Note:
This module is available from N3uron version 1.22.0.
Prompts are reusable, parameterized instructions that guide AI models in performing specific industrial and operational tasks. They serve as templates that can be invoked by MCP clients to initiate predefined workflows.
Each prompt combines instructional text with optional arguments that allow dynamic customization at invocation time. For example, a prompt for analyzing production efficiency can accept arguments for the production line, time range, and target metrics, making it flexible enough to work across different contexts.
Basic Configuration
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Enabled | Enables or disables this prompt. When disabled, the prompt will not be discoverable or invokable by MCP clients, even if they have the necessary permissions. The default value is Yes. |
Name | Unique identifier for the prompt. This is the name that MCP clients use to invoke the prompt. Must be unique across all prompts in this MCP Server instance. Use descriptive, lowercase names with underscores. |
Title | Human-readable display name for the prompt. This title appears in prompt listings and helps users understand the prompt's purpose. Use clear, concise title case. |
Description | Detailed explanation of what the prompt does, when to use it, and what outcome it produces. This description helps users and AI systems understand the prompt's purpose and appropriate use cases. Be clear about the expected context and results. |
Prompt | The actual instructional text that guides the AI model. This is the core content that defines the task, methodology, output format, and any specific requirements or constraints. You can use argument placeholders in the format «argument_name», which will be replaced with actual values when the prompt is invoked. The prompt text can be as detailed as necessary to ensure consistent, high-quality results. |
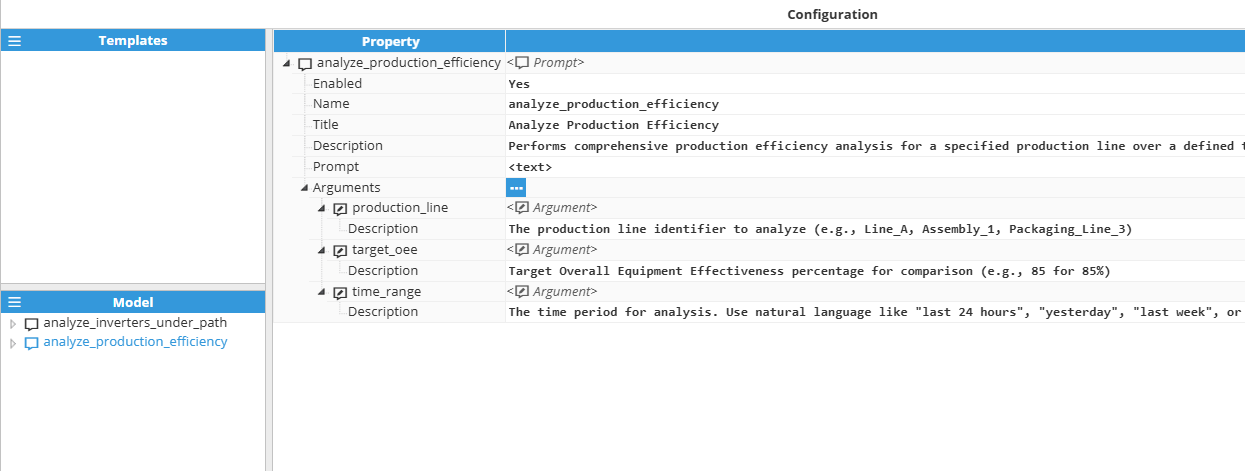
Arguments
Arguments make prompts dynamic and reusable by allowing values to be provided at invocation time. Each argument is defined within the prompt configuration and can be referenced in the prompt text using the placeholder syntax «argument_name». When an MCP client invokes the prompt, it supplies values for these arguments, which are then substituted into the prompt text before being sent to the AI model.
For example, if you define an argument named production_line, you can reference it in your prompt text as «production_line». When the prompt is invoked with the value "Line_A", all occurrences of «production_line» in the prompt will be replaced with "Line_A".
Setting | Description |
|---|---|
Name | Identifier for the argument. This name is used in the prompt text placeholder «argument_name» and must be provided by the client when invoking the prompt. Use descriptive, lowercase names with underscores. |
Description | Explanation of what the argument represents and how it should be used. This helps clients understand what values to provide. Include format requirements, acceptable values, or examples when helpful. |
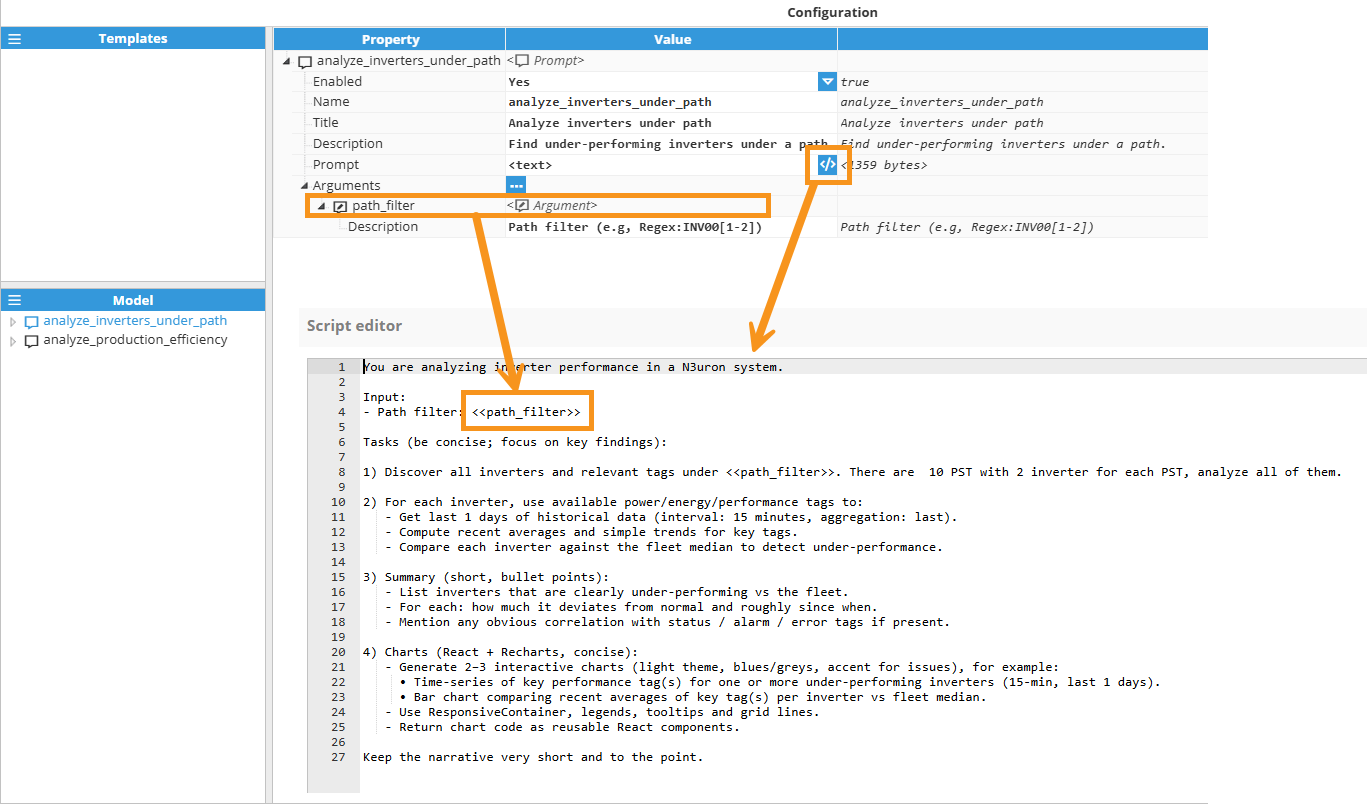
Argument Usage
Consider a prompt for alarm investigation with an argument named alarm_type:
Argument name: alarm_type
Argument description: The severity level of alarms to investigate (e.g., warning, critical, diagnostics)
Prompt text: "Check that all alarms with level «alarm_type» are correct and provide a summary of findings."
When invoked with alarm_type = "warning", the AI model receives:
"Check that all alarms with level warning are correct and provide a summary of findings."
Prompt Examples
The following examples demonstrate effective prompts for common industrial DataOps and IIoT scenarios. These templates can be adapted to your specific environment and operational needs.
Production Line Analysis
Name: production_efficiency_analysis
Title: Production Efficiency Analysis
Description: Analyzes production efficiency metrics for a specific line over a defined period, identifying bottlenecks, downtime causes, and optimization opportunities.
Arguments:
line_name: The production line identifier (e.g., Line_A, Assembly_1)
time_period: Analysis period (e.g., last 24 hours, last week, yesterday)
target_oee: Target Overall Equipment Effectiveness percentage
Prompt:
"Analyze production efficiency for «line_name» over «time_period». Calculate actual OEE and compare it to the target of «target_oee»%. Identify the top three factors impacting efficiency, quantify their impact, and provide specific recommendations for improvement. Include data on cycle times, downtime events, quality reject rates, and throughput variations."
Alarm Root Cause Investigation
Name: alarm_root_cause_analysis
Title: Alarm Root Cause Investigation
Description: Performs multi-step investigation to identify the root cause of recurring or critical alarms, correlating with process variables, equipment status, and historical patterns.
Arguments:
alarm_path: Full path to the alarm tag
investigation_hours: How many hours back to investigate
Prompt:
"Investigate the alarm at «alarm_path» by analyzing the past «investigation_hours» hours. First, retrieve the alarm history to identify activation patterns and frequency. Then, examine related process tags (temperature, pressure, flow, level) for correlations. Check for equipment status changes, operator actions, and upstream/downstream process variations. Analyze whether this alarm is a symptom or root cause. Provide a ranked list of probable root causes with supporting evidence and recommended corrective actions."
Predictive Maintenance Assessment
Name: equipment_health_assessment
Title: Equipment Health Assessment
Description: Evaluates equipment health based on operational parameters, vibration data, temperature profiles, and performance trends to predict maintenance needs.
Arguments:
equipment_tag: Equipment identifier or tag path
baseline_period: Historical period for baseline comparison (e.g., 30 days, 3 months)
Prompt:
"Assess the health of equipment «equipment_tag» by comparing current operational parameters against the baseline from «baseline_period» ago. Analyze vibration patterns, temperature trends, power consumption, cycle counts, and performance metrics. Identify any degradation trends or anomalies. Calculate a health score from 0-100 and categorize the maintenance urgency as: immediate (next 7 days), planned (next 30 days), or routine (next maintenance window). Provide specific indicators supporting your assessment and recommended actions."
Energy Consumption Optimization
Name: energy_optimization_analysis
Title: Energy Consumption Optimization
Description: Analyzes energy consumption patterns across facilities or processes, identifies waste, and recommends optimization strategies to reduce costs and improve sustainability.
Arguments:
facility_area: Facility or area to analyze (e.g., Building_3, HVAC_Zone_A)
analysis_period: Time period for analysis
energy_cost_per_kwh: Energy cost in currency per kWh
Prompt:
"Analyze energy consumption for «facility_area» during «analysis_period». Identify consumption patterns, including peak demand times, baseline load, and anomalous spikes. Compare production vs non-production periods. Calculate the total energy cost at «energy_cost_per_kwh» per kWh. Identify the top five energy waste sources and quantify potential savings for each. Provide actionable recommendations with estimated ROI and implementation complexity (low/medium/high)."
Quality Control Analysis
Name: quality_defect_investigation
Title: Quality Defect Investigation
Description: Investigates quality defects by correlating reject rates with process parameters, material batches, equipment performance, and environmental conditions.
Arguments:
product_code: Product identifier experiencing quality issues
defect_type: Type of defect (e.g., dimensional, visual, functional)
investigation_batches: Number of recent production batches to analyze
Prompt:
"Investigate «defect_type» defects in product «product_code» across the last «investigation_batches» production batches. Calculate defect rates per batch and identify trends. Correlate defect occurrences with process parameters (temperature, pressure, speed, material properties), equipment used, operator shifts, raw material batches, and environmental conditions. Use statistical analysis to identify significant factors. Determine if defects cluster by time, equipment, or materials. Provide root cause hypothesis with confidence level and recommended corrective actions prioritized by impact."
Process Optimization Recommendation
Name: process_optimization_advisor
Title: Process Optimization Advisor
Description: Analyzes process performance data to identify optimization opportunities and recommend specific parameter adjustments for improved throughput, quality, or efficiency.
Arguments:
process_name: Process identifier or tag group
optimization_goal: Primary objective (throughput, quality, energy, cost)
analysis_days: Number of days of historical data to analyze
Prompt:
"Analyze process «process_name» over the past «analysis_days» days to optimize for «optimization_goal». Identify the current operating envelope and performance characteristics. Find periods of best performance and analyze the parameter settings during those periods. Detect inefficiencies, suboptimal settings, or process drift. Recommend specific parameter adjustments (setpoints, control limits, timing) with quantified expected improvements. Identify trade-offs between conflicting objectives. Suggest a phased implementation approach with validation checkpoints."
Shift Performance Comparison
Name: shift_performance_comparison
Title: Shift Performance Comparison
Description: Compares performance metrics across different operational shifts to identify best practices, training needs, or systematic issues affecting specific shifts.
Arguments:
area_or_line: Production area or line to analyze
comparison_weeks: Number of weeks to include in comparison
Prompt:
"Compare shift performance for «area_or_line» over the past «comparison_weeks» weeks. Segment data by shift (day/evening/night or A/B/C) and calculate key metrics for each: production output, quality rate, downtime duration, alarm frequency, changeover time, and safety incidents. Identify statistically significant differences between shifts. For the best-performing shift, document the practices and parameters that contribute to success. For underperforming shifts, identify specific improvement opportunities. Recommend knowledge transfer actions and targeted training needs."
Note:
These prompt examples demonstrate common industrial use cases but should be customized to match your specific tag naming conventions, process terminology, operational requirements, and KPIs. The effectiveness of prompts improves significantly when they reference actual tag paths, use domain-specific terminology familiar to operators, and align with established operational procedures and reporting standards.
Note:
Not all MCP clients implement the full MCP feature set; some support only tool invocation and do not support prompt invocation.