API configuration
API parameters define the communication between the module and N3uron's bootstrap..png) Figure 3: API parameters
Figure 3: API parameters
API configuration includes the following parameters:
- Event rate: Event exchange rate between bootstrap and the module, displayed in milliseconds. Default value is 1.000ms and minimum value is 100ms.
- Timeout: Maximum time to wait for a response from bootstrap, displayed in milliseconds. Minimum value is 100ms and default value is 5.000ms. In nodes dealing with a high number of tags, this time can be increased to avoid timeouts when communicating with bootstrap.
- Keep-alive period: Time between keep-alive checks with bootstrap, displayed in milliseconds. Set to 0 to disable keep-alive checks for this module. The default value is 60.000ms. When the module fails to respond to keep-alive requests, bootstrap restarts the module process.
Once the API parameters are set, the configuration settings must be saved and the module restarted to apply the new values.
Logger configuration
These parameters define how the module logs its activity..png) Figure 4: Logger configuration
Figure 4: Logger configuration
Parameters:
- Enabled: When enabled, the module sends the logs to a text file located in <installation_folder>/N3uron/log/<module_name>. The default value is set to Enabled.
- Level: Level of detail in the information sent to the log file.
- Error: only logs errors
- Warning: logs errors and warnings.
- Info (default): logs errors, warnings, and general information messages.
- Debug: logs most of the module activity for debugging and troubleshooting purposes.
- Trace: logs all module activity. This mode may log a huge amount of data, so it’s not recommended for production environments.
- Days to keep: log files are automatically deleted when they become older than the number of days indicated here. The default value is 7 days.
Module configuration
Users can configure data storage by selecting Historian from the explorer tree menu. The following screenshot shows the different available options for Historian configuration: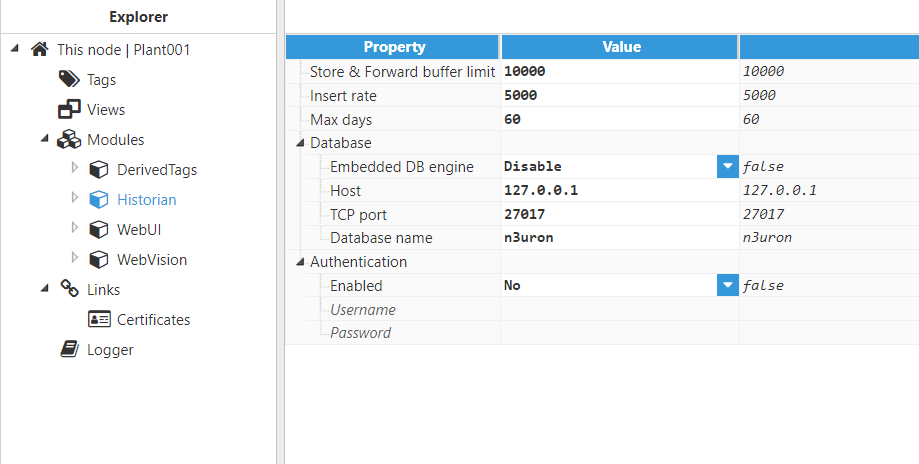 Figure 5: Historian parameters
Figure 5: Historian parameters
Parameters:
- Store & forward buffer limit: Maximum number of events that can be stored in the memory buffer for batch insertions in the database. If the max size is reached, links with remote nodes will automatically be paused. Once the number of events stored in the buffer decreases to a level below half the set limit, the links will automatically be enabled again. A value of `0` disables the buffer limit so that the links will never be paused. However, this is not recommended, especially in nodes receiving a large volume of events, since it may result in RAM overflow when the number of events received is higher than the number of the events processed.
- Insert rate: Specifies the time between data insertions in the buffer to the database, displayed in milliseconds. Insertions are processed in batches by date, starting with the oldest data. The minimum value is 1000ms.
- Max days: Number of days that stored data is kept in the target database for. Data older than the specified number of days will automatically be deleted.
- Database
- Embedded DB engine: enables or disables the embedded MongoDB engine and uses it as the target database. When disabled, this module needs access to an external MongoDB instance.
- Host: Hostname or IP address of the target external MongoDB engine. Only applicable when not using the embedded DB engine.
- TCP port: Specifies the TCP port used to connect to the database. The default setting is the MongoDB default TCP port 27017. Valid range: 1 to 65535.
- Database name: Name of the database where data will be stored. If authentication is enabled, authentication will be carried out against this database.
- Authentication:
- Enabled: enables or disables authentication to the external MongoDB engine.
- Username: Username used to authenticate with the MongoDB database.
- Password: Password used to authenticate with the MongoDB database.
Tag configuration
After configuring the Historian module, users can configure historization of specific tags. The following screenshot shows the different available options for configuring the Tag history section: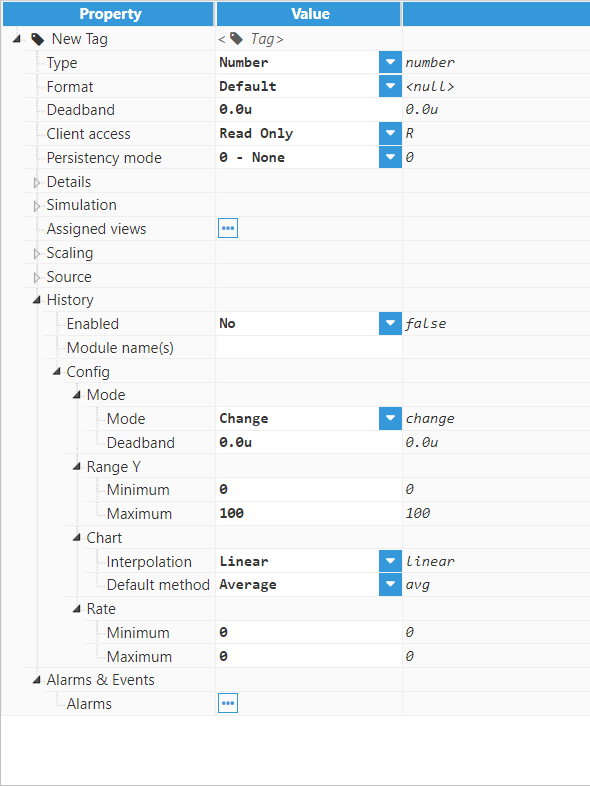 Figure 6: Tag history configuration
Figure 6: Tag history configuration
History parameters:
- Enabled: enables historization of the tag.
- Module name(s): specifies the name(s) of the module(s) that will historize the tag. A comma separated list can be used for multiple modules. For local Historian modules, use HistorianModuleName or ./HistorianModuleName. For remote Historian modules, use NodeName/HistorianModuleName.
- Mode: available mode is “Change”, which stores all changes outside of the deadband.
- Deadband: specifies the deadband for Change mode.
- Range Y:
- Minimum: Default Y-axis minimum value, in engineering units.
- Maximum: Default Y-axis maximum value, in engineering units.
- Chart:
- Interpolation: available options are “step” and “linear”. If “step” is selected, tags are trended as a step. If “linear” is selected, tags are trended as a line.
- Default method: available options are “last” and “average”. If “last” is selected, the last value in the period is provided. If “average” is selected, the average value during the period is provided.
- Rate:
- Minimum: minimum historization rate, displayed in milliseconds.
- Maximum: maximum historization rate, displayed in milliseconds.
Data retrieval
Historian stores events (changes in value, quality, or timestamp). Data can be retrieved from the storage in different modes:
- Raw: Data retrieved contains all values for all events stored in the database.
- Aggregated: Data is consolidated into aggregation periods. The following aggregation methods are available:
- avg: Time-weighted average.
- min: Minimum value during the aggregation period.
- max: Maximum value during the aggregation period.
- first: First value during the aggregation period.
- last: Last value received during the aggregation period.
- Delta: The data retrieved contains all the values of all events displaying incremental changes compared to any previous event that is larger than the configured deadband. It only contains the second event (the one taking place after the first event that surpassed the deadband).
- Filter: Data retrieved contains all the values for all events displaying changes compared to any previous event that is larger than the configured deadband. In this case it contains both events, the one before the change that surpassed the deadband and the one after the change.
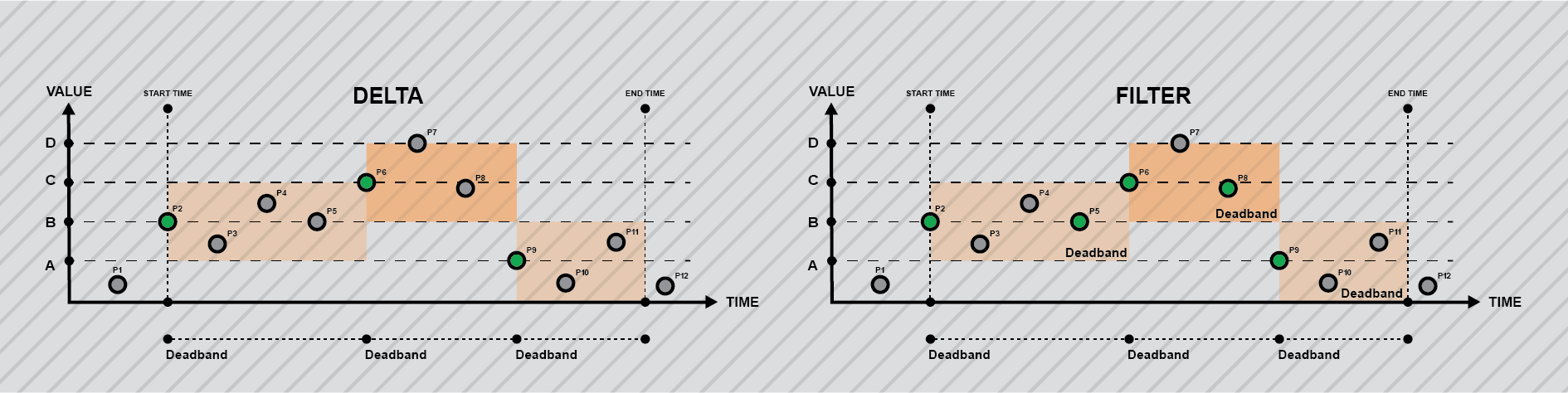
Figure 7: Delta and Filter chart
Data stored in Historian can be retrieved using the following methods:
- WebUI: Includes a rich HTML5 interface to retrieve and visualize data in charts and data tables (raw and aggregated data). Data can also be exported to CSV files. The historical data retrieved can be located in the same N3uron node as the WebUI or in a different N3uron node, providing that the nodes are connected through a N3uron Link.
- REST API Server: By using the optional RestApiServer module, historical data can be retrieved in JSON format using REST API calls (raw data and aggregated data). The historical data retrieved can be located in the same N3uron node as the REST API server or in a different N3uron node, providing the nodes are connected through a N3uron Link. Several examples of historical data retrieval can be found in the Rest Api Server Manual.
- WebVision: Includes a component to retrieve and visualize data in charts and data tables similar to the interface provided by WebUI. Data can be also exported to CSV files. The historical data retrieved can be located in the same N3uron node as the WebUI or in a different N3uron node, providing that the nodes are connected through a N3uron Link.
- MongoDB client: Direct connection to the MongoDB database to retrieve data in raw mode.
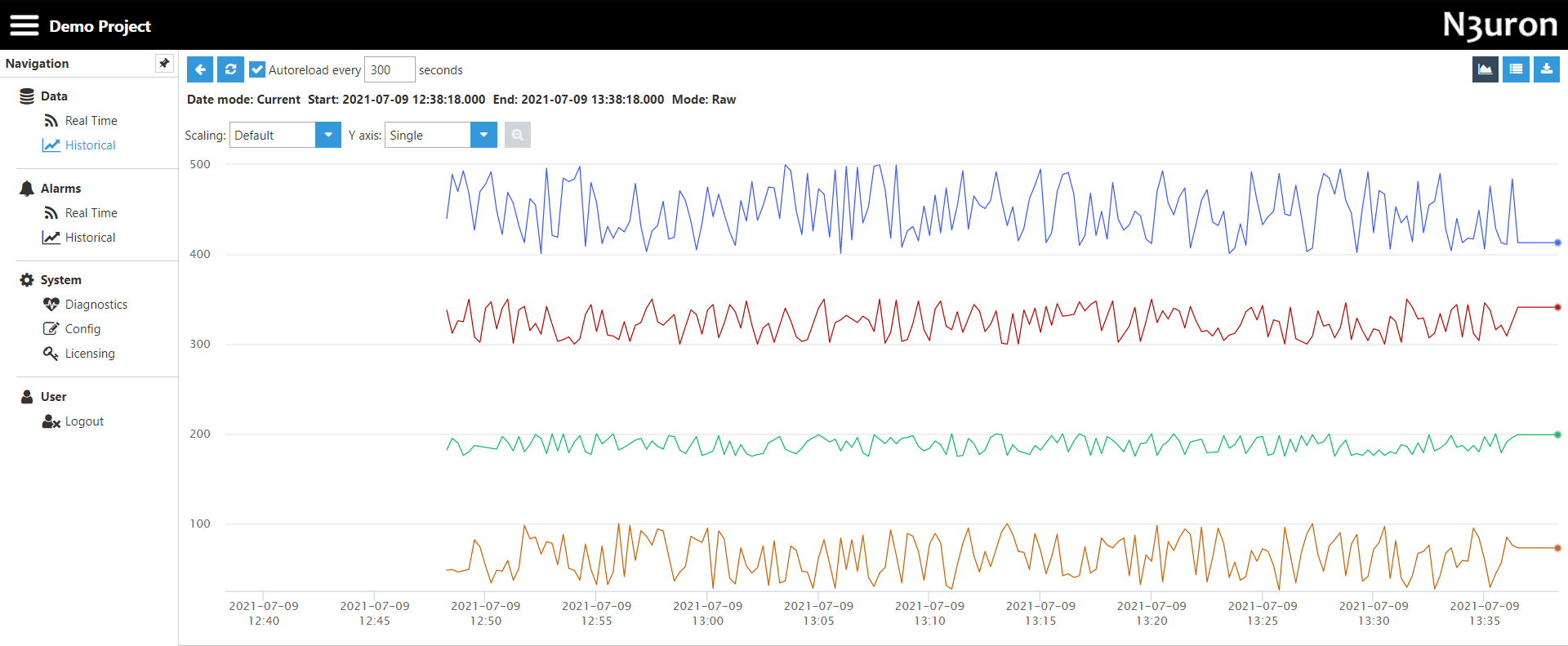
Figure 8: Historian charts from the WebUI