Note:
This module is available from N3uron version 1.22.0.
Note:
Before starting the configuration, a new module instance must be created. Click here for more information about creating Module instances.
Recommendation:
Ensure your data model includes well-structured, contextualized metadata with clear descriptions, engineering units, and proper normalization for each data point. Implement a consistent naming hierarchy with meaningful, readable paths—this enables AI agents to navigate and interpret your data model efficiently on the first pass, minimizing tool calls, token consumption, and time to insight. While descriptive prompts, system prompts, or RAG-based reference materials can compensate for cryptic naming, comprehensive naming conventions and metadata provide the most reliable foundation for effective AI integration.
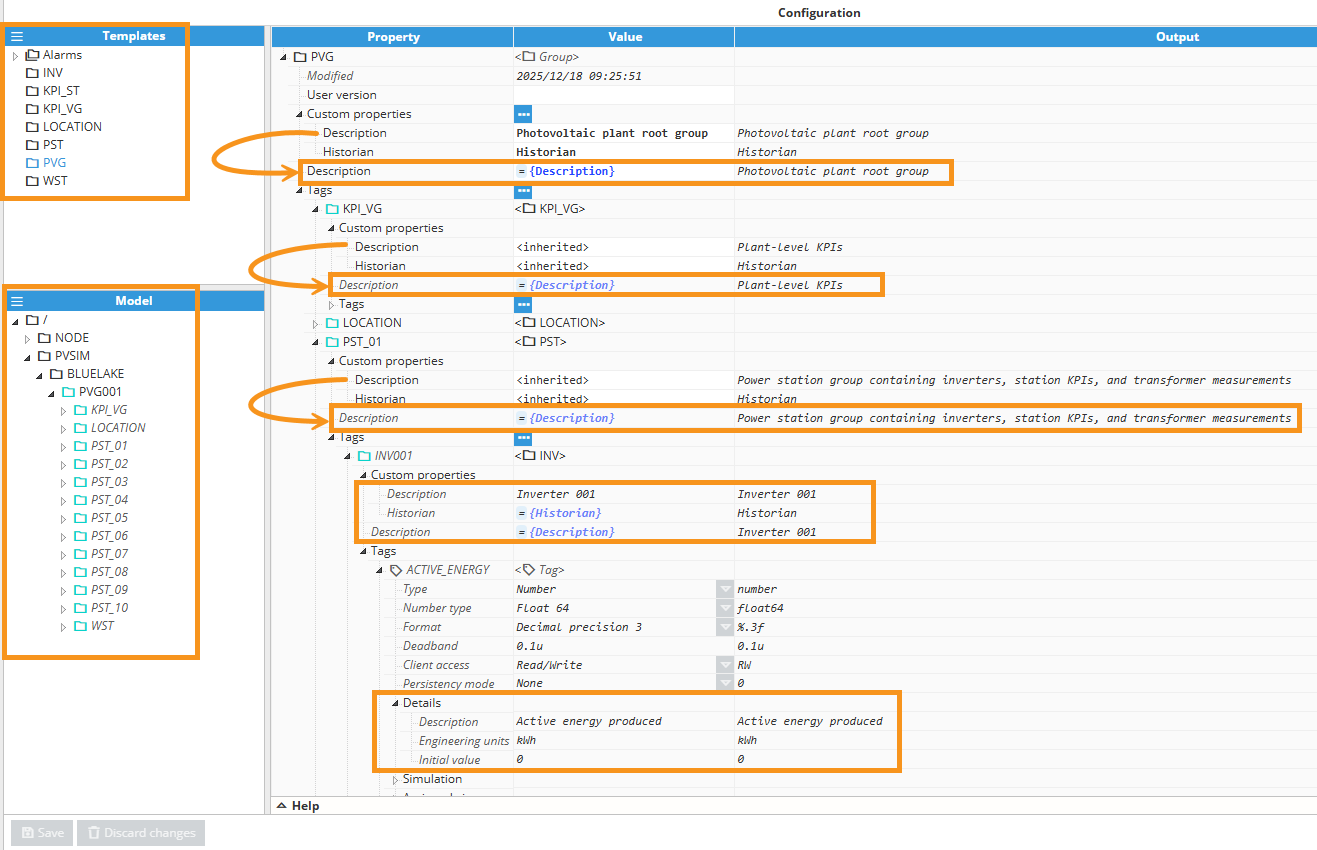
N3uron’s Templates help you standardize tag structures and metadata across assets by defining them once and creating reusable instances that inherit the template’s properties. This makes it easy to apply consistent descriptions, units, and configuration patterns at scale—while keeping models readable and maintainable as projects grow.
Templates Overview
Module Configuration
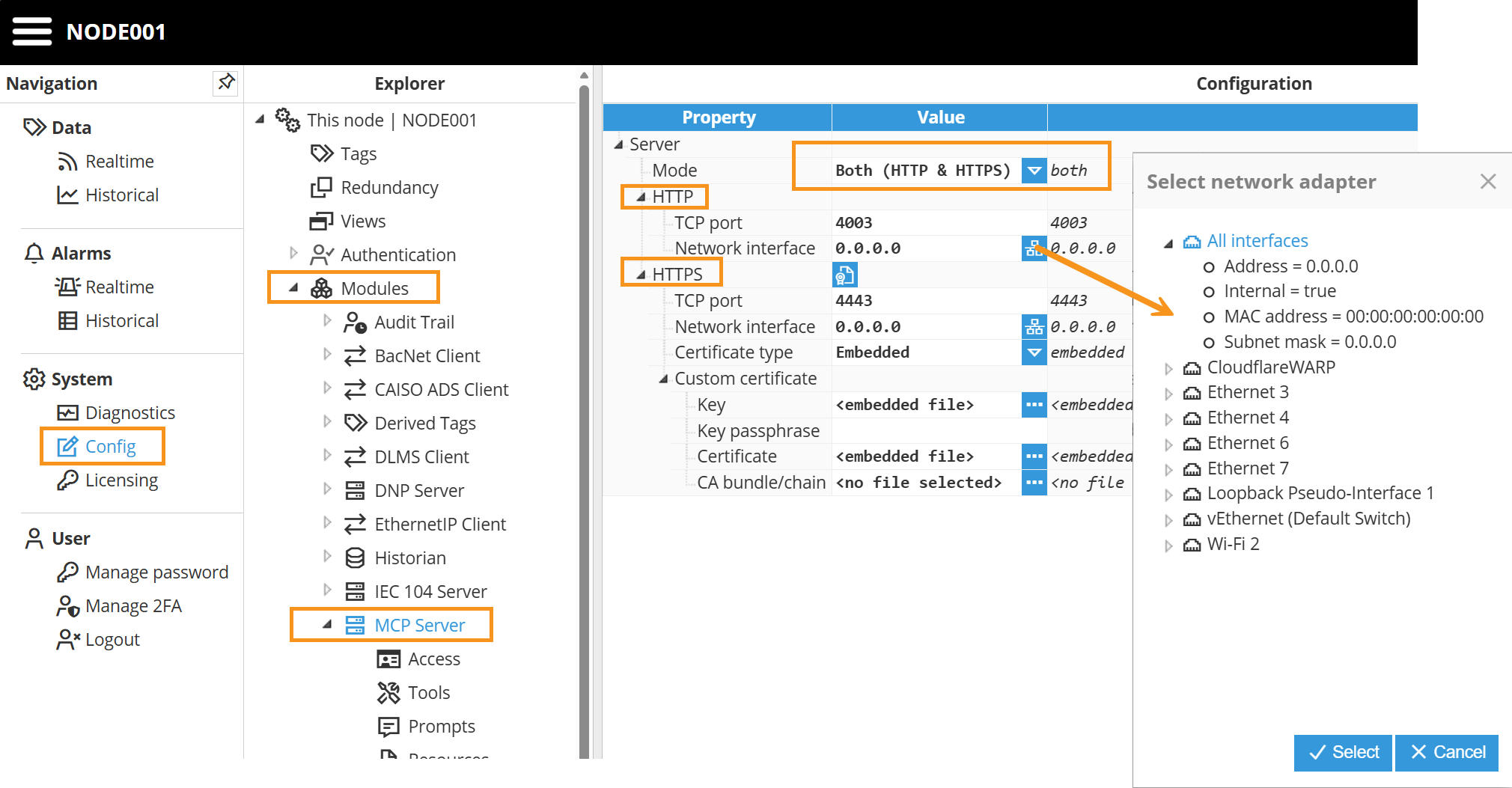
By selecting the MCP Server in the explorer tree menu under the Modules section, users can configure how the module accepts connections. The following screenshot shows the different available options for MCP Server Configuration:
.png)
Server:
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Mode | Selects which protocol(s) the MCP Server will listen on (HTTP, HTTPS, or both if available). |
HTTP:
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
TCP port | Specifies the HTTP port number for connecting to the MCP Server. The valid range is 1 to 65535. Any other application on the same machine may not use this port. (e.g., 4003 in the example). |
Network interface | Specifies the interface for accessing the MCP Server via HTTP. You can either select the network interface by clicking the browse button or enter the IP address manually (e.g., 0.0.0.0 to listen on all interfaces). |
HTTPS:
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
TCP port | Specifies the HTTP port number for connecting to the MCP Server. The valid range is 1 to 65535. Any other application on the same machine may not use this port. (e.g., 4003 in the example). |
Network interface | Specifies the interface for accessing the MCP Server via HTTPS. You can either select the network interface by clicking the browse button or enter the IP address manually (e.g., 0.0.0.0 to listen on all interfaces). |
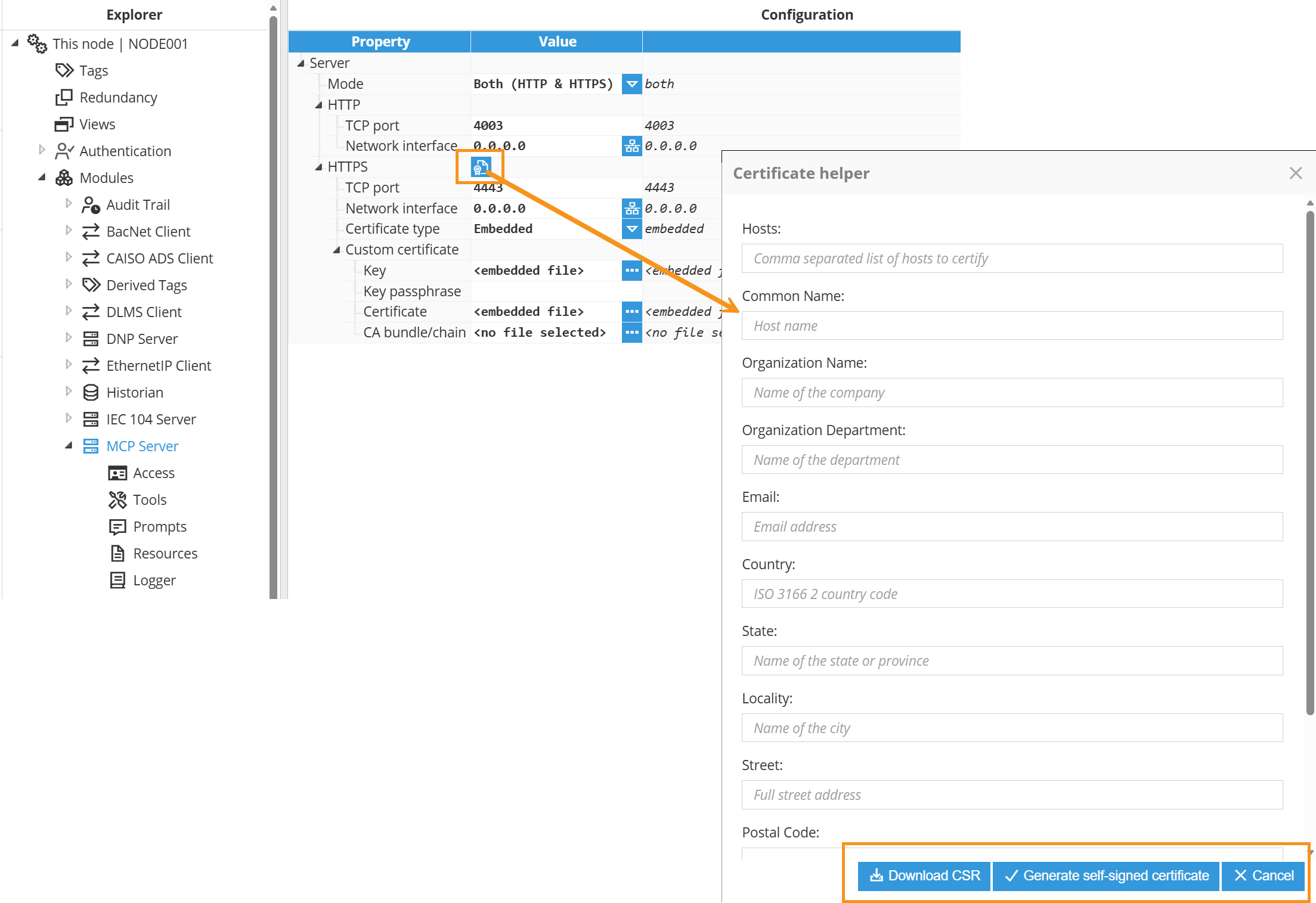
Certificate helper: Facilitates establishing HTTPS connections with custom self-signed certificates, offering control over the certificate generation process. To open the self-signed Certificate helper, right-click on the icon next to the HTTPS title section, and then fill out the form.
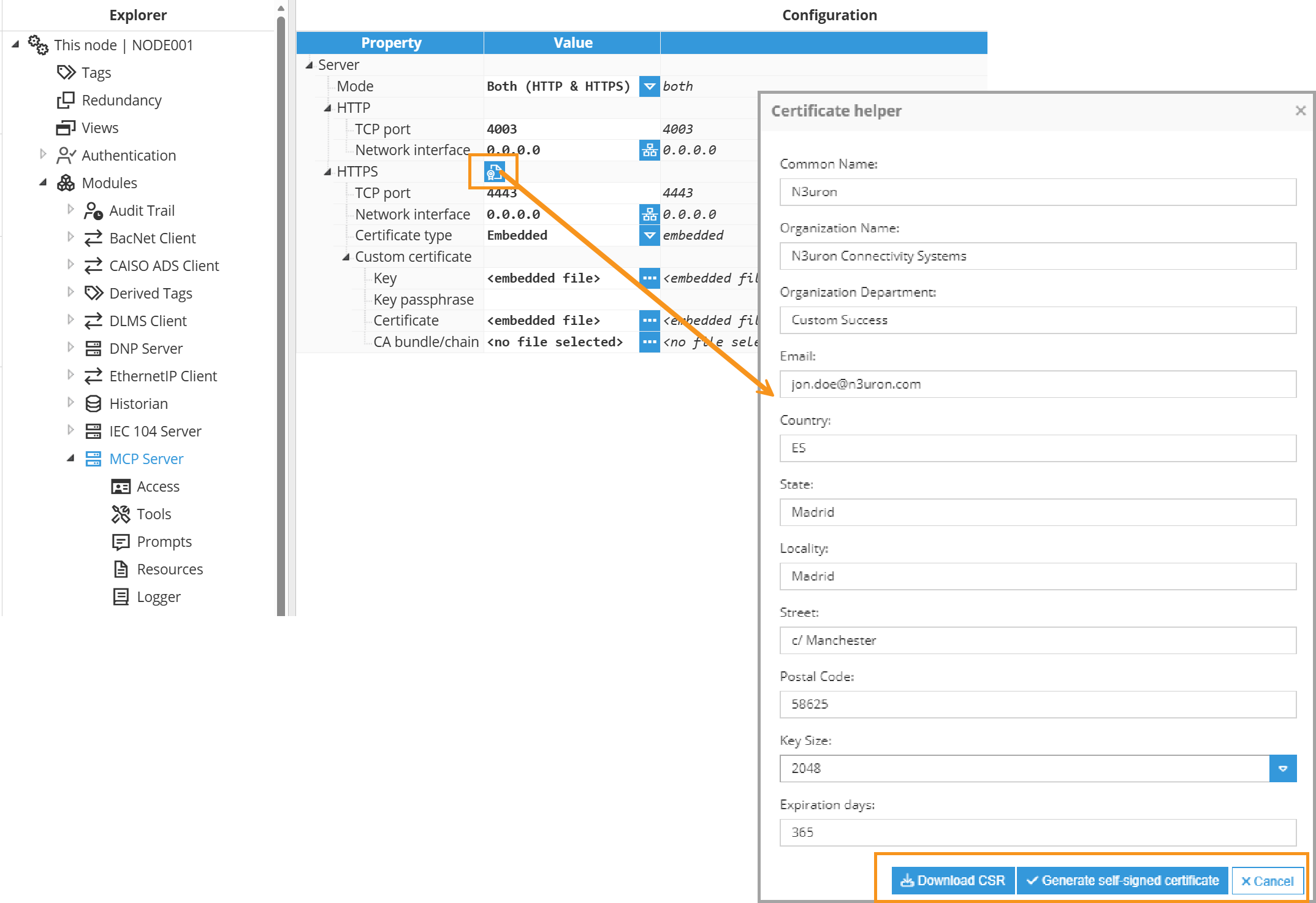
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Common Name | The fully qualified domain name (FQDN) for which the certificate is being requested. This is typically the domain name of the server where the certificate will be installed (e.g., www.example.com). |
Organization Name | The legal name of the organization or company that is requesting the certificate. |
Organization Department | The specific department or division within the organization that is requesting the certificate. |
The email address associated with the organization or individual requesting the certificate. | |
Country | The two-letter ISO code representing the country where the organization is located (e.g., US for the United States, CA for Canada, ES for Spain). |
State | The full name or abbreviation of the state or province where the organization is located. |
Locality | The city or locality where the organization is located. |
Street | The street address of the organization's physical location. |
Postal Code | The postal or ZIP code of the organization's location. |
Key Size | The size of the cryptographic key pair to be generated for the certificate, measured in bits. Common key sizes include 2048 bits or 4096 bits. |
Expiration Days | The number of days until the certificate expires. This determines the validity period of the certificate before it needs to be renewed. |
When filling out the form to generate the CSR, ensure that all information provided is accurate and matches the organization's official details. This information will be embedded in the CSR and subsequently used to issue the SSL/TLS certificate.
Certificate type:
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Self-signed | The server will automatically create and sign a certificate using an internal certification authority, which can be downloaded by clicking on the ellipsis button on the right side of the Self-signed certificate field. This certification authority is valid for all the MCP Server instances and must be imported into each MCP Client that will access the MCP Server via HTTPS. |
Embedded | The provided certificates will be embedded in the configuration file. When selecting the Embedded option, the following custom certificate parameters will be available:
|
File path | File path where the certificate files are located, with a hot-reload option. The path is relative to the data/<instance name>/cert/ folder. When selecting the File path option, the following custom certificate parameters will appear:
|
Note:
The key for the embedded certificate file will be secure and cannot be downloaded.
Access Configuration
The MCP Server enforces token-based access control for exposed tools, prompts, resources, and the published tag model. Clients must present a valid token, and the server then enforces the configured permission rules to determine what the client can discover and what it is allowed to invoke.
.gif)
Access Token:
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Enabled | If disabled, none of the access permissions granted will apply to this token. |
Token | The Bearer Token value is automatically generated when you click the button on the right side. |
Custom extensions access permissions:
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Custom tools access | Allow access to custom defined tools. |
Custom prompts access | Allow access to custom defined prompts |
Custom resources access | Allow access to custom defined resources. |
Note:
Custom tools, prompts and resources have only two options: Allow, which grants full visibility to the MCP Client, or None, that provides neither visibility nor accessibility. Read or write access to the API is controlled within the actual Custom tool script.
Default Tools access permissions:
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Alarm | Access to the tag alarm system. Allows querying, filtering, and managing alarm states, including active, cleared, acknowledged, and unacknowledged alarms across the tag namespace. |
Backup | Access and manage the node backup system. Allows creating, exporting, importing, and restoring complete node configuration snapshots, including all modules, tags, alarms, and settings. Essential for system maintenance, updates, and disaster recovery. |
Certificate | Manage X.509 certificates and certificate stores for modules. Handles SSL/TLS certificates for secure communications, including client certificates, server certificates, and certificate authorities. Supports various certificate types for different module needs. |
License | Manage node licensing system. Control software licenses, view license details, add new licenses, and handle license migrations. Essential for ensuring proper software authorization and managing licensed features. Manage node licensing system. Control software licenses, view license details, add new licenses, and handle license migrations. Essential for ensuring proper software authorization and managing licensed features. |
Link | Access and monitor node links and connections. Manage communication links between nodes in distributed architectures, including monitoring link status, health, and connectivity information across the network. |
Log | Access and manage system log files. Browse available log files from different modules and system components, and export log data for analysis, troubleshooting, and audit purposes. Essential for system monitoring and diagnostics. |
Module | A comprehensive module management system to control the entire module lifecycle (start, stop, restart), manage configurations, monitor instances, and handle installed modules. It’s essential for managing data sources, publishers, and custom modules within the ecosystem. |
Redundancy | Access to redundancy status with primary/backup nodes. If the primary fails, the backup node automatically takes over. |
System | Access and control node system functions. Monitor node health, restart services, manage system identifiers, and get system status information. Essential for node administration and system maintenance. |
Tag | The core tag namespace provides access to the tag model, enabling browsing of tag hierarchies, reading current values, retrieving detailed tag information, accessing historical data, and writing values. It serves as the primary interface for data acquisition and control. |
Tools access options:
None (zero tool visibility), Read (allow read operations), Read/Write (allow read and write operations).
Default Resources access permissions:
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Logs | If enabled, logs can be accessed through the API. |
Alarms | If enabled, Alarms can be accessed through the API. |
Tags | If enabled, Tags will be accessible via the API. |
Resources access options:
Yes or No to allow the namespaces Logs, Alarms or Tags to be expose as resources.
Note:
Allowing Logs, Alarms, and Tags to be accessible as resources enables the MCP Clients to subscribe to changes in these namespaces. However, keep in mind that not all MCP Clients support this capability.
Model Context Protocol - Resources documentation
Tag model access filters:
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Mode | Specifies whether the filter must include or exclude tags. |
Path | Specifies the path of the tag or group of tags to be filtered. |
Regex Pattern | This is a regular expression for filtering which tags will be included. By default, it is set to .*, meaning no filter is applied, and everything is allowed within the selected path. Further information about regular expressions can be found at RegExr. |
Note:
It is a mandatory to add a filter even when the whole model is going to be published.
Include filters are applied first and exclude filters are applied to the include filters' results.
MCP Client connection examples
To connect an MCP client to the N3uron MCP Server, the client must be able to reach the server and present valid credentials.
Required:
MCP Server endpoint (reachable from the client): http(s)://<hostname or ip address>:<port>/mcp
Authorization Bearer Token.
When using HTTPS, the client's trust in the server certificate requires the client to recognize and accept the server’s TLS certificate. This involves providing the certificate authority (CA) or a self-signed certificate if applicable; otherwise, the connection will fail.
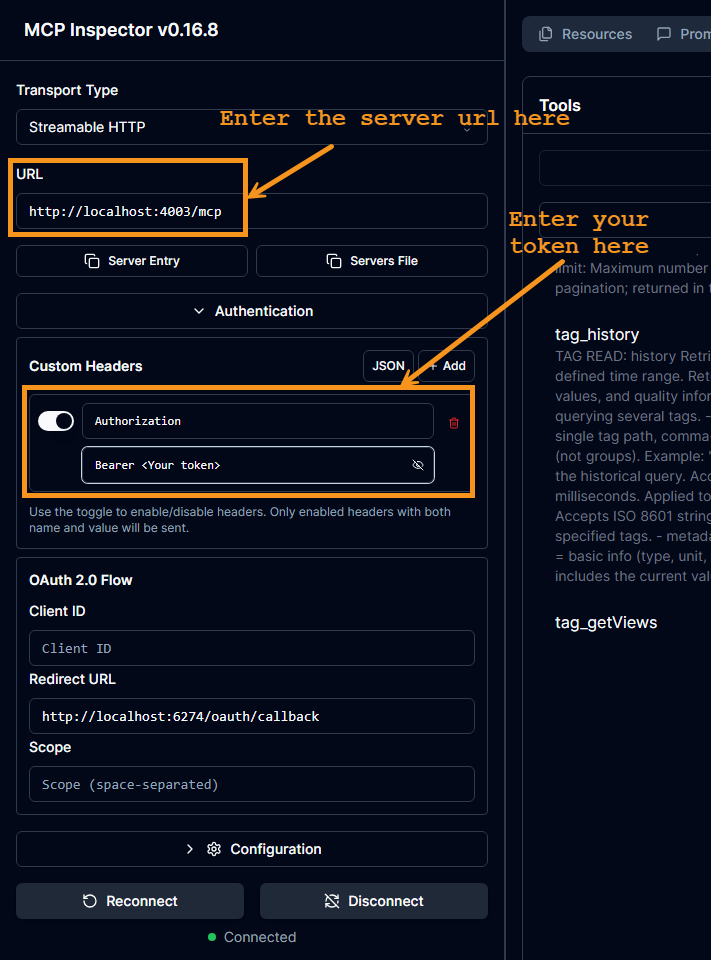
MCP Inspector (testing client)
Run the MCP Inspector
npx @modelcontextprotocol/inspectorIn the MCP Inspector UI:
Select Transport Type: Streamable HTTP
Set Server URL to http(s)://<host>:<port>/mcp
Add header: Authorization: Bearer <token>
Connect, then list and invoke tools, prompts, and resources to validate the end-to-end behavior.
Further information at this link: MCP Inspector - Model Context Protocol
Claude Desktop (claude_desktop_config.json)
{
"mcpServers":
{
"n3remote":
{
"command": "mcp-remote",
"args":
[
"https://<n3uron-host>:<https-port>/mcp",
"--header",
"Authorization: Bearer <YOUR_TOKEN>",
],
"env": { "NODE_EXTRA_CA_CERTS": "/path/to/n3uron_CA.crt" },
},
"n3local":
{
"command": "mcp-remote",
"args":
[
"http://localhost:<http-port>/mcp",
"--header",
"Authorization: Bearer <YOUR_TOKEN>",
],
},
},
}
Further information at this link: Claude Desktop – Model Context Protocol (MCP)
AnythingLLM Desktop (anythingllm_mcp_servers.json)
{
"mcpServers":
{
"n3remote":
{
"type": "streamable",
"url": "https://<n3uron-host>:<https-port>/mcp",
"headers": { "Authorization": "Bearer <YOUR_TOKEN>" },
"env": { "NODE_EXTRA_CA_CERTS": "/path/to/n3uron_CA.crt" },
},
},
}
Further information at this link: Docs - AnythingLLM
Librechat (librechat.yaml)
mcpServers:
n3remote:
type: streamable-http
url: "https://<n3uron-host>:<https-port>/mcp"
headers:
Authorization: "Bearer <YOUR_TOKEN>"
timeout: 900000
autoConnect: true
Further information at this link: Github - LibreChat
Agentic Automation and Orchestration Platforms
Agentic automation/orchestration platforms provide a structured way to run AI-driven workflows across systems—combining model reasoning with triggers, actions, branching, and approvals.
By connecting the N3uron MCP Server, agents in these workflows can discover and use N3uron-exposed tools and resources via the Model Context Protocol (MCP).
This also supports multi-agent collaboration, including:
Agent handoffs as a workflow progresses (optionally gated by human approval)
Sharing context and intermediate results between steps/agents so work can be delegated and resumed reliably
Chaining actions through MCP for end-to-end trigger → decide → act execution.
Agent-to-agent communication can be standardized using an interoperability protocol such as Agent2Agent (A2A).
Further information at these links: