Retrieving data using WebUI
In this example, historized data will be monitored using WebUI.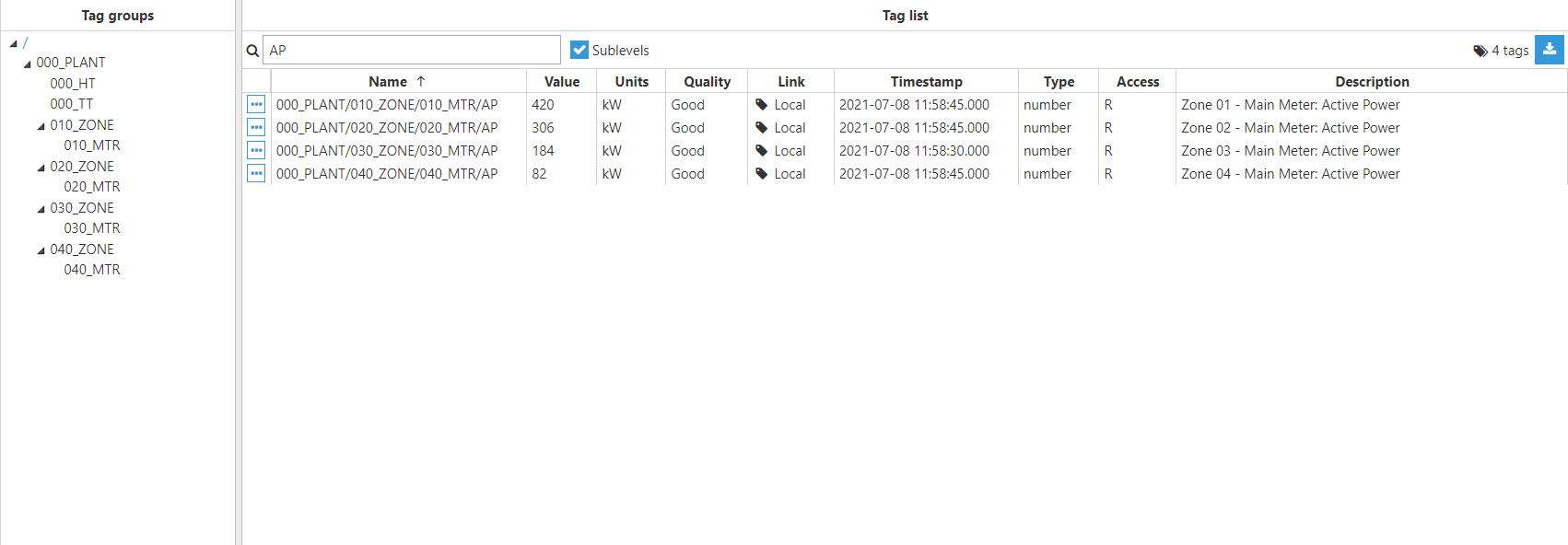
Figure 9: Tags used for this example
- Step 1: Add a new module in the “Modules” section, choose a name, and select “Historian” as the “Module type”.
- Step 2: Configure the Logger and API settings for the Historian module. In this example, the default configuration is left unedited since, in most cases, this is a valid configuration.
- Step 3: Configure the module. For this example, the configuration was left as per default.
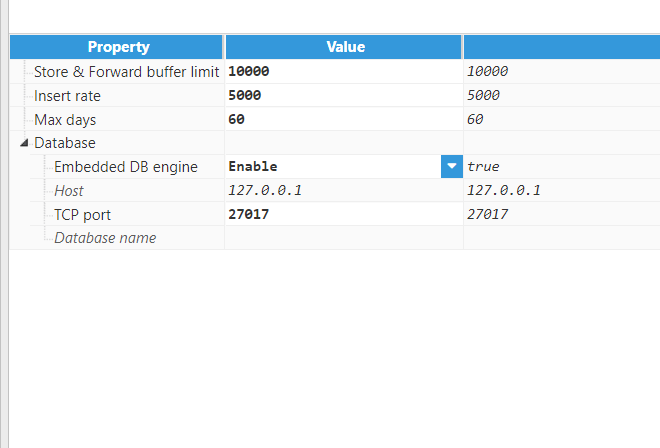
Figure 10: Module configuration
- Step 4: Configure the Tags History section.
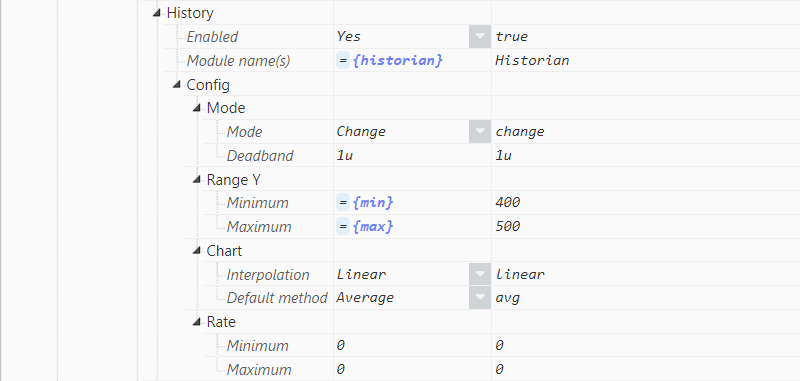
Figure 11: Tag configuration
- Step 5: In the Data/Historical section, navigate to Tag list three to drag and drop the tags that will be historized to Selected tags, configure data retrieval parameters (Date mode, Interval, and Mode) and apply historization. In this example, the chosen parameters are Current for Date mode (other available options are: Absolute and Relative), 1 hour for Interval, and Raw for Mode (other available options are: Aggregated, Delta, and Filter).
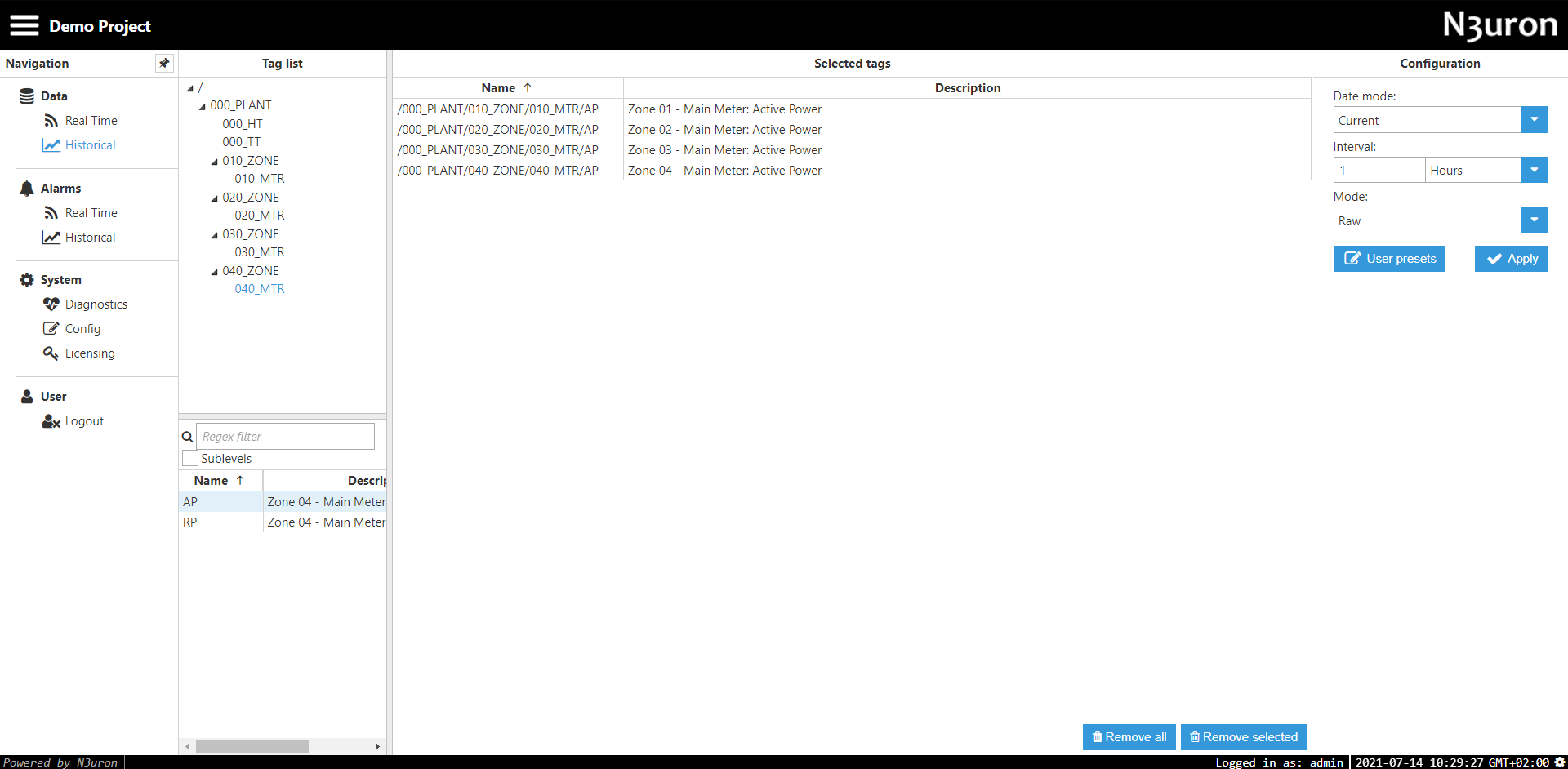
Figure 12: Data visualization configuration
Result: Figure 13: Chart of historical data
Figure 13: Chart of historical data
Storing data using an external MongoDB engine
In this example, data will be stored and monitored in an external MongoDB engine. The GUI (graphical user interface) for MongoDB used for this example is MongoDB Compass.
- Step 1: Add a new module in the “Modules” section, choose a name and select “Historian” as the “Module type”.
- Step 2: Configure the Logger and API settings for the Historian module. In this example, the default configuration is left unedited since, in most cases, this is a valid configuration.
- Step 3: Configure the module by disabling the Embedded DB engine and configure the rest of the parameters.
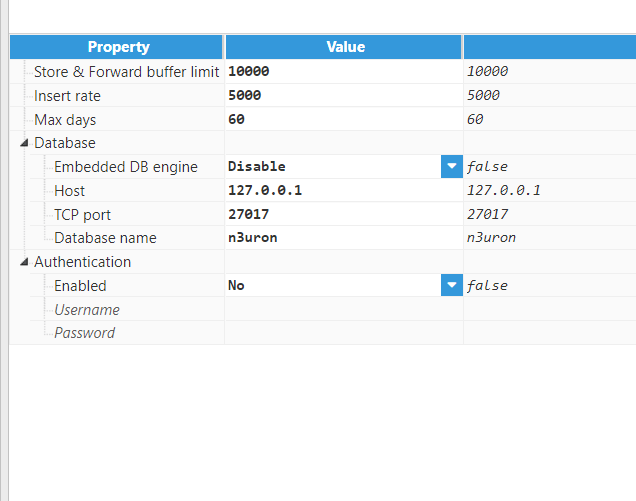
Figure 14: Historian module configuration
- Step 4: Configure the MongoDB client and connect it to N3uron’s Historian.
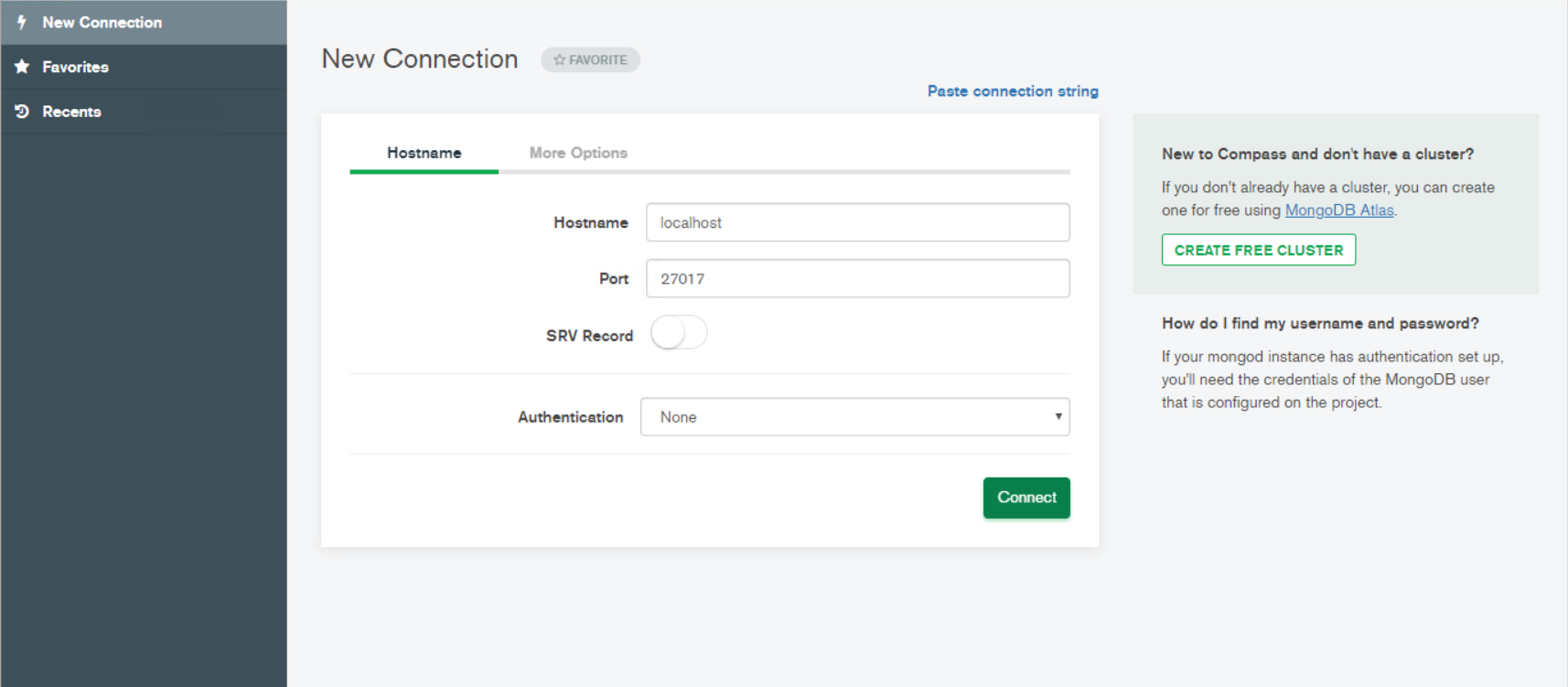
Figure 15: MongoDB compass configuration
Result: A database named “n3uron” (as configured previously in the module configuration section) is automatically created by Historian. This database contains the following collections: Tags collection, Samples collection (everyday a new collection is created), and Alarms collection (everyday a new collection is created).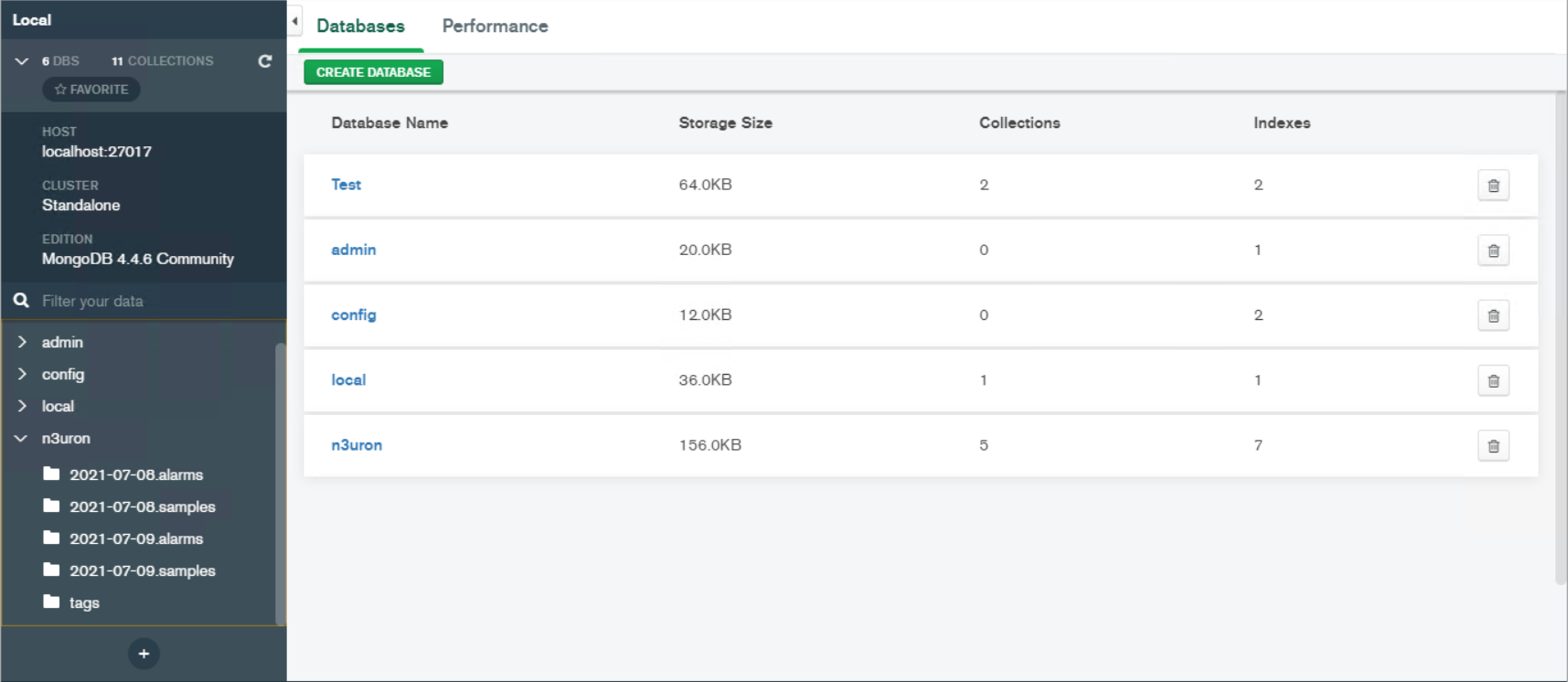
Figure 16: Databases created in compass
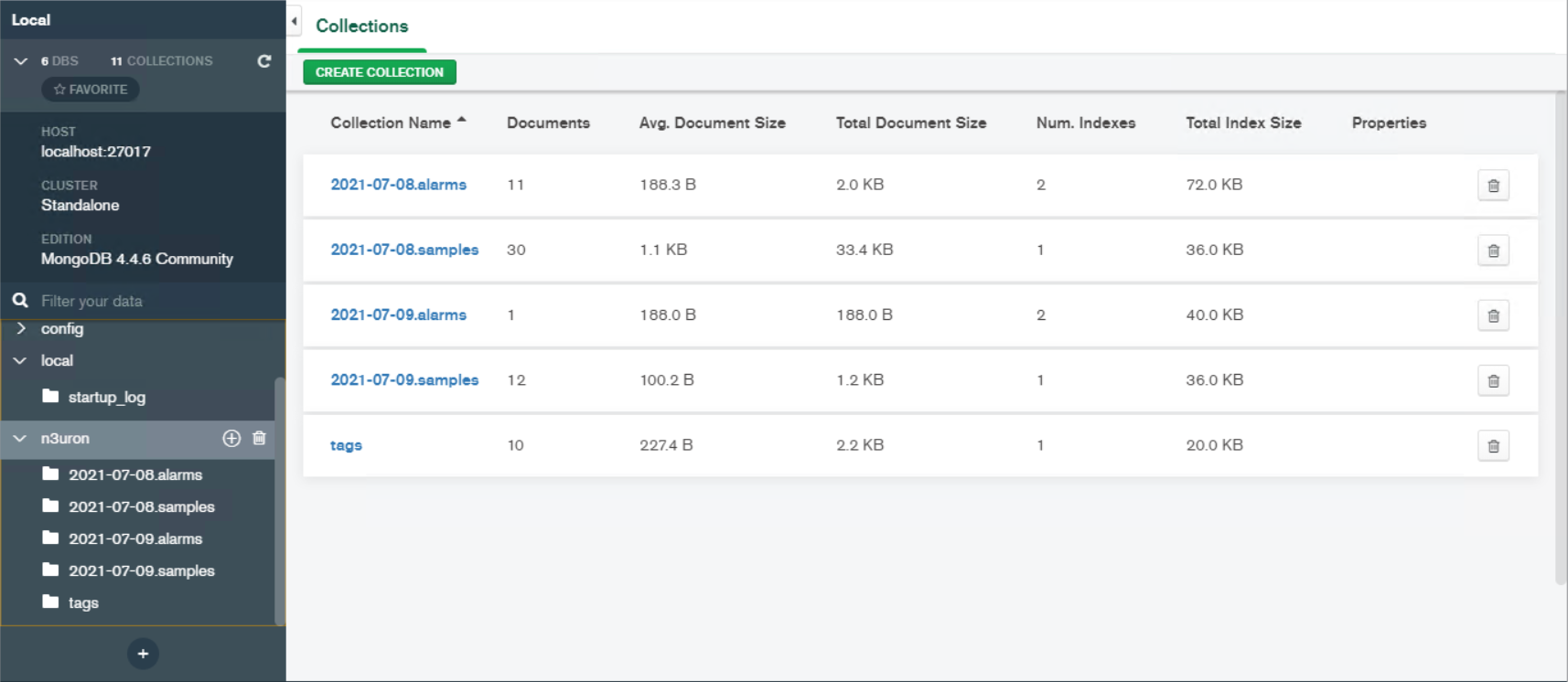
Figure 17: Collections inside the database
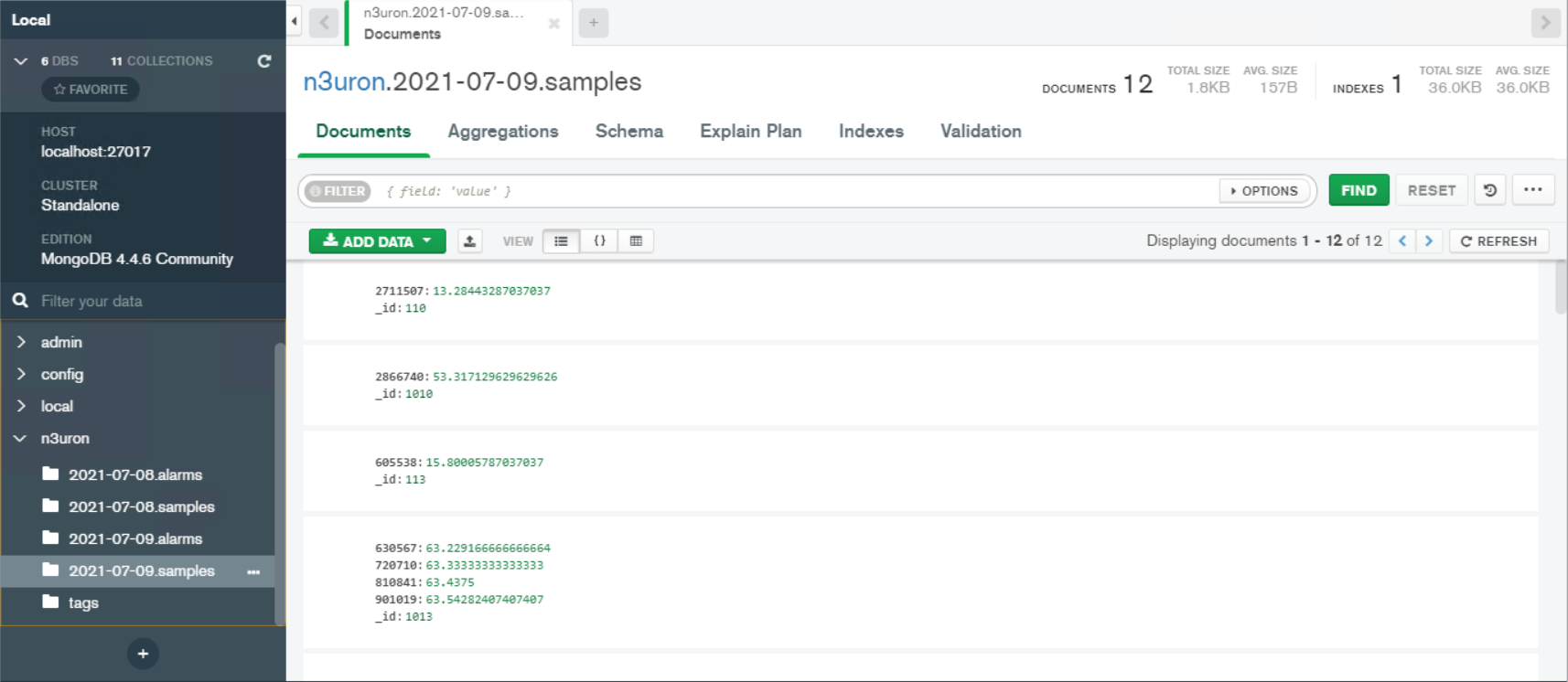
Figure 18: 2021-07-09 samples collection
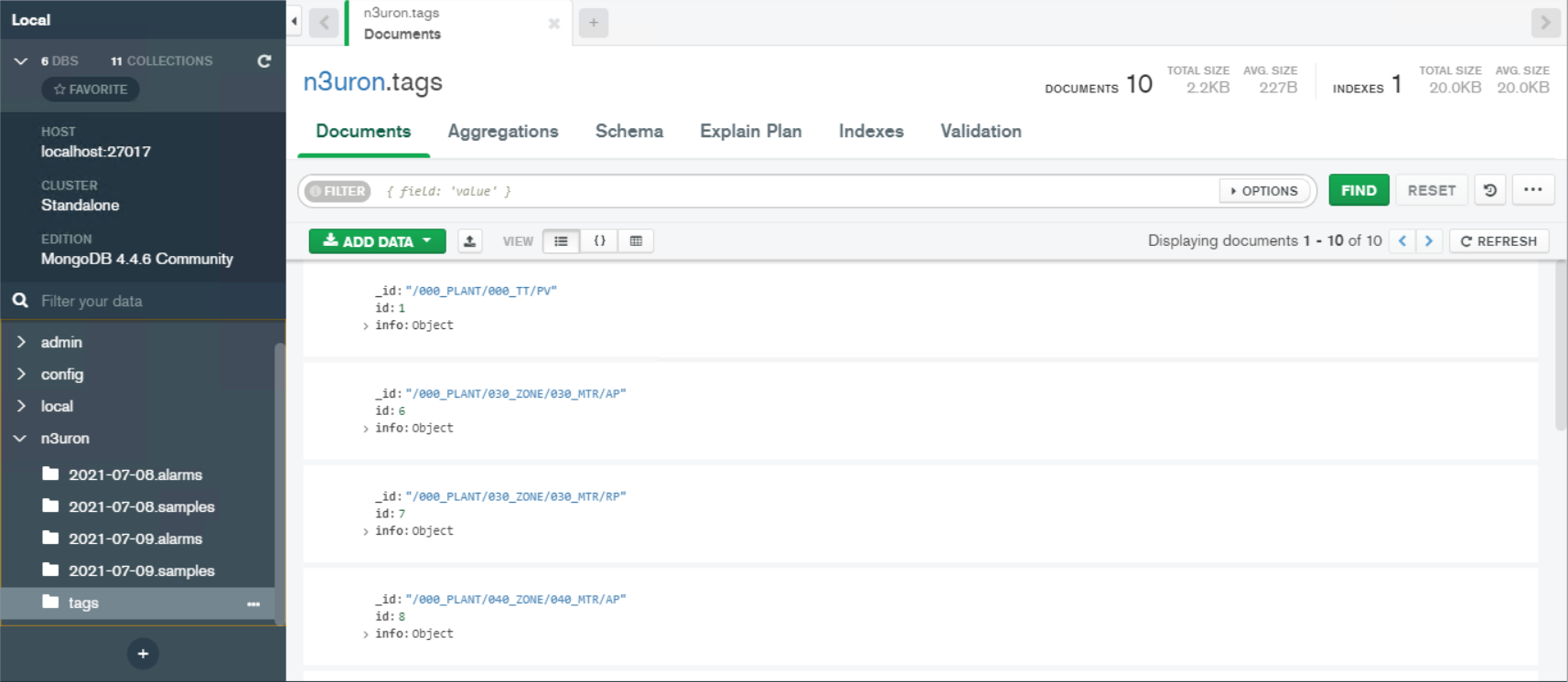
Figure 19: Tags collection