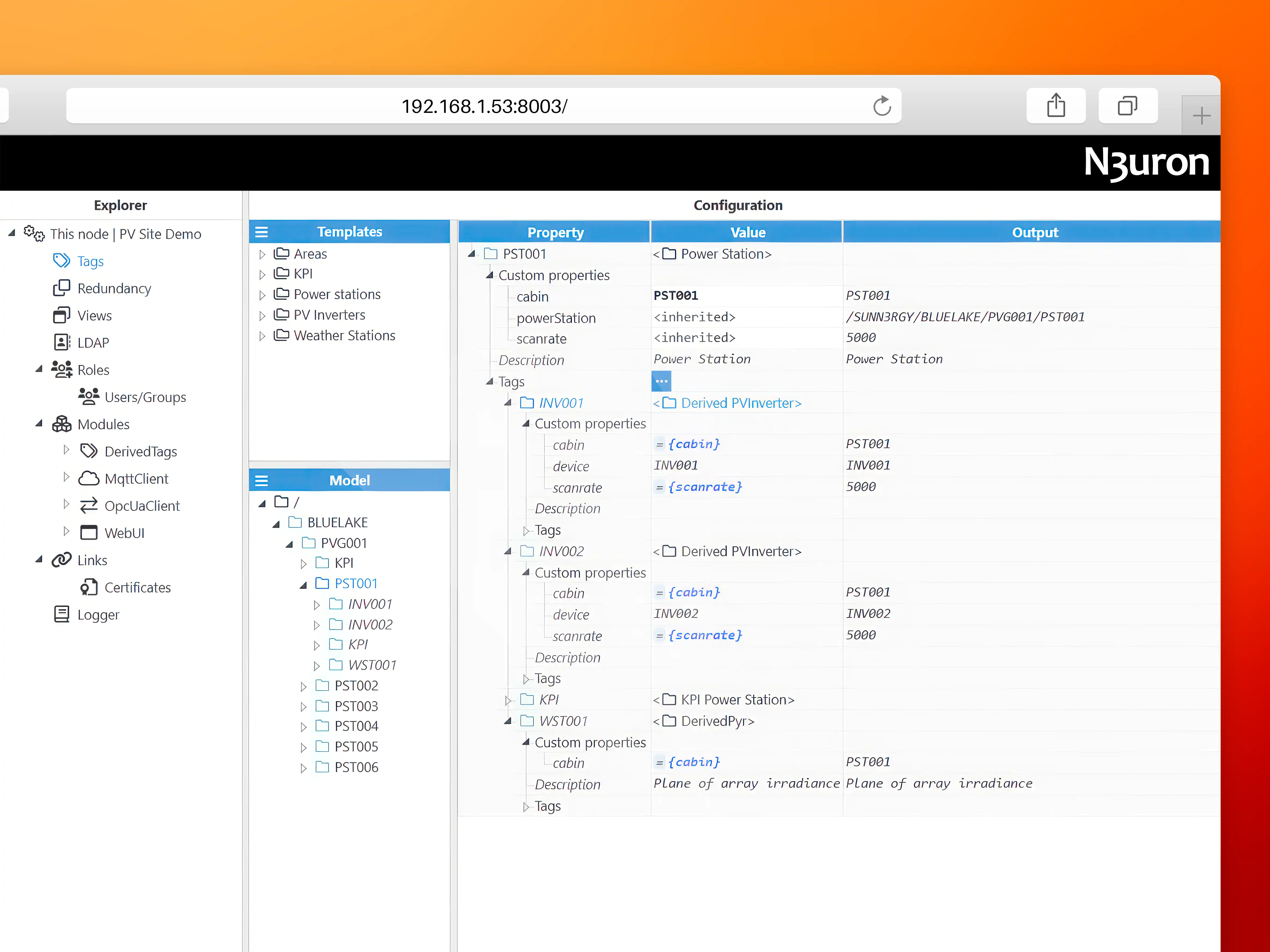
As shown below, the template definition for Power Stations includes two inverters (INV01 and INV02), a Weather Station (WST001), and a KPI folder with some calculated and aggregated data computed using the Derived Tags module. A template usually has several custom properties that act as variables and can be referenced by the items within the template.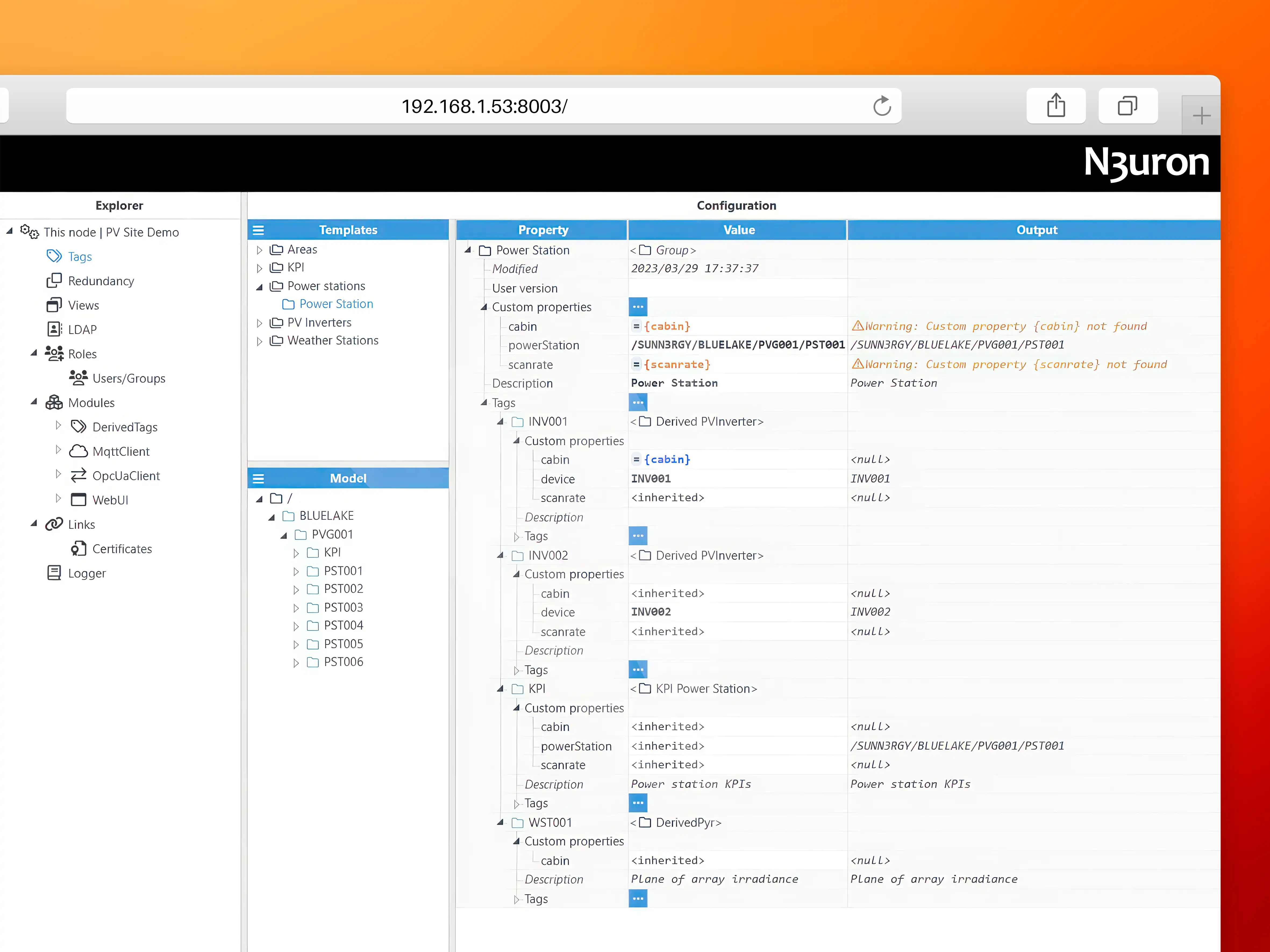
The image below shows how to reference Custom Properties in expressions, when configuring tags.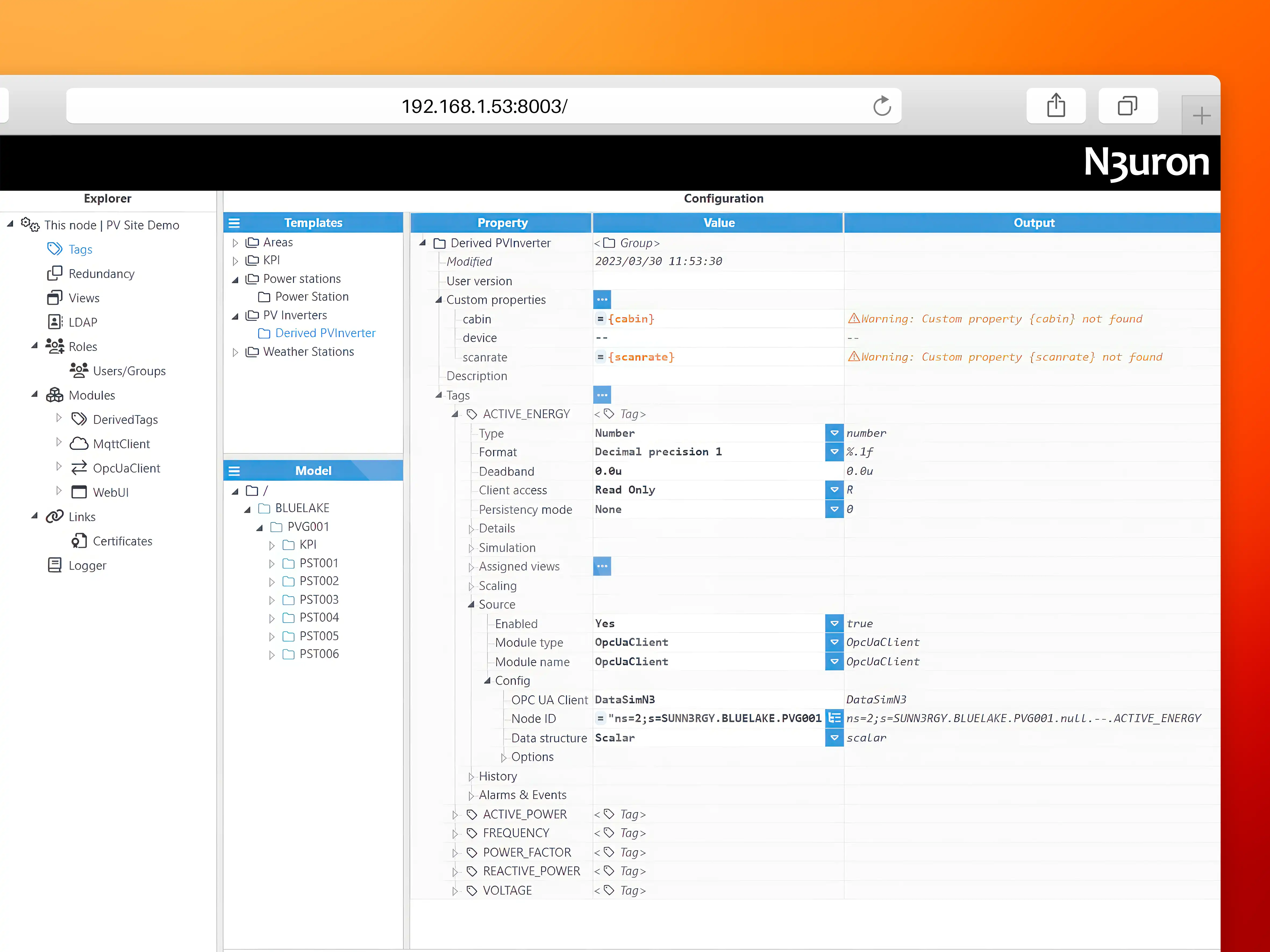
As you continue to explore the N3uron instance, you will also find that the node includes an MQTT Client that is already configured to push data to the local Mosquitto MQTT broker.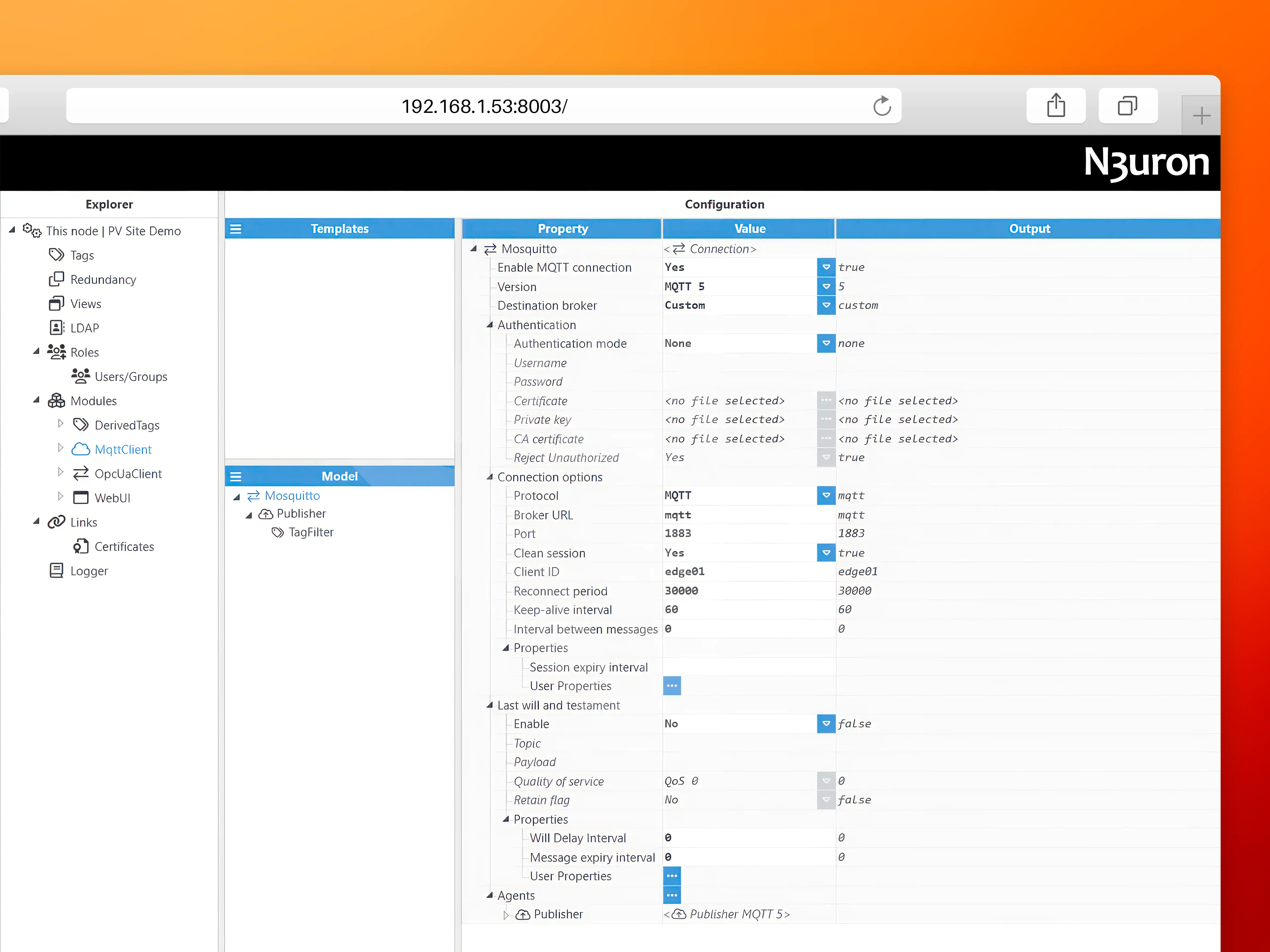
A Publisher has been created to push all tags within the /BLUELAKE/PVG001/ directory to an MQTT topic named N3URON/BLUELAKE/ The InfluxDB payload format has been selected in the configuration for seamless message serialization.
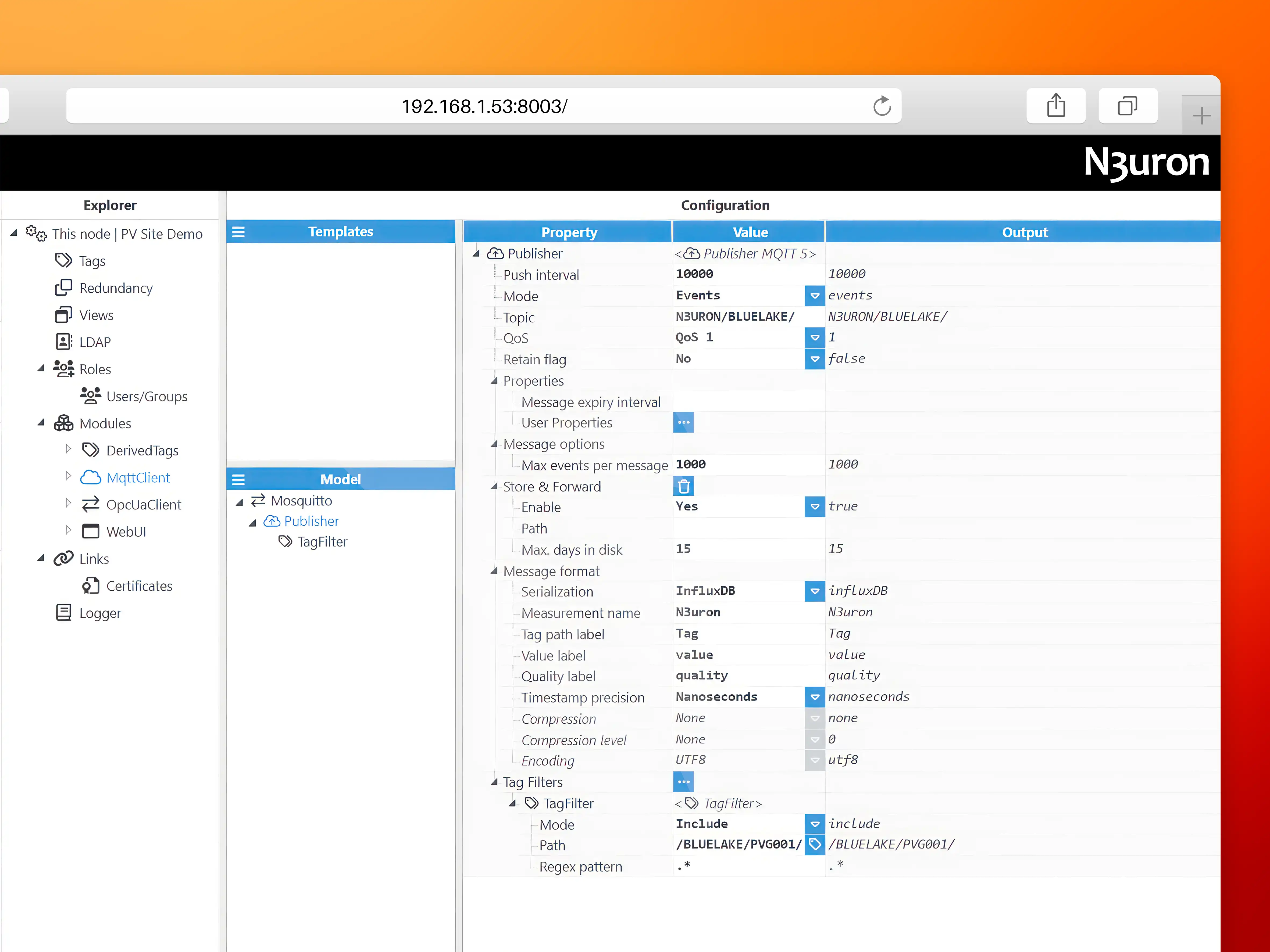
Configure Grafana
- Step 1: Go to http://<Local-IP>:3000/ and login to Grafana.
- User: admin
- Password: n3uron
- Step 2: Click on Add your first data source.
- Step 3: Select InfluxDB as data source.
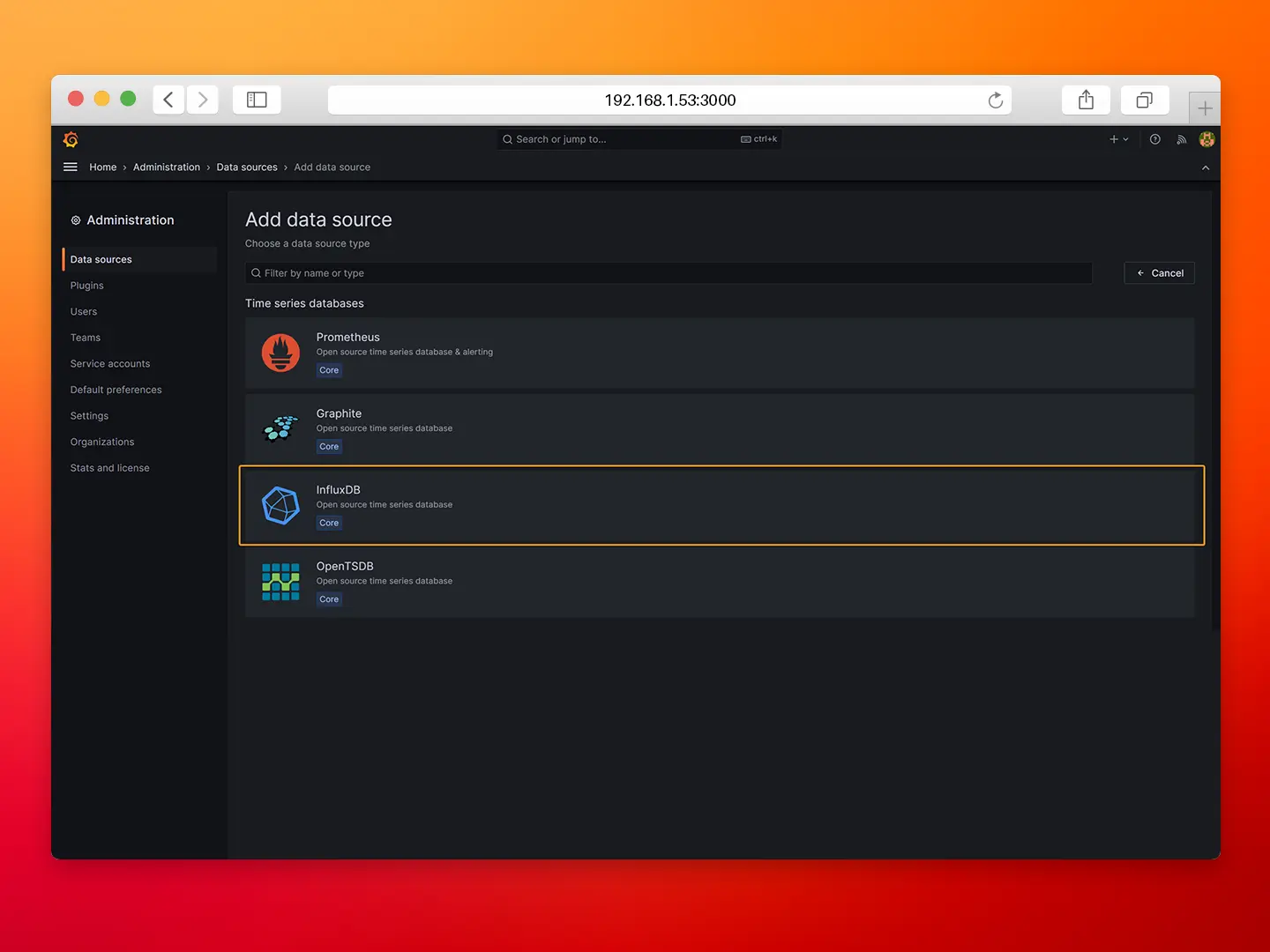
- Step 4: Configure the InfluxDB connection as follows.
- Query Language: Flux
- URL: http://influxdb:8086
- Organization: N3uron
- Token: iXm3eMP5ioUUntSZuHYWzjJPT
- Default Bucket: demo
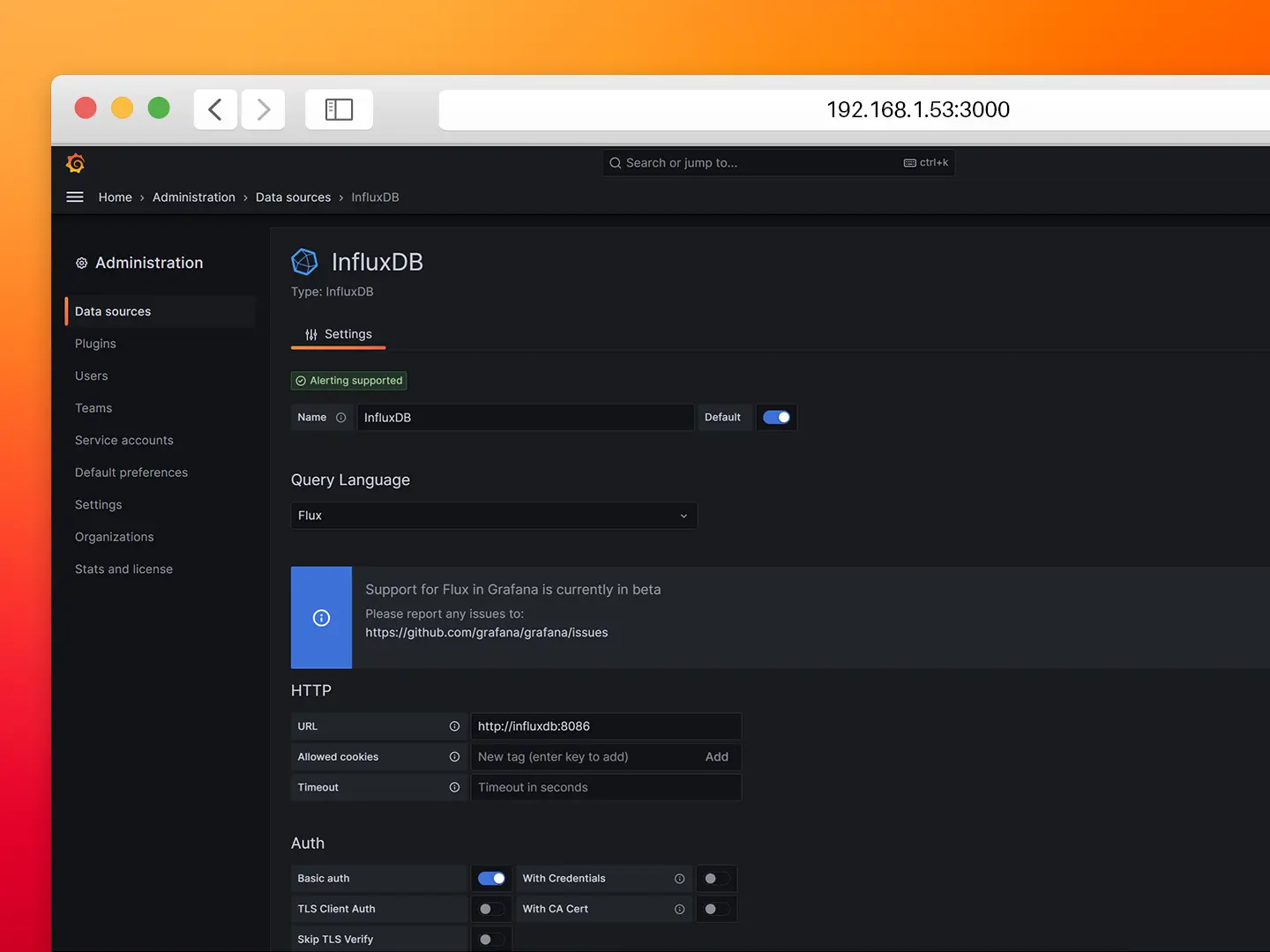
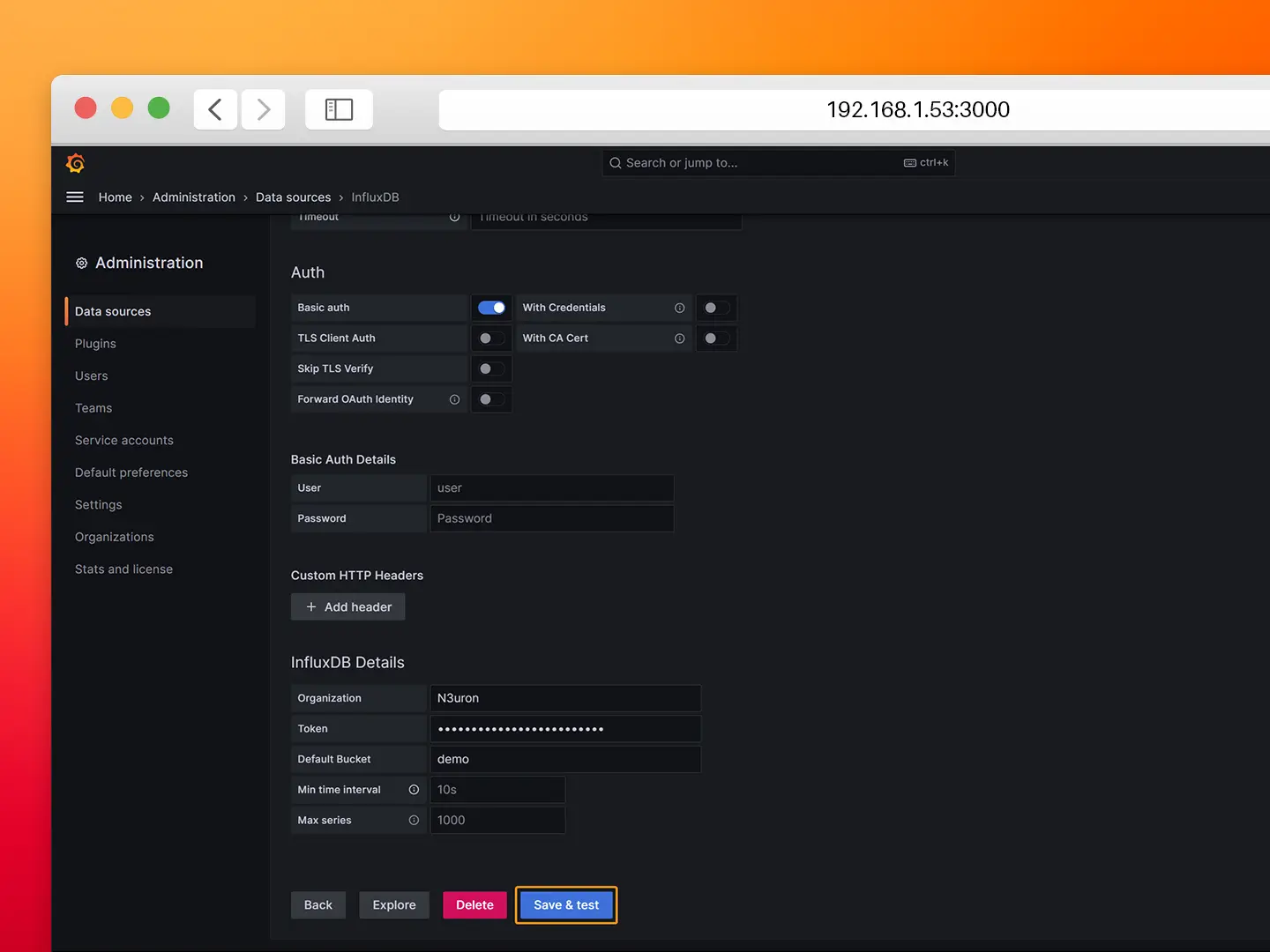
- Step 5: Click on Save & Test. If you encounter any error with the data source review your settings.
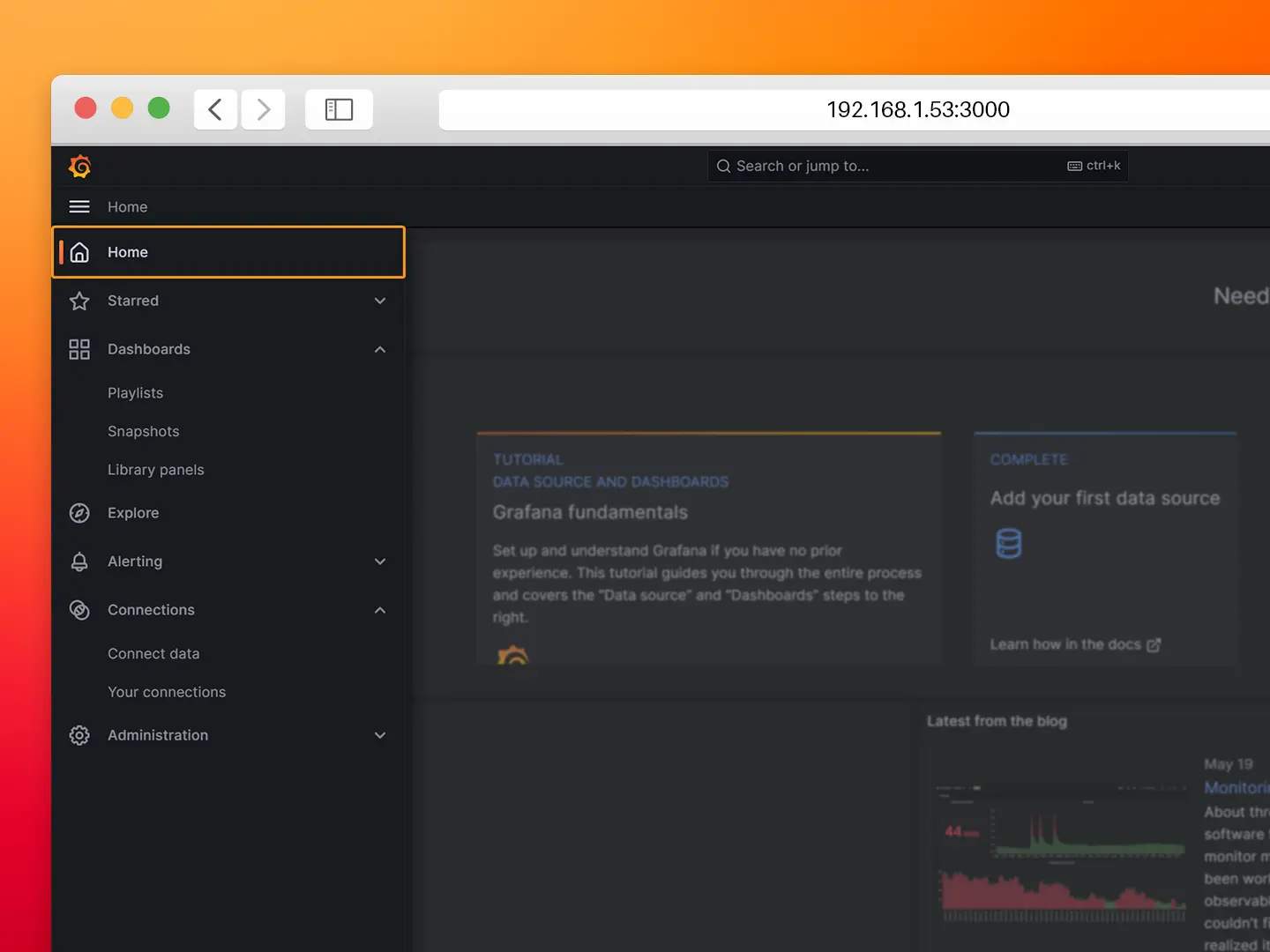
- Step 6: Hover the mouse over the Home menu and select Dashboards.
- Step 7: Click on New→ Import.
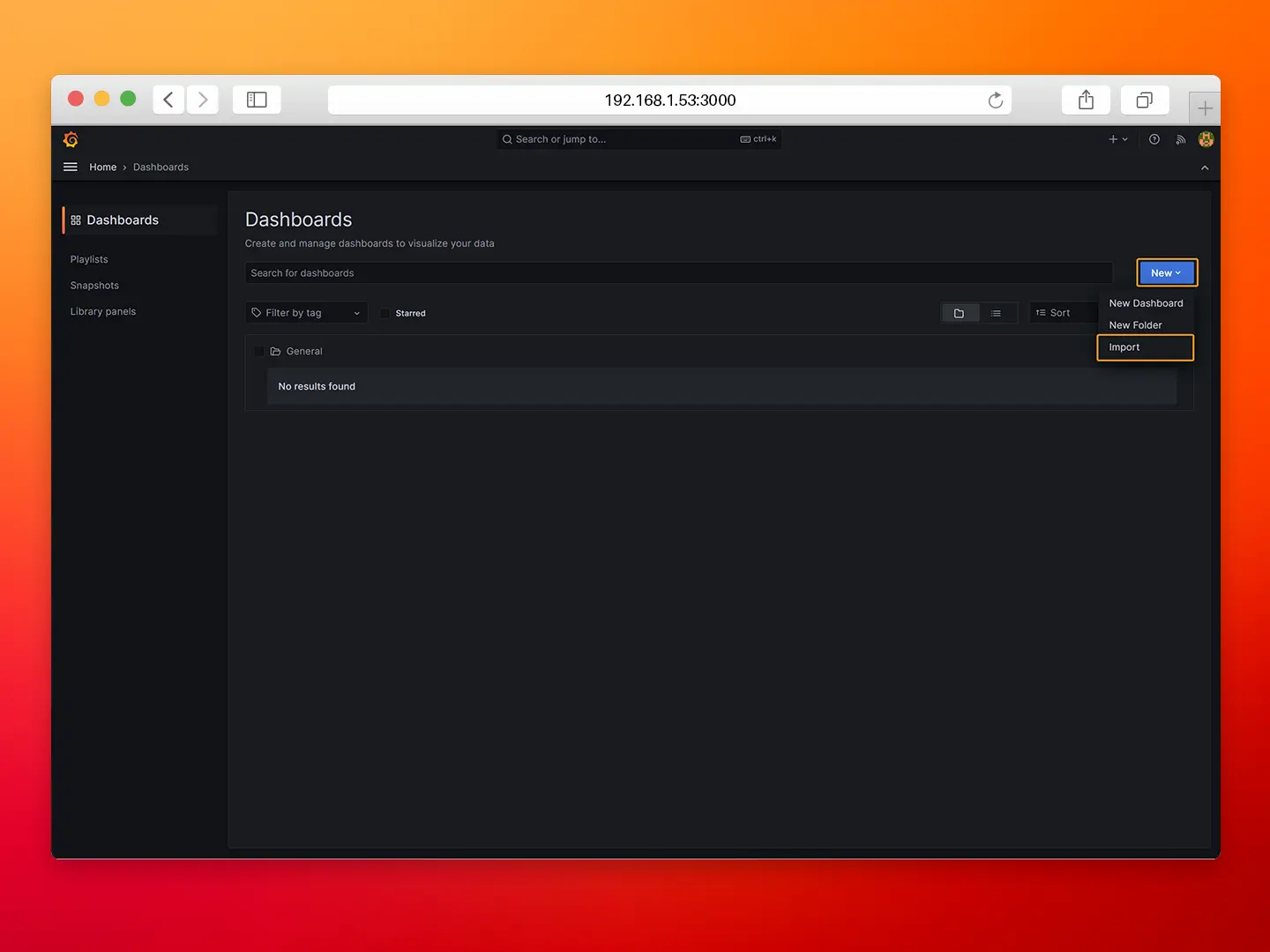
- Step 8: Load the dashboard from Grafana.com.
- ID: 18803
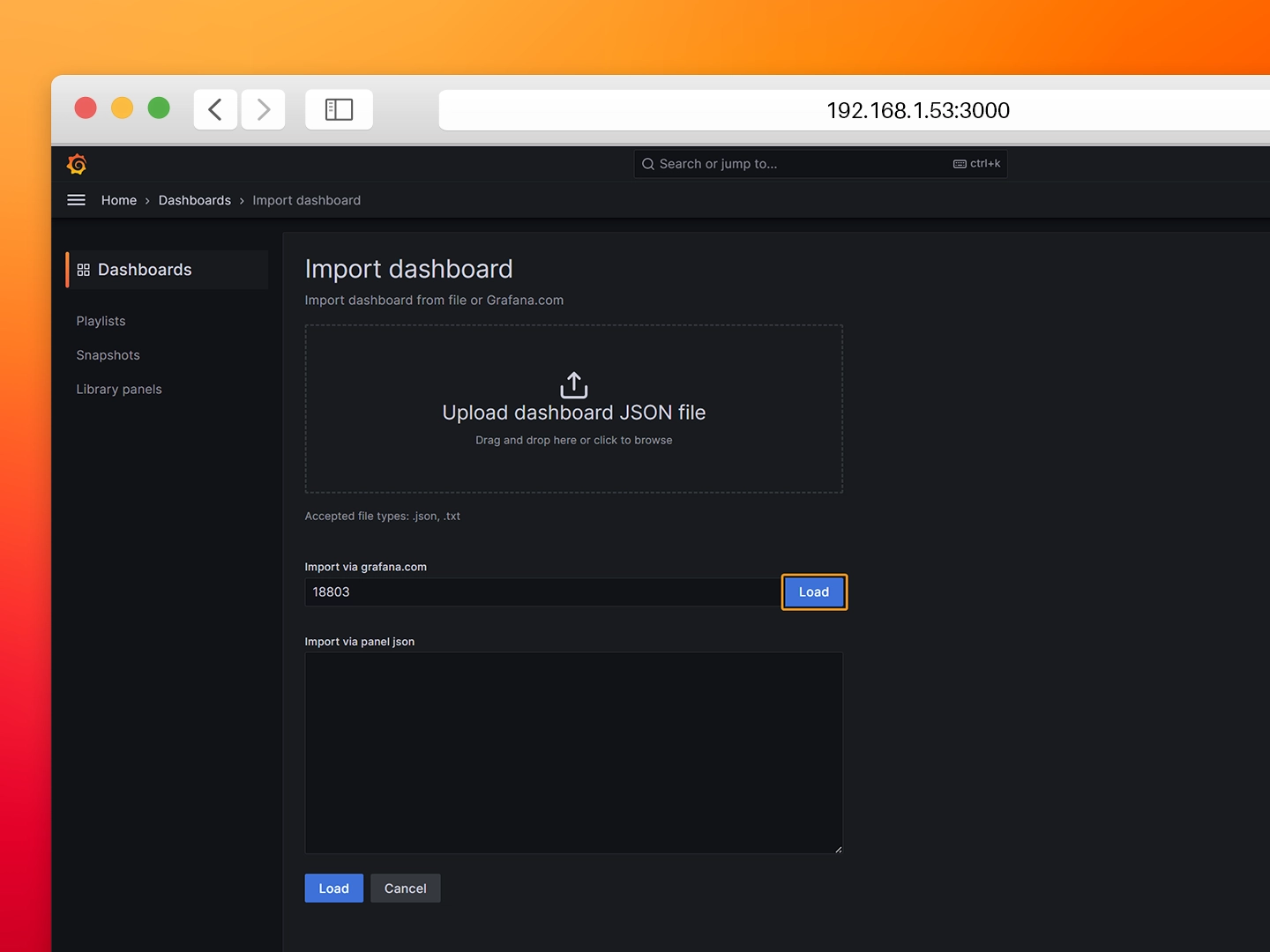
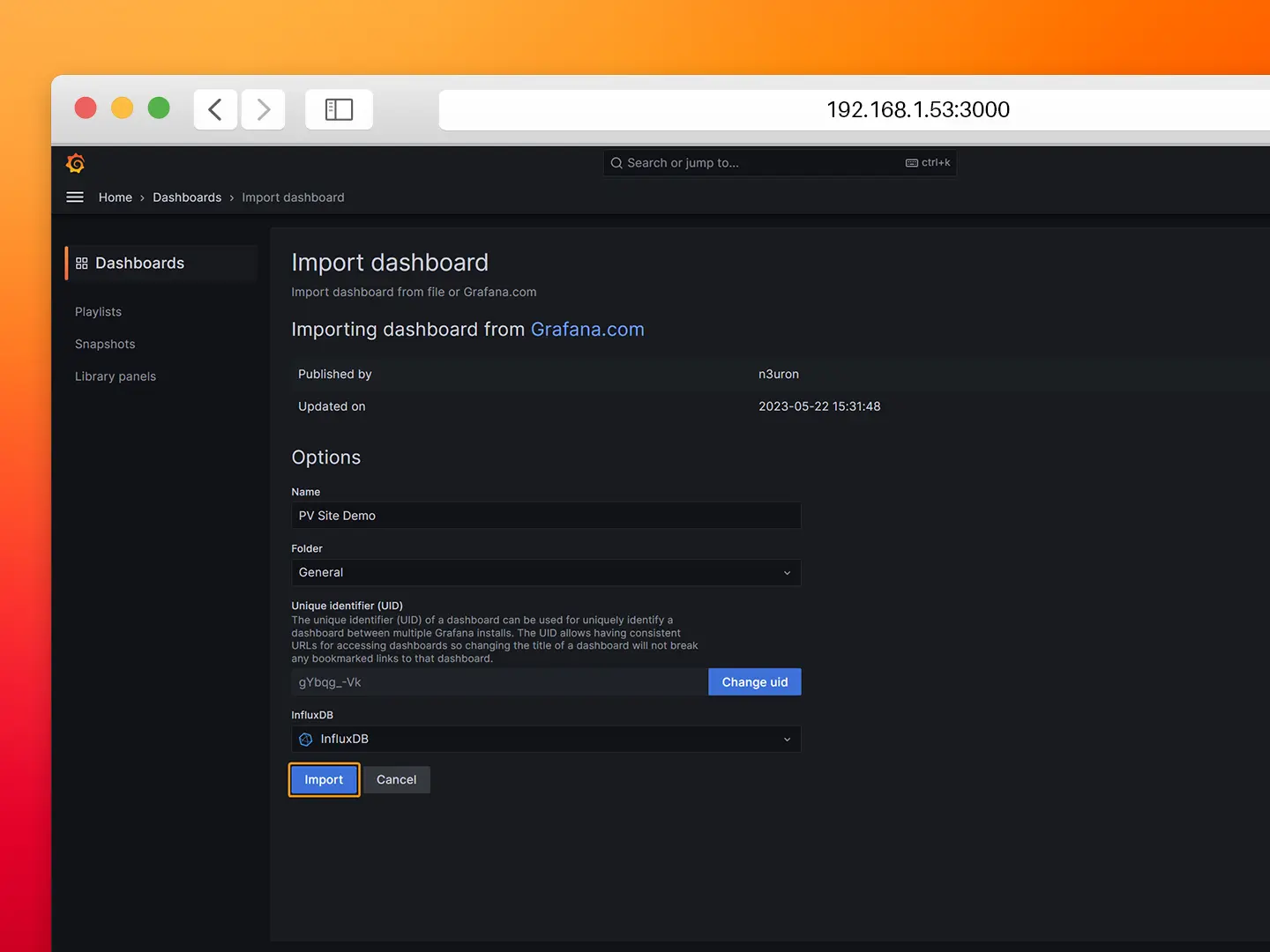
- Step 9: Select the previously created InfluxDB data source and click on Import.
Conclusion
In summary, we have seen how the integration of balena with N3uron and other applications in a containerized architecture provides businesses with a powerful tool to harness the full potential of their data.
Deploying and managing this solution at the Industrial Edge has never been easier, thanks to balena’s user-friendly features. With simple provisioning for new hardware, automatic OS updates, seamless software deployments and unified management from their dashboard, balena streamlines operational processes. With N3uron and balena, the possibilities are endless.
Optimize your operations, discover new insights and stay ahead of the curve with N3uron. Take the first step on your digital journey by downloading the containerized version of the N3uron platform from Downloads. Select the modules you need to build your custom solution and unlock the full potential of your data.
