Channel set up
The first step when configuring a connection to the meter is to create a new channel. A channel represents the physical medium of connecting one or more devices. In this example, the name of the new channel is COM1, since it is communicating to the meter through an optical probe connected to serial port 1.
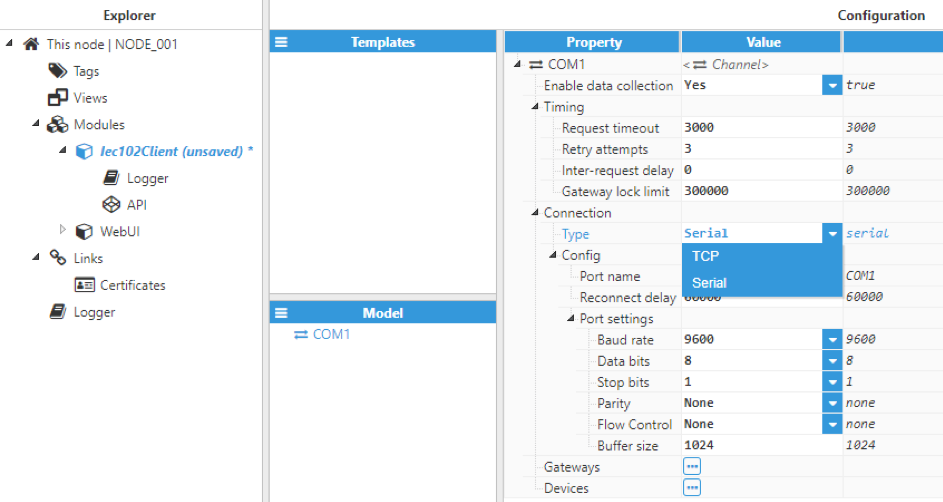 Figure 3. Iec102Client settings
Figure 3. Iec102Client settings
Each channel requires the following parameters to be set:
- Data collection: When disabled, the channel will remain inactive. The default value is set to enabled.
- Timing:
- Request timeout: Time waiting for a valid response before retrying or moving to the next request, displayed in milliseconds. The valid range is 100ms to 600000ms. The default value is 3000ms.
- Retry attempts: Number of communication retries before considering the target device to be unreachable and moving to the next request. The valid range is 0 to 100. The default value is 3, meaning that for each unresponsive request, the driver will make a total of 4 attempts (1 initial request and 3 retries).
- Inter-request delay: Time between a valid response and the next request, displayed in milliseconds. This parameter may be used when a target device fails due to receiving the requests too quickly. The valid range is 0ms to 600000ms. The default value is 0ms, which means that the next request will be sent as soon as a valid response has been received.
- Gateway lock limit: Maximum time that the quality of associated tags should remain set to Good whilst an update is paused due to another application being connected to the devices in this channel through a gateway (if any). When this time expires, all associated tags will automatically be set to Bad – out of service. This value is expressed in milliseconds. A value of 0 will disable this limit, allowing any data updates on this channel to be paused, and tags to retain a Good quality status indefinitely whilst other applications are connected through the gateways in this channel.
- Connection:
- Type: Defines the connection type.
- TCP: Connects via a TCP socket.
- Serial: Connects via a serial port.
- Type: Defines the connection type.
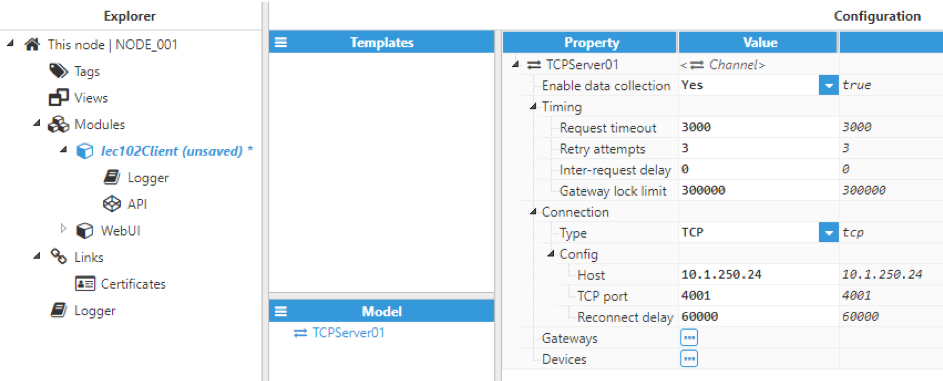 Figure 4. TCP channel configuration
Figure 4. TCP channel configuration
Each TCP channel includes the following parameters:
- Host: Hostname or IP address of the target device.
- TCP port: TCP port of the target device. The valid range is 1 to 65535. The default value is 4001.
- Reconnect delay: Time before attempting to re-open a failed connection, displayed in milliseconds. The minimum value is 1000ms. The default value is 60000ms.
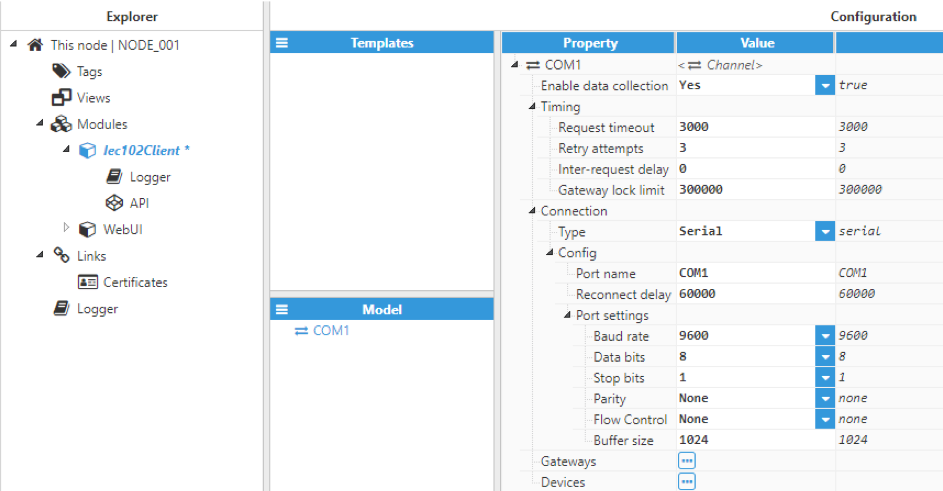
Figure 5. Serial channel configuration
A serial channel includes the following parameters:
- Port name: Serial port as displayed by the operating system. For example, if N3uron is running in Windows, valid port names would be COM1, COM2, and so forth. If running on Linux, valid port names could be /dev/ttyS0, /dev/ttyS1, and so forth.
- Reconnect delay: Time before trying to re-open a failed serial port, displayed in milliseconds. The minimum value is 1000ms. The default value is 60000ms.
- Port settings:
- Baud rate: Serial port transfer speed.
- Data bits: Number of data bits per data word. Valid values are 5, 6, 7, or 8.
- Stop bits: Number of stop bits per data word. Valid values are 1 or 2.
- Parity: Data parity type. Valid options are none, even, mark, odd, or space.
- Flow control: Enables the use of RTS and DTR control lines.
- Buffer size: Serial communication buffer capacity.
Gateways
Sometimes the port used to connect to the electrical meter must also be used by other applications, for instance for downloading the load profile. In this case, concurrent access to the port would cause collisions and communication errors. Adding a gateway to a channel permits a third-party application to access the meter whilst avoiding these issues.
The gateway on a channel listens a TCP port and waits for any connections. When a third-party application connects, communication of all devices in this channel is paused, permitting a transparent connection between the application and any device in the channel. Once the application disconnects from the gateway, the driver will resume communication to the devices.
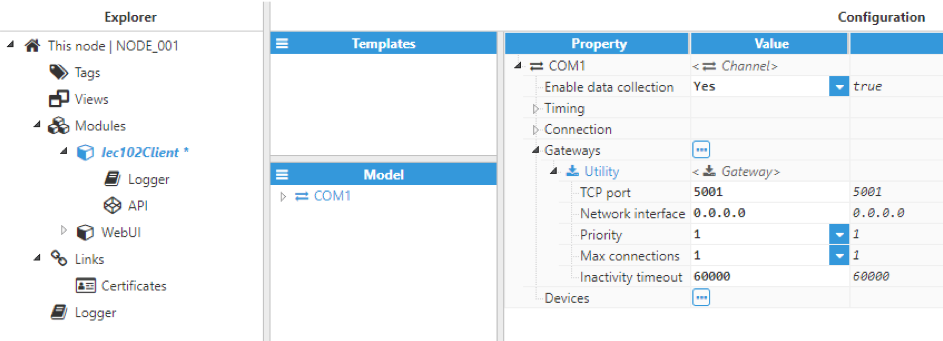 Figure 6. Gateway configuration
Figure 6. Gateway configuration
Configuration of a gateway includes the following parameters:
- TCP port: The gateway listens to this port for any incoming connections. The selected port must not be used by any other gateway or application in the same machine. The valid range is 0 to 65535. The default value is 5001.
- Network interface: Permitted interface for incoming connections.
- 0.0.0.0 allows connections from any network interface available within the machine.
- 127.0.0.1 or localhost only allows connections from local applications.
- Use a specific IP address for a network card in the machine to only allow connections from this interface.
- Priority: The priority of this gateway over the rest of gateways on this channel. The valid range is 1 (highest priority) to 10 (lowest priority). The priority must be different for each gateway sharing the same channel. The default value is 1.
- Max connections: The number of maximum concurrent connections supported. For future use, only 1 connection is permitted in this version. If more connections are required, another gateway should be set up.
- Inactivity timeout: When an application is connected but remains inactive (no traffic), it will automatically be disconnected from the gateway after this time. This allows data collection to be resumed in order to continue to update any tags associated to this channel. This value is expressed in milliseconds. The default value is 60000ms. A value of 0 will disable this functionality, stopping any applications from being automatically disconnected from the gateway, even if this application remains inactive indefinitely.
Device configuration
Each channel can connect to one or more electrical meters. A typical example of a channel containing a single device would be a direct TCP or serial connection to an IEC-102 device. An example of multiple devices in the same channel would be when several IEC-102 devices with different link addresses are connected within the same serial bus.
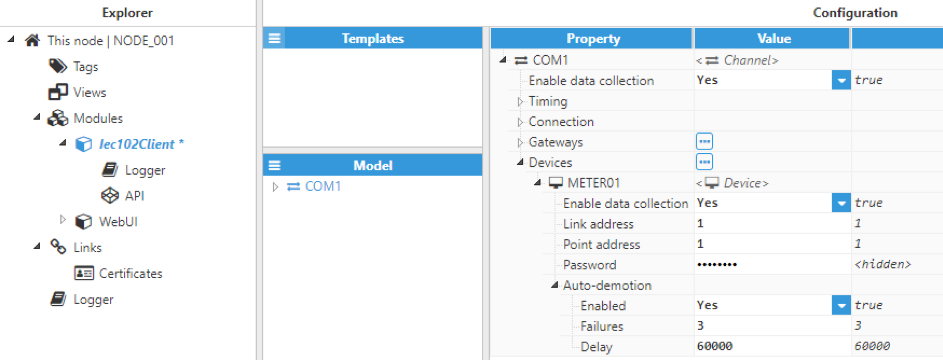 Figure 7. Device configuration
Figure 7. Device configuration
The device configuration settings contain the following options:
- Enable data collection: Enables or disables data collection on the specified device. When disabled, the channel will remain inactive. The default value is set to enabled. If disabled, data will not be sent to the device and the quality status of tags will remain as Bad – Uninitialized.
- Link address: In IEC-102, each device must have a unique 16-bit address. This parameter specifies the IEC-102 link address of the target device. The valid range is 0 to 65535. The default value is 0.
- Point address: Specifies the point address of the target device. The valid range is 0 to 65535. The default value is 0.
- Password: Specifies the password required to access the device in read-only mode.
- Auto-demotion: Defines whether a device should be temporarily set to "off-scan" when not responding. If set to "off-scan", read requests will not be sent to the device and any data associated with these read requests will automatically remain as "bad quality" while demoted. By placing a non-responsive device offline for a specific time period, the driver can continue to optimise communications with other devices in the same channel. Once this demotion period has been reached, the driver will re-attempt to communicate with the non-responsive device. If the device is responsive, it will be set to "on-scan". Otherwise, the "off-scan" time period will restart after the specified number of failures has been reached.
- Enabled: When set to enabled, if the specified number of successive failures is reached, data collection for this device will be set to “off-scan” during the specified interval.
- Failures: Specifies how many consecutive rounds of request timeouts and retry attempts must occur before the device is set to "off-scan". The minimum value is 1. The default value is 3.
- Delay: Time the device is set to "off-scan" for when the max consecutive failures value has been reached. When the specified interval expires, the driver will reset the device to "on-scan" and allow another communication attempt to be made. The minimum value is 1000. The default value is 60000 milliseconds.
Tag configuration
The channel and device configuration options define the settings to be applied when establishing connections to the target device. After configuring these options, users will be able to create and configure any tags associated to data received from IEC-102 electrical meters, as seen in the following example:
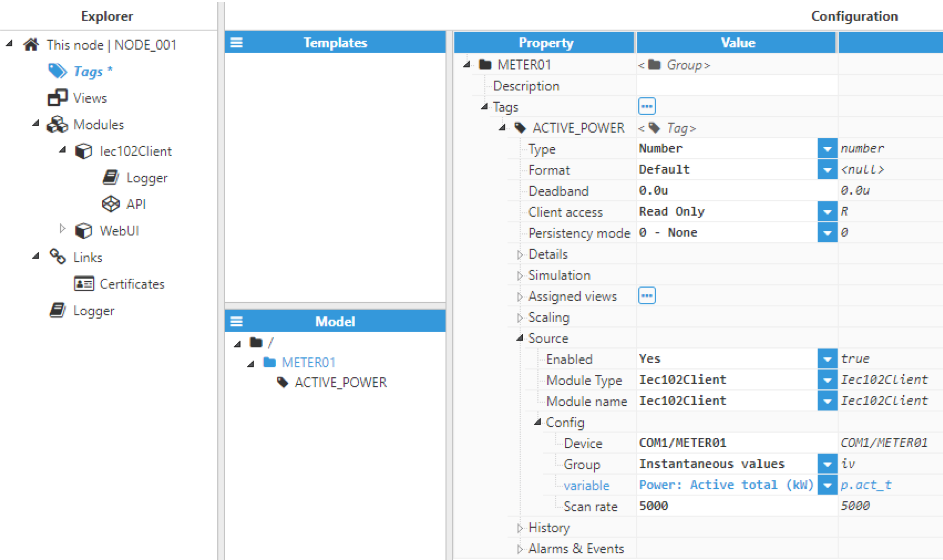 Figure 8. Configuring IEC-102 tag sources
Figure 8. Configuring IEC-102 tag sources
Source configuration settings contain the following parameters:
- Enabled: When disabled, tags won’t be updated with the values received from the device, but instead, will essentially act as memory tags. When set to enabled, the tag value will be continuously updated with the values received from the field device. The default value is set to disabled.
- Module type: Defines the driver type used to retrieve values from the field. In this example, Iec102Client must be selected from the drop-down menu. If Iec102Client does not appear in the drop-down menu, this means that this driver has not been installed on this machine yet and must therefore be installed.
- Module name: Defines the Iec102Client instance created.
- Config:
- Device: This refers to the device that has already been created in previous steps and will act as the data source. It should be referenced using the following format: channel/device.
- Group: Defines the tag data group. This version only supports instantaneous values.
- Variable: Defines the electrical signal assigned to the tag, according to the IEC 60870-5-102 protocol specification. The following signals are available:
- Energy: Active imported (kWh)
- Energy: Active exported (kWh)
- Energy: Reactive Q1 (kVArh)
- Energy: Reactive Q2 (kVArh)
- Energy: Reactive Q3 (kVArh)
- Energy: Reactive Q4 (kVArh)
- Power: Active total (kW)
- Power: Reactive total (kVAr)
- Power: Power factor total
- Power: Active phase 1 (kW)
- Power: Reactive phase 1 (kVAr)
- Power: Power factor phase 1
- Power: Active phase 2 (kW)
- Power: Reactive phase 2 (kVAr)
- Power: Power factor phase 2
- Power: Active phase 3 (kW)
- Power: Reactive phase 3 (kVAr)
- Power: Power factor phase 3
- V-I: Current phase 1 (A)
- V-I: Voltage phase 1 (V)
- V-I: Current phase 2 (A)
- V-I: Voltage phase 2 (V)
- V-I: Current phase 3 (A)
- V-I: Voltage phase 3 (V)
- Scan rate: Poll interval for the specified tag, displayed in milliseconds. The minimum value is 100ms.