DataSets are elements used to gather and present data using multiple data sources. The DataSets project folder contains the templates for DataSets that are ready to be instantiated inside each component. For performance reasons, the data from a dataset is not loaded until an instance from the same dataset exists and is referenced by another element.
Historical Datasets
Historical DataSets present data organized into [date, value] pairs, where the date is a timestamp and value is the value associated to that given date. Data from Historical DataSets is retrieved from N3uron historian. Historical DataSets include the following options:
- Tag: Path of the tag to be loaded.
- Autoreload: Configuration of data autoreload.
- Enabled: Activate/deactivate data autoreloading.
- Interval: Autoreload interval in seconds.
- Date mode: Allows users to select different ways of displaying the data start and end dates.
- Relative: Allows users to select the start and end date in accordance with the current date.
- Absolute: Allows users to select a start and end date as absolute dates.
- Current: Allows users to select an interval between the current moment and a previous moment defined by the offset.
- Date: Configuration for different Date modes:
- Relative: Start and end dates are configured using an offset displayed in days or weeks and a time offset in milliseconds
- Offset: Offset relative to current moment.
- Time: Absolute offset over the relative offset.
- Absolute: Allows dates to be specified as absolute values.
- Start: Absolute start date.
- End: Absolute end date.
- Current: Allows users to specify the date between a selected negative offset and the current moment.
- Offset: Negative offset from current date.
- Units: Offset units (seconds, minutes or hours).
- Relative: Start and end dates are configured using an offset displayed in days or weeks and a time offset in milliseconds
- Mode: Configuration of data representations.
- Aggregated: Allows users to aggregate data using different methods.
- Raw: Presents data exactly as it is stored in the historical database.
- Delta: Only presents values when they have changed beyond the deadband value. Includes all values after the change.
- Filter: Only presents values when they have changed beyond the deadband value. Includes all values before and after the change.
- Mode configuration: Configuration properties for different modes.
- Aggregated:
- Aggregation method: Type of aggregation applied to data. Choose between:
- Tag configuration: Value configured within the tag.
- Avg: Weighted-time average for the selected aggregation interval.
- Min: Minimum value for the selected aggregation interval.
- Max: Maximum value for the selected aggregation interval.
- First: First value for the selected aggregation interval.
- Last: Last value for the selected aggregation interval.
- Aggregation interval: Interval for the aggregated data:
- Value: Interval value.
- Units: Value units.
- Aggregation method: Type of aggregation applied to data. Choose between:
- Raw: No special configuration, raw values only.
- Delta and Filter:
- Deadband: Defines the data change threshold.
- Aggregated:
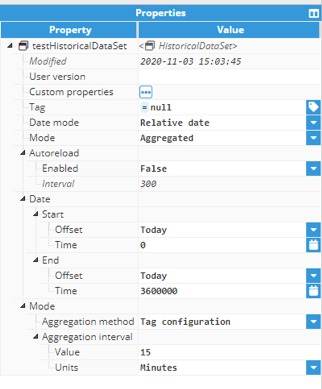 Figure 45: Historical dataset properties
Figure 45: Historical dataset properties
Derived Datasets
Derived DataSets can contain any type of data organized into pairs, but they are mostly used to allow modifications to be made to the data returned by another dataset. For example, to multiply all values by two or sum all values from two different DataSets. Derived DataSets include the following properties.
- DataSet: Field containing the dataset. Users can reference DataSets, introduce DataSets manually and create expressions using mathematical operations.
- DataSets: Instance list of accessible datasets to operate within the Dataset field.
 Figure 46: Example combination of a historical dataset, mathematical operation, and a manually written dataset
Figure 46: Example combination of a historical dataset, mathematical operation, and a manually written dataset